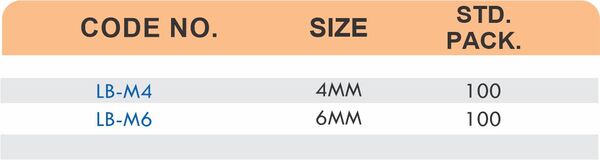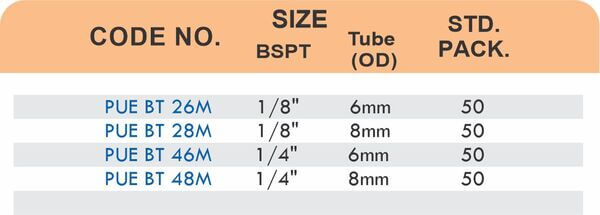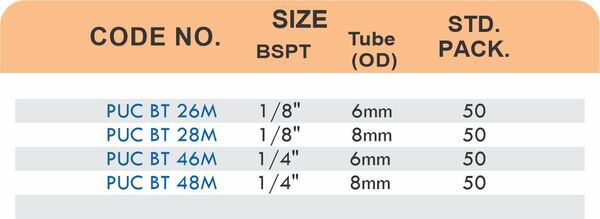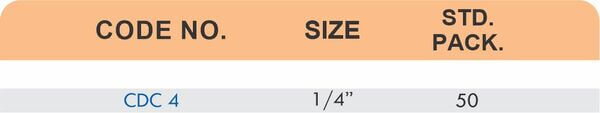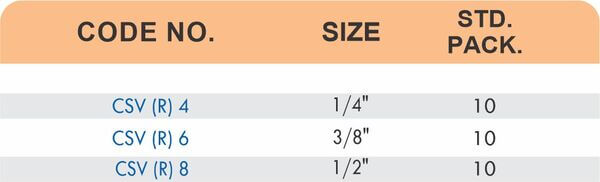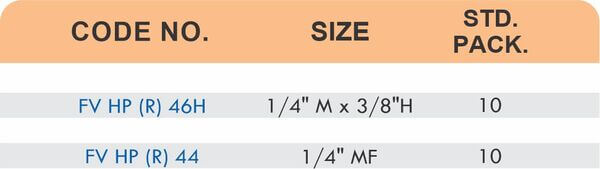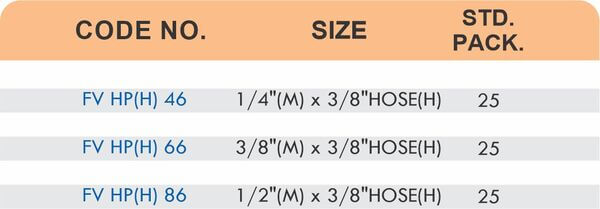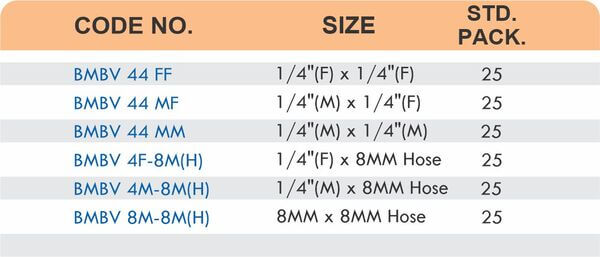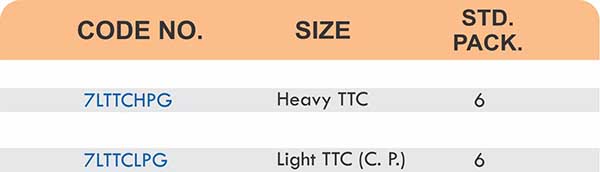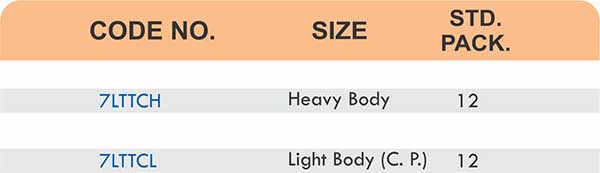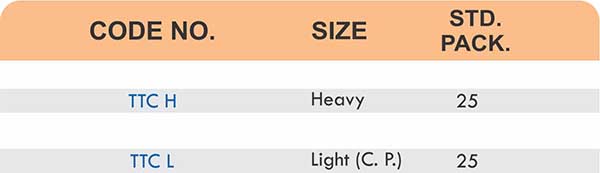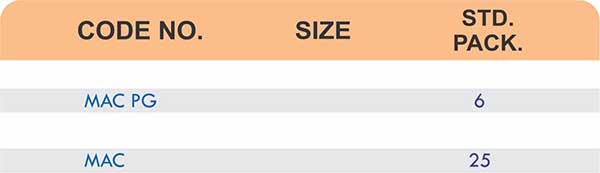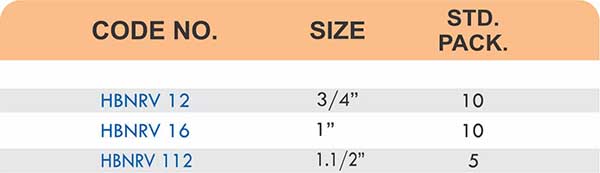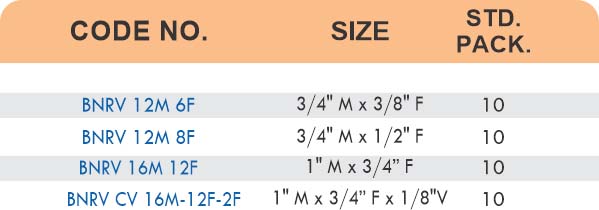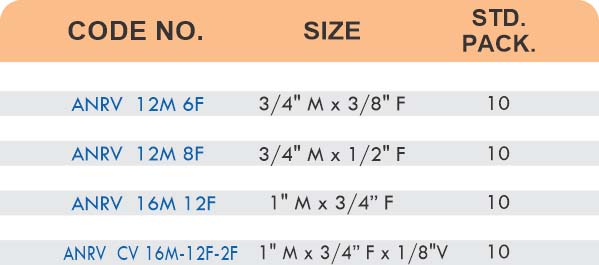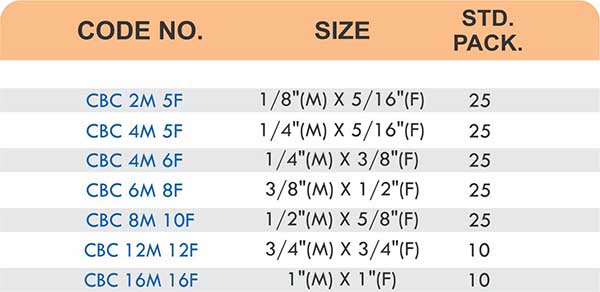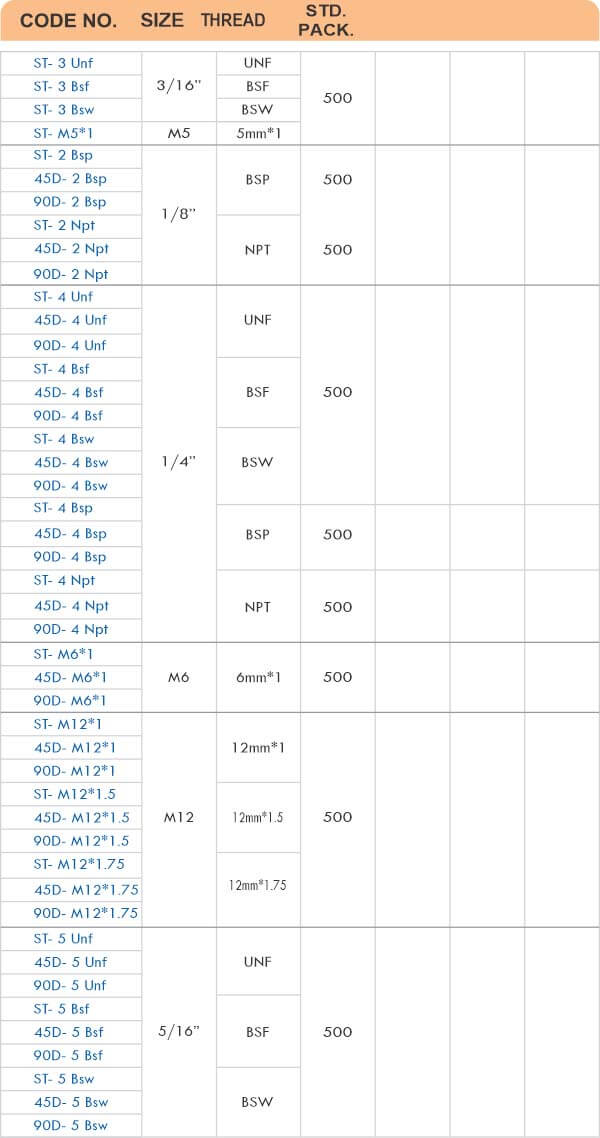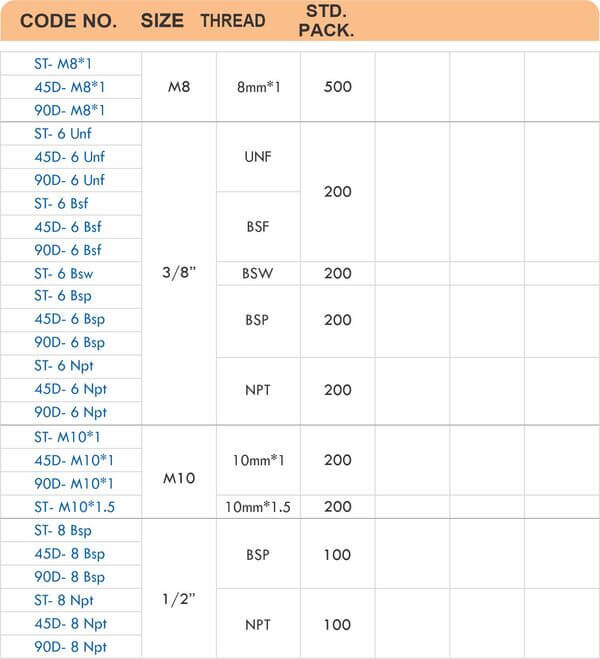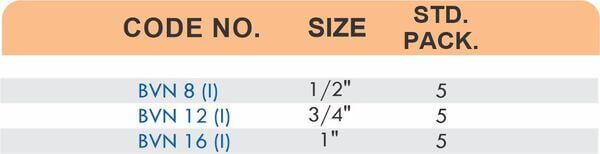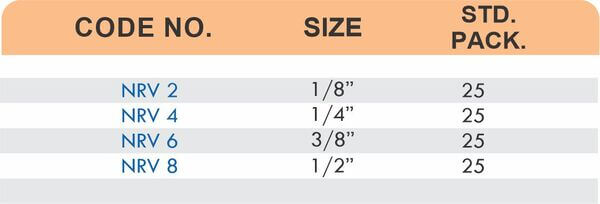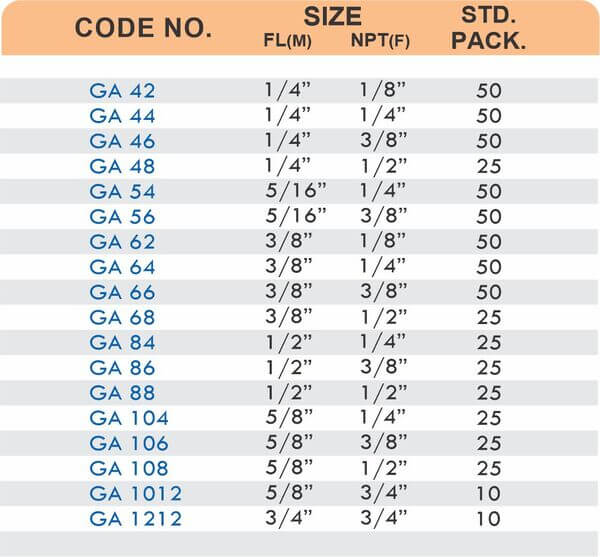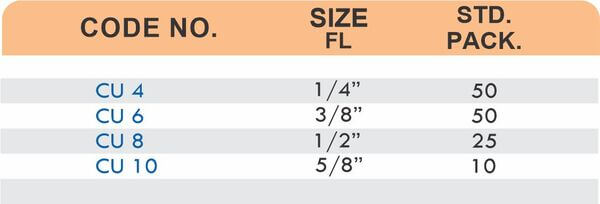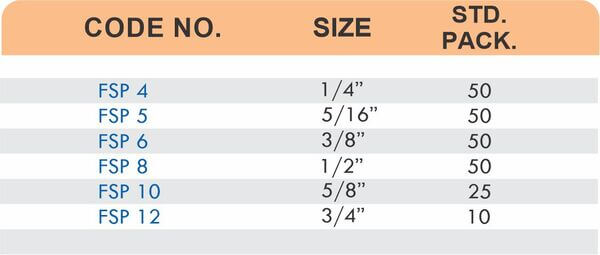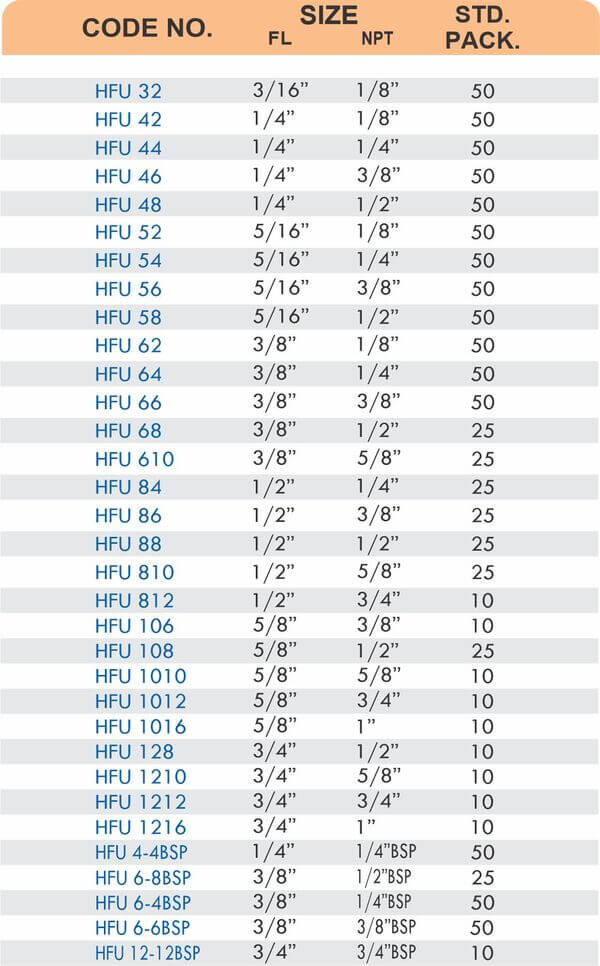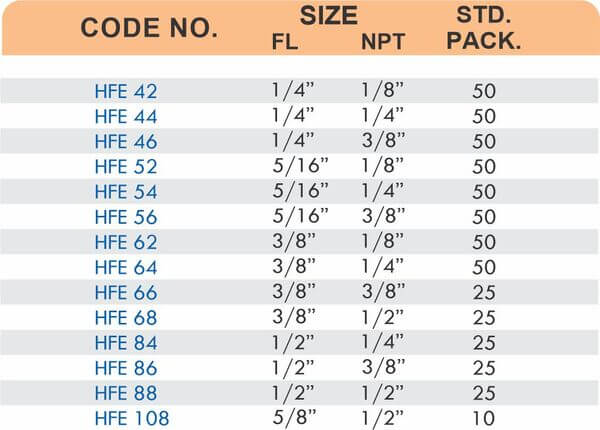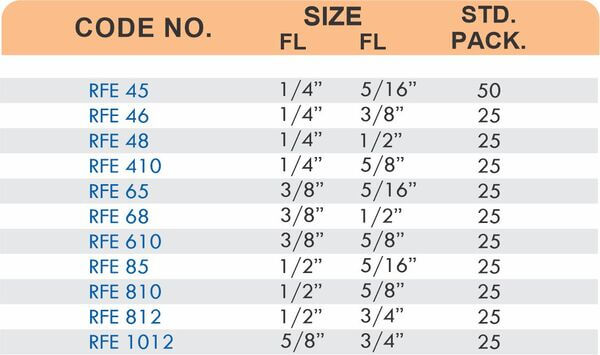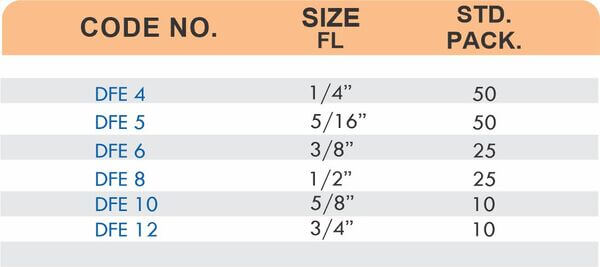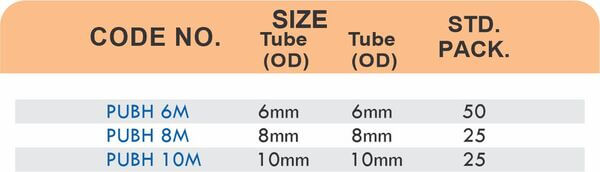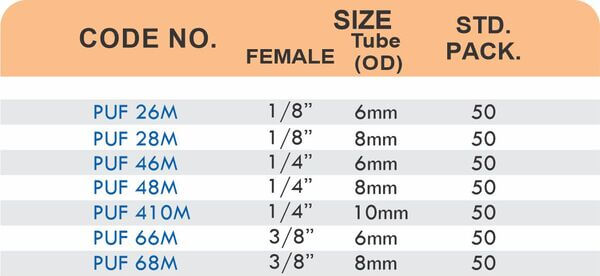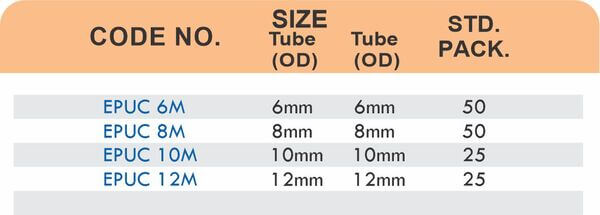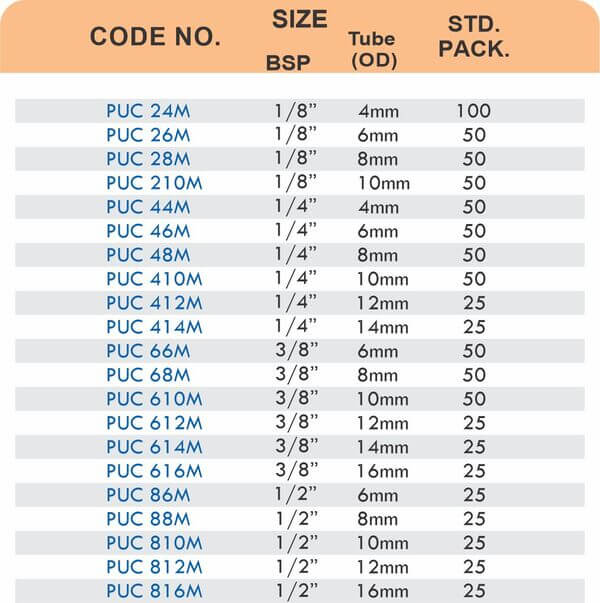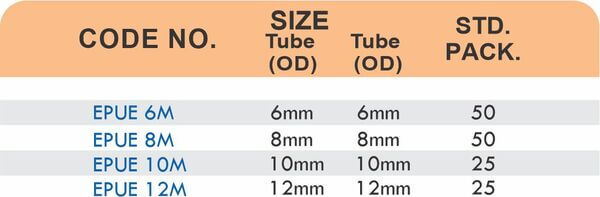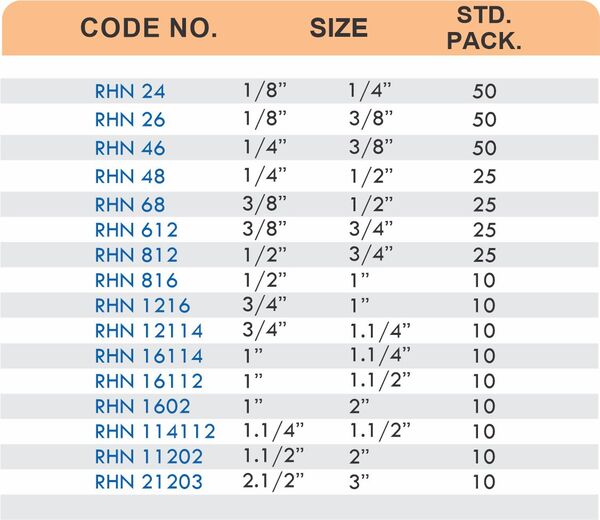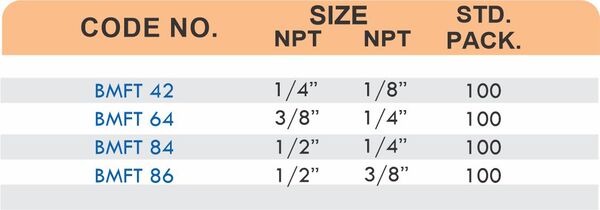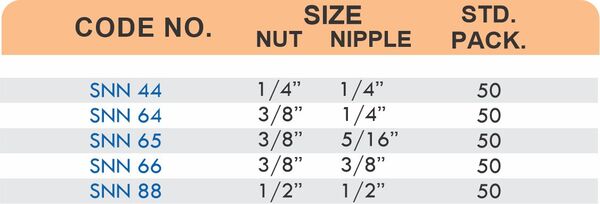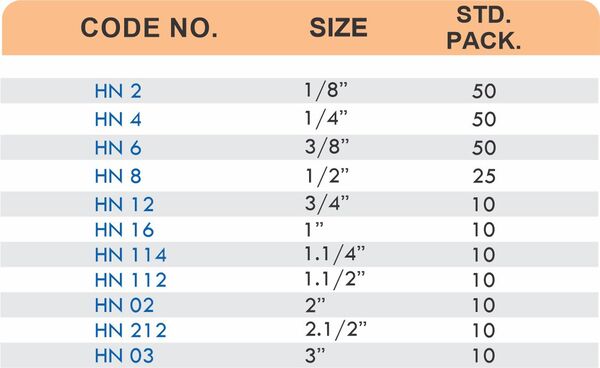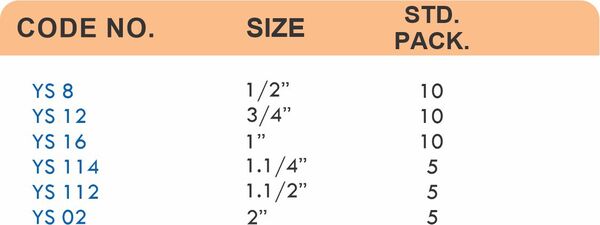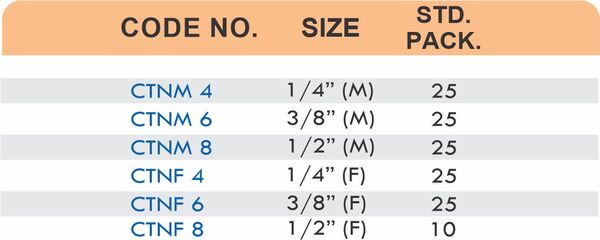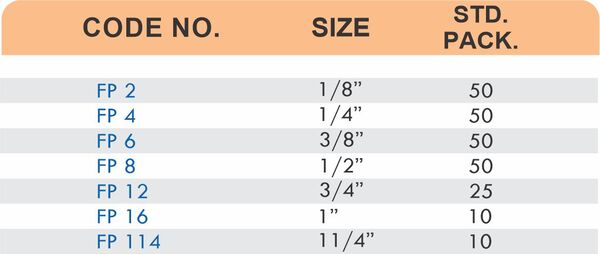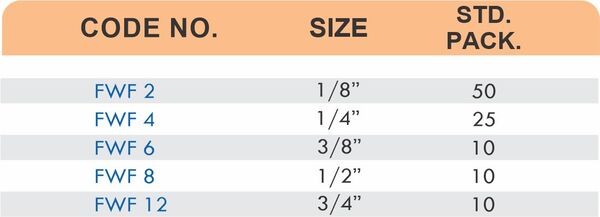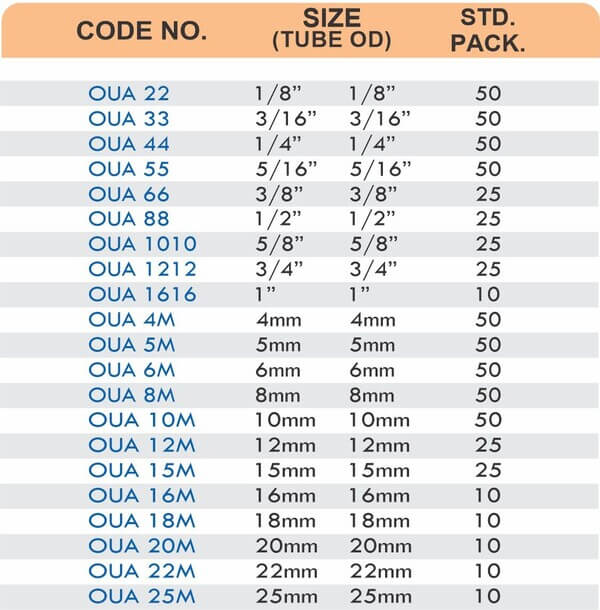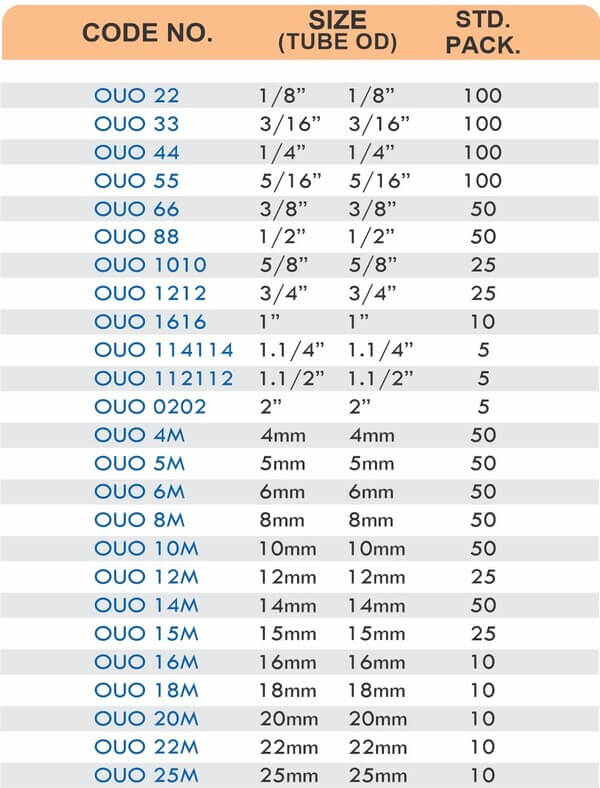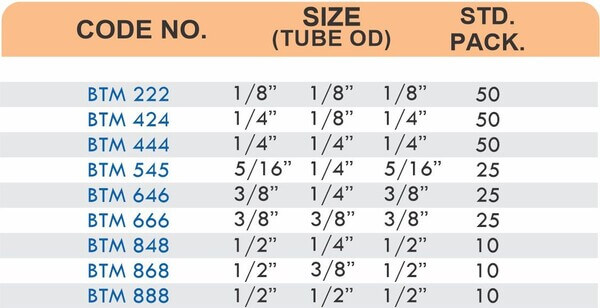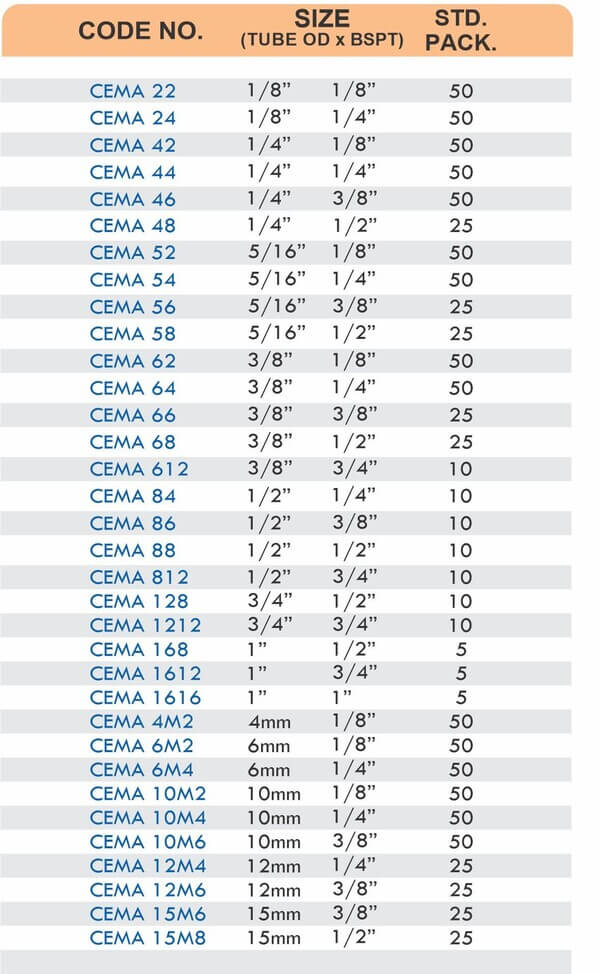
Durable Brass Hose Fittings for Fluid Handling Systems
Introduction
Hose failures account for 80% of hydraulic system downtime, and the failure point is almost always at the fitting connection. Weak plastic fittings crack under pressure, while steel variants corrode and seize during disassembly. Brass hose fittings solve both problems through corrosion resistance and mechanical strength that keeps fluid systems running for decades without leaks or replacement cycles.
This guide covers the major brass hose fitting types, their performance in different fluid applications, pressure and temperature specifications, installation techniques that prevent failures, and selection criteria that match fittings to system demands without compromising reliability.
What Are Brass Hose Fittings?
Brass hose fittings connect flexible hoses to rigid pipes, valves, or equipment in fluid handling systems. The basic designs include barbed ends that grip hose interiors, threaded connections for pipe attachment, and compression mechanisms for high-pressure sealing.
The brass alloy combines copper and zinc to create material harder than pure copper while maintaining superior corrosion resistance compared to steel. This composition withstands contact with water, petroleum products, and many chemicals without degrading.
Unlike plastic fittings that become brittle with age or crack under UV exposure, brass maintains structural integrity for decades. The material doesn’t spark when struck, making it safe for flammable fluid systems where steel creates ignition risks.
Types of Brass Hose Fittings
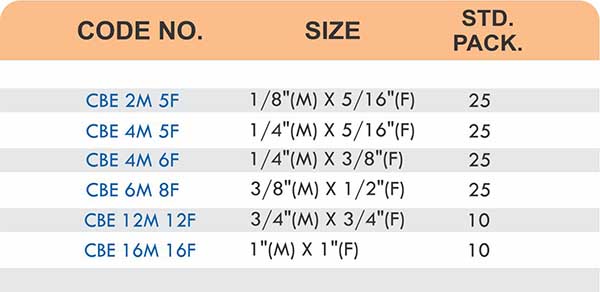
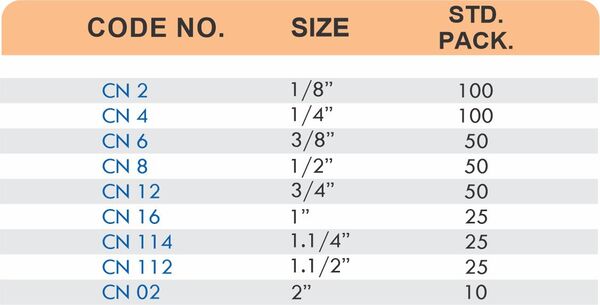
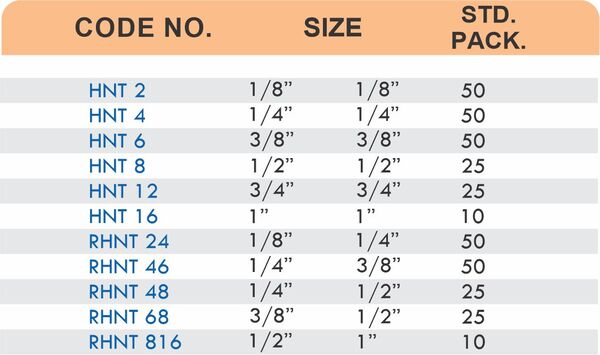
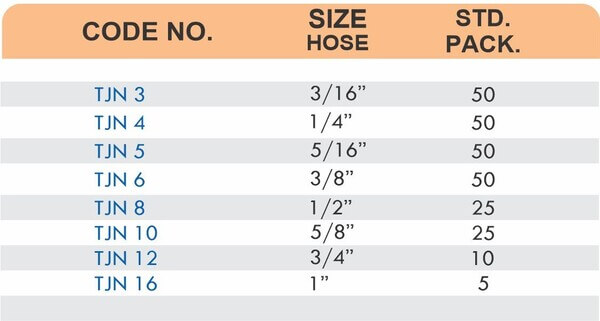
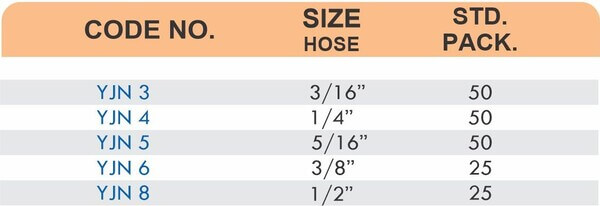
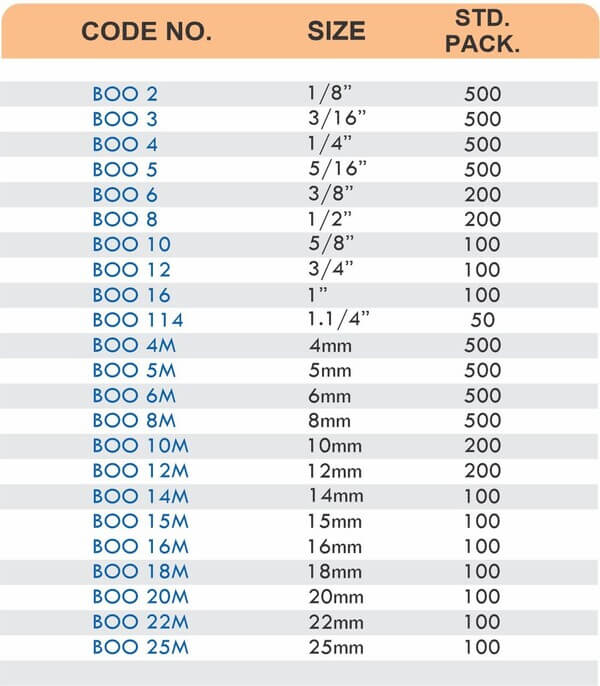
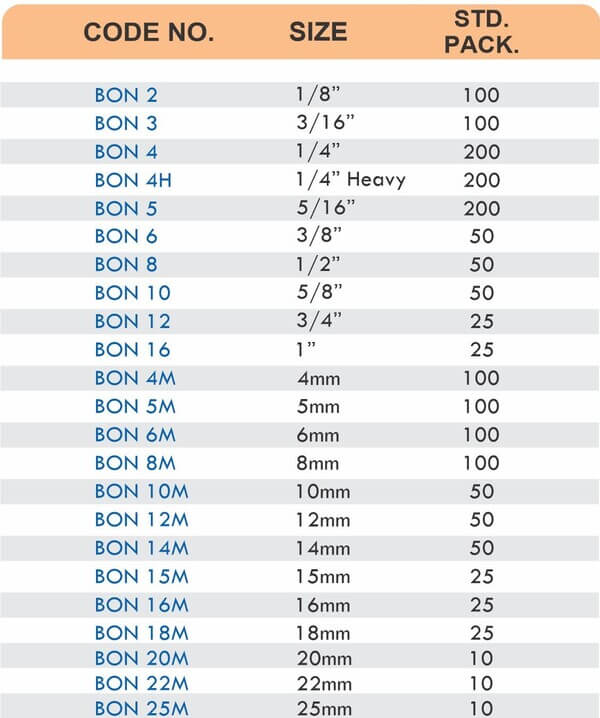
Hose Barb Fittings
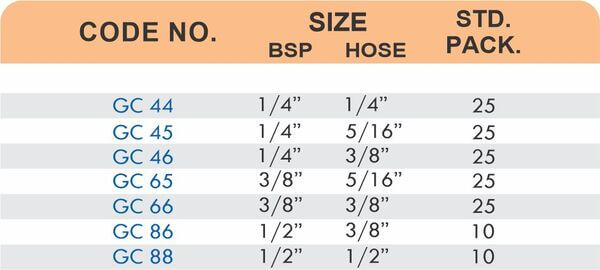
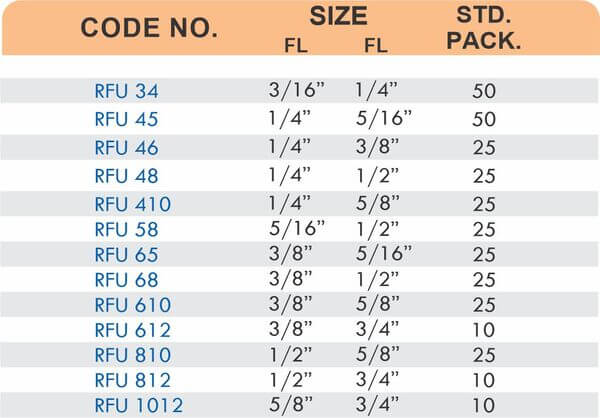
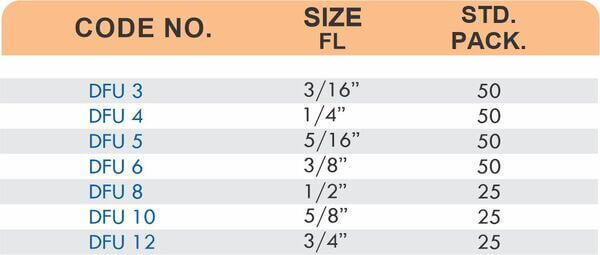
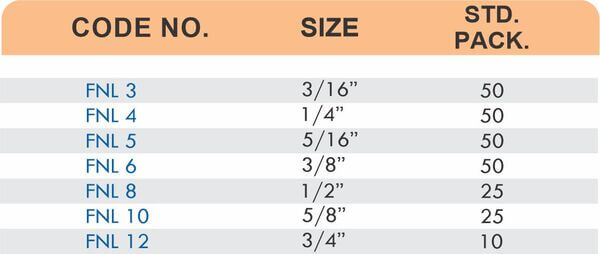
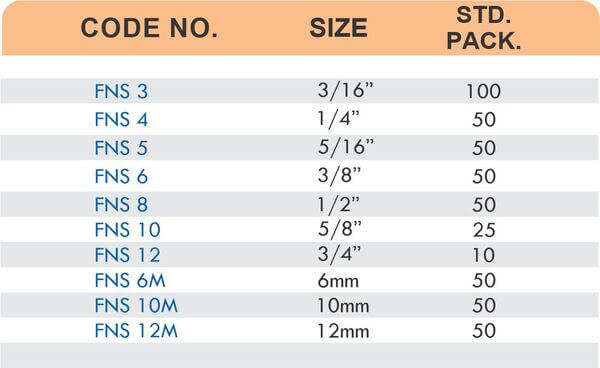
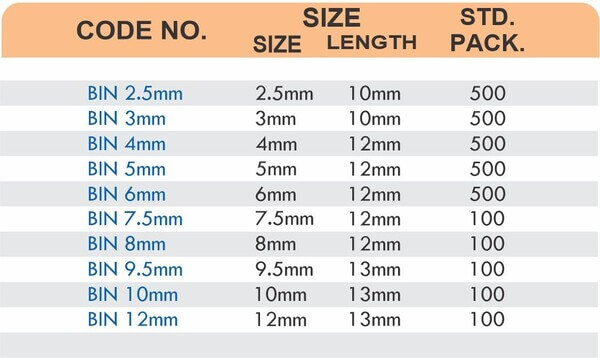
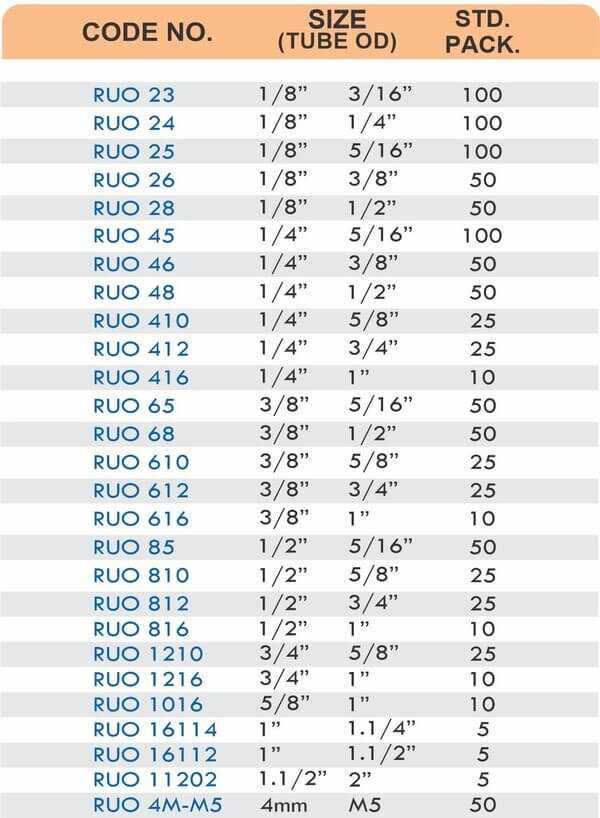
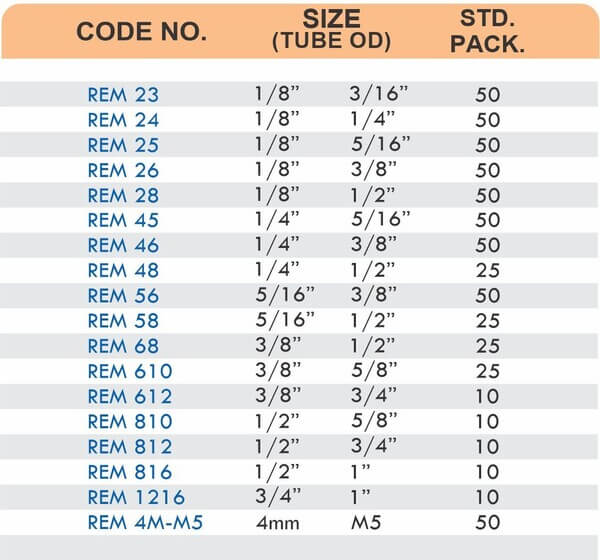
Barbed fittings feature tapered or ridged surfaces that wedge into hose interiors when pushed on. The barbs create mechanical grip that resists pull-out forces under pressure. Worm gear clamps or crimp rings secure the connection permanently.
Single-barb designs suit low-pressure applications like irrigation. Multi-barb variants with three or more ridges handle higher pressures in hydraulic and fuel systems.
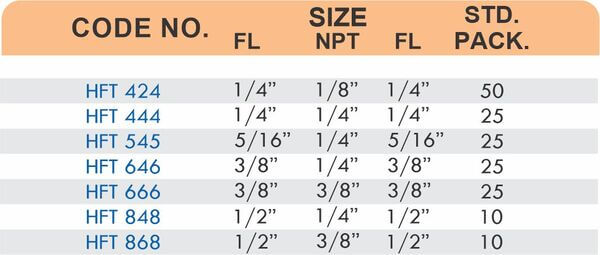
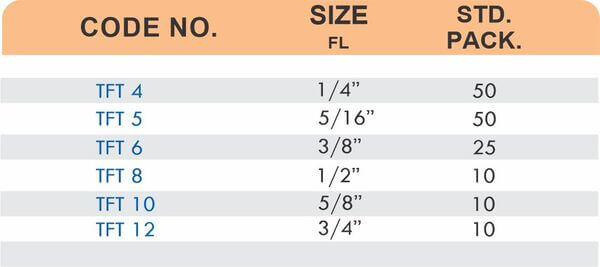
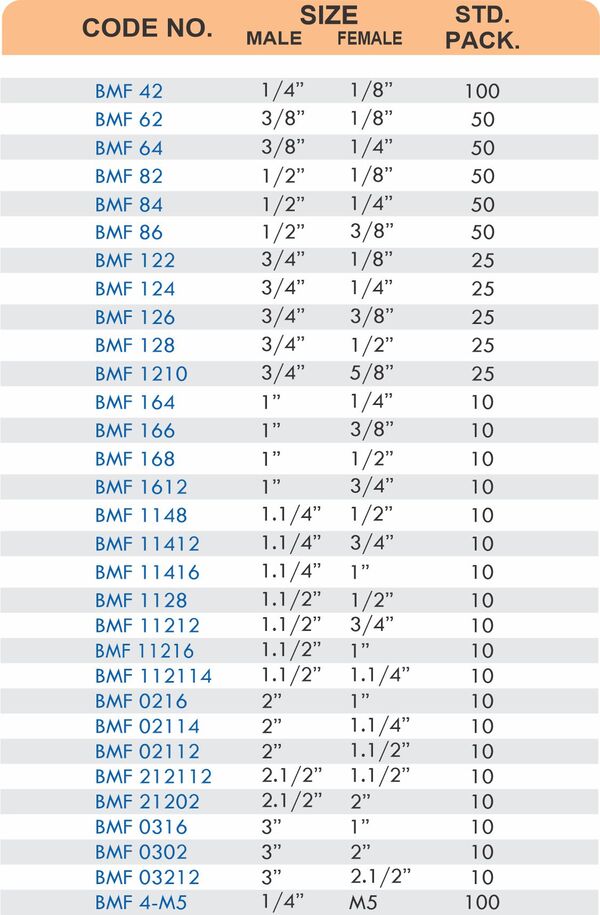
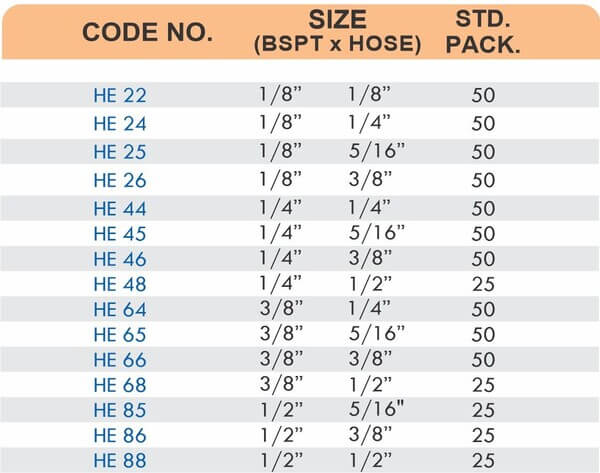
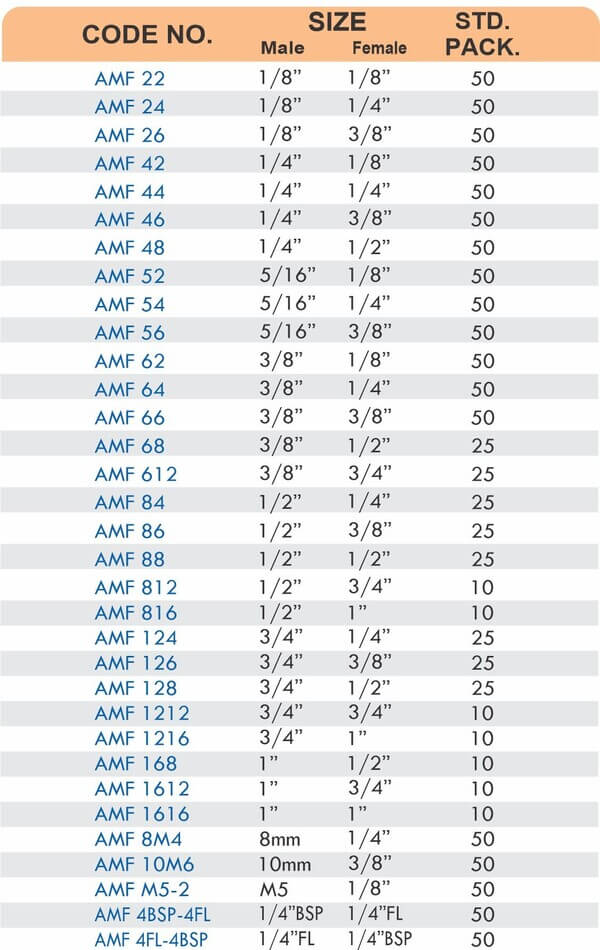
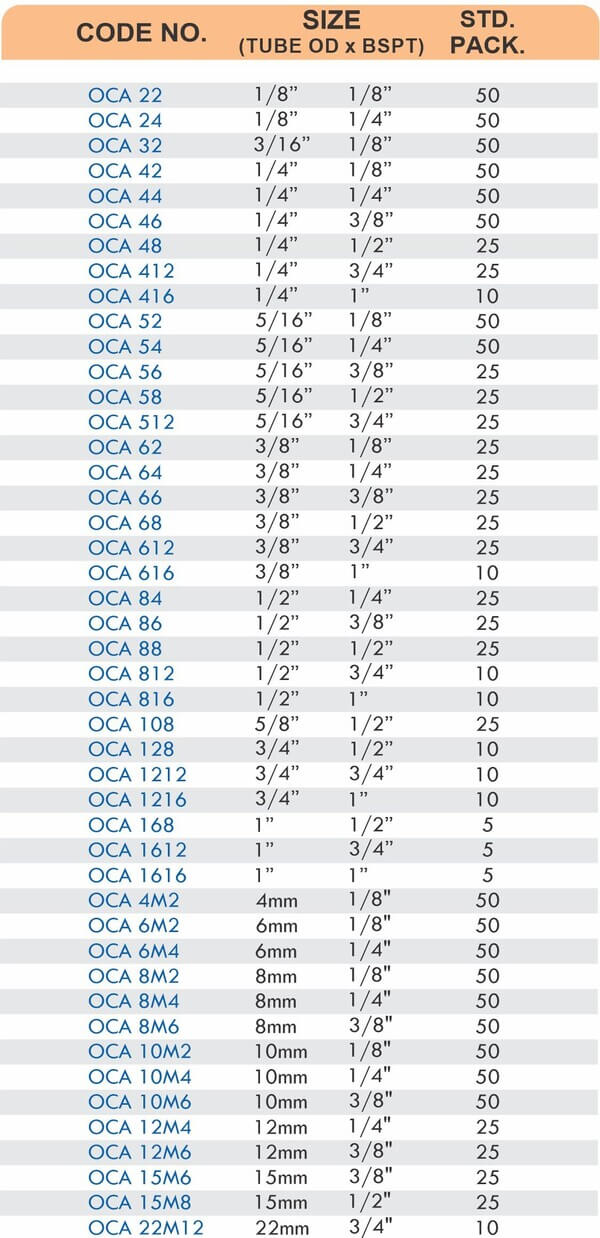
Threaded Hose Adapters
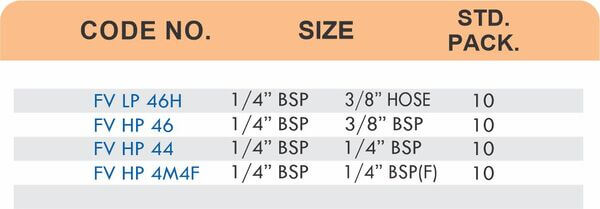
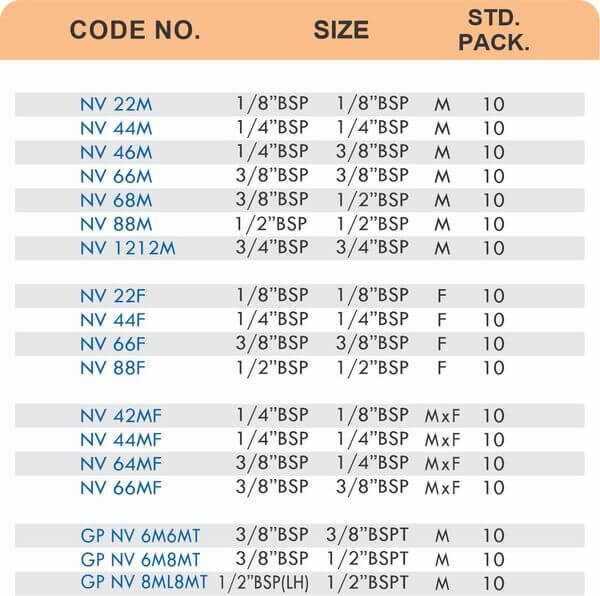
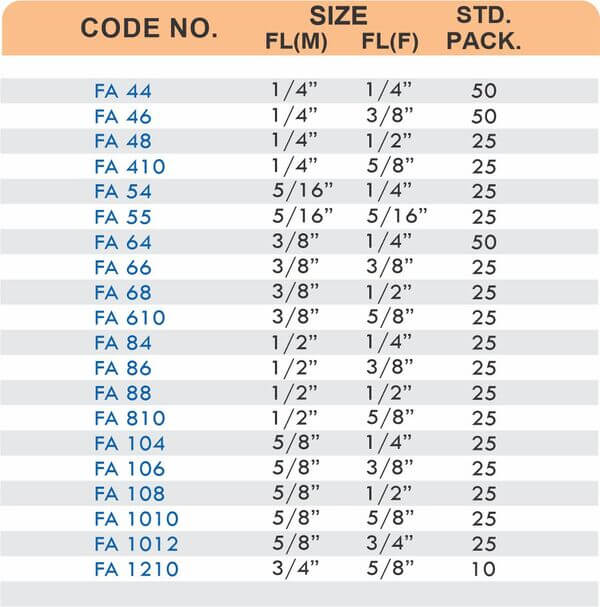
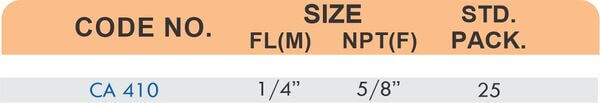
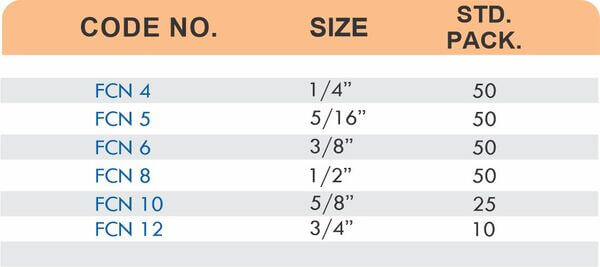
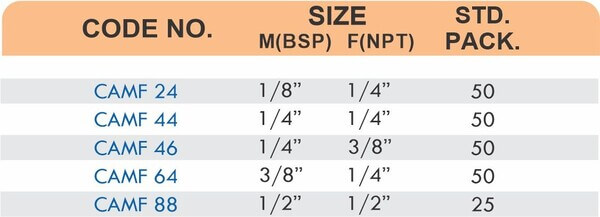
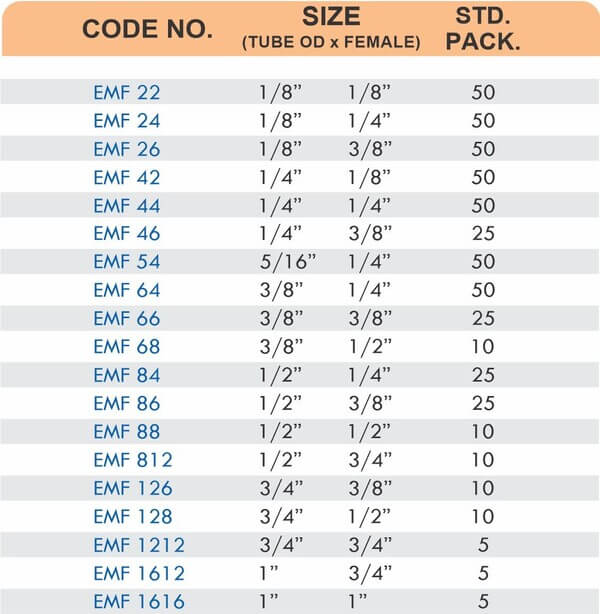
These fittings combine hose barbs on one end with NPT, BSP, or metric pipe threads on the other. Male threads screw into female ports on valves and equipment. Female threads accept male pipe nipples for system connections.
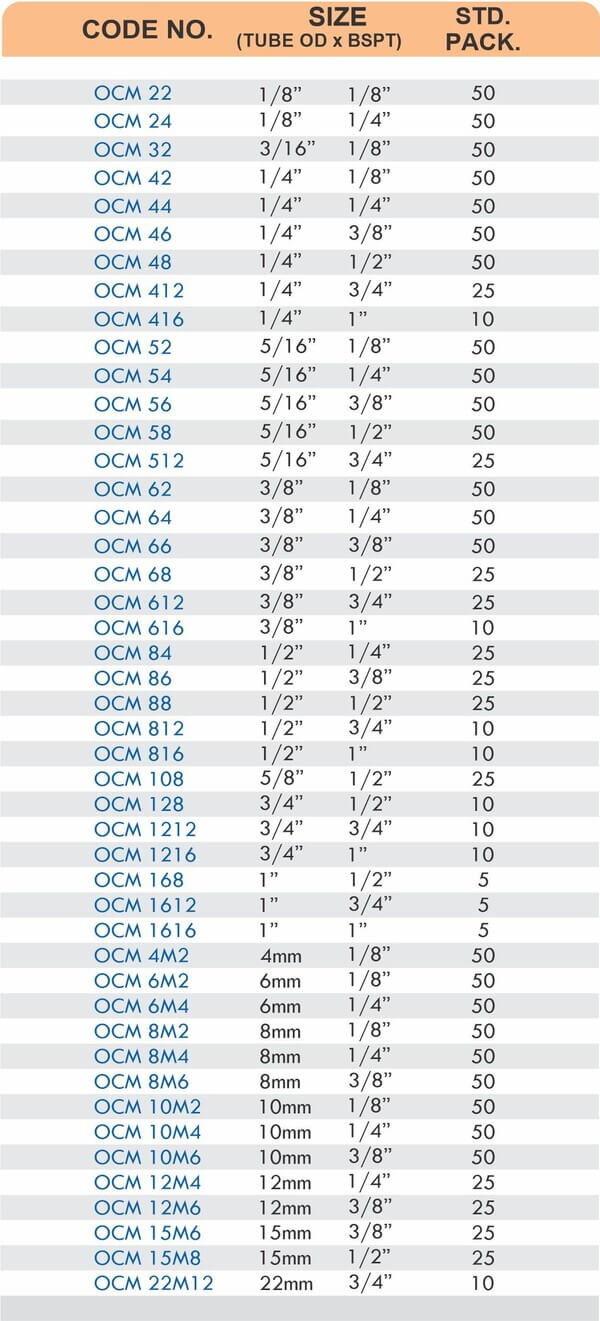
Straight, elbow, and tee configurations change hose direction or create branch points. Reducer adapters transition between different hose diameters within the same system.
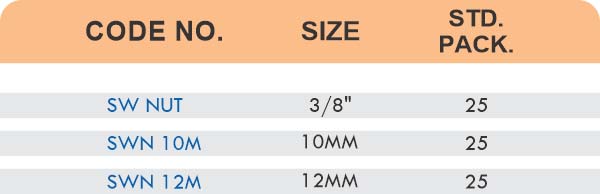
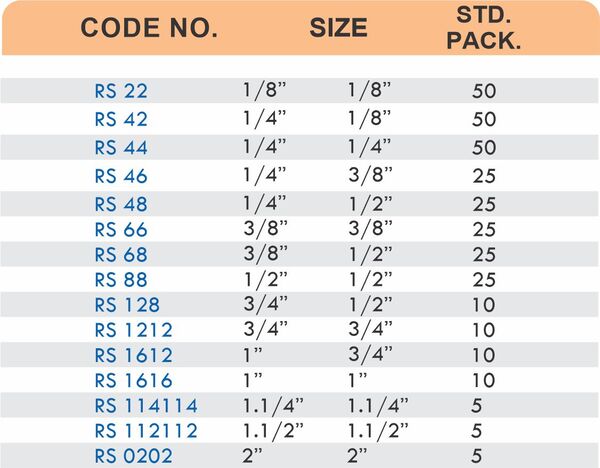
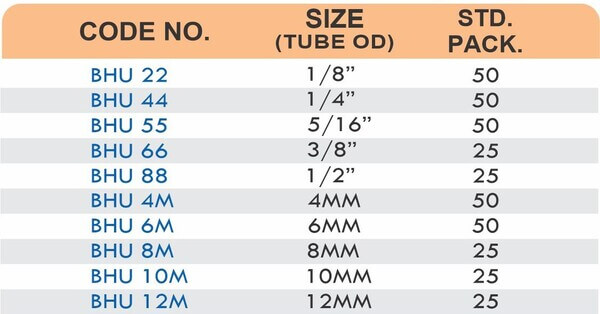
Compression Hose Fittings
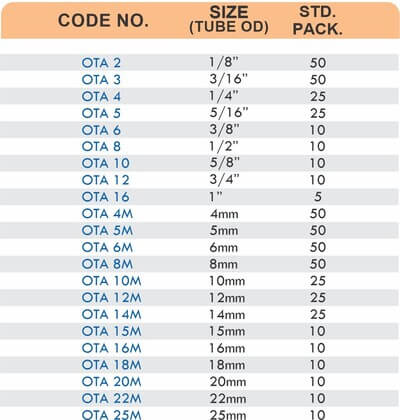
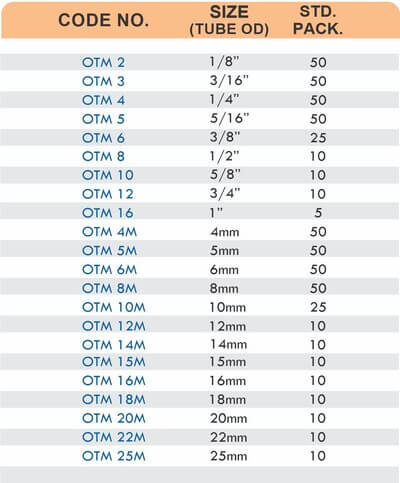
Compression designs use ferrules and nuts to secure hoses without barbs or clamps. They create leak-proof seals at pressures exceeding 1500 PSI. The connections disassemble for maintenance without cutting hoses.
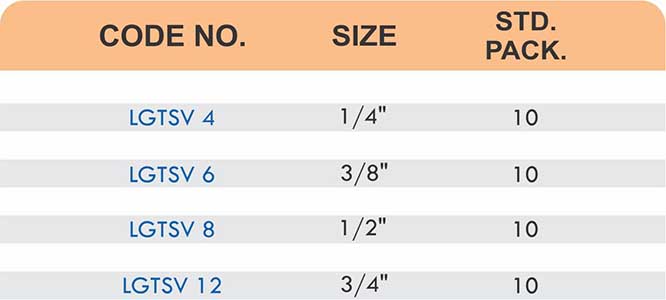
Quick-Connect Couplings
Camlock and bayonet-style quick connects enable tool-free attachment and removal. They suit applications requiring frequent hose changes like chemical transfer or mobile equipment refueling. The brass construction resists corrosion from repeated connection cycles.
Durability Advantages
Corrosion Resistance
Brass withstands continuous moisture exposure without rusting. Water systems, fuel lines, and chemical transfer applications benefit from brass’s natural oxidation resistance. The material forms a protective patina that prevents deeper corrosion.
Field data shows brass hose fittings in outdoor irrigation systems last 15+ years without replacement, while galvanized steel corrodes within 5 years.
Pressure Handling
Small-diameter brass barb fittings (6-12mm) handle pressures up to 300 PSI when properly clamped. Compression-style brass fittings withstand 1500+ PSI in hydraulic applications. Threaded adapters match pipe pressure ratings, typically 500-2000 PSI depending on thread size.
The material doesn’t crack under pressure spikes that fracture plastic fittings. Brass deforms slightly before failure, providing visible warning rather than sudden catastrophic leaks.
Temperature Stability
Brass maintains strength from -40°F to +250°F. Hot water, steam condensate, and heated hydraulic oil don’t soften the fittings. Sub-zero coolant lines won’t crack during freeze-thaw cycles that destroy plastic connections.
Fluid Handling Applications
Industrial Hydraulics
Mobile equipment and manufacturing machinery use brass hose fittings for hydraulic power transmission. The fittings resist petroleum-based hydraulic oils while handling vibration from moving equipment. Their reusability supports maintenance cycles without replacing components.
Automotive Systems
Fuel lines from tank to engine use brass barb fittings secured with clamps resistant to gasoline and diesel. Brake fluid systems depend on brass’s compatibility with glycol-based fluids. Power steering and cooling systems benefit from brass’s temperature range and corrosion resistance.
Agricultural Irrigation
Pump-to-field hose connections use brass barb fittings that resist fertilizer corrosion and UV exposure. The fittings withstand seasonal connection-disconnection cycles for equipment storage. Threaded brass adapters create distribution points for multi-zone watering systems.
HVAC and Pneumatics
Compressed air lines use brass fittings for their leak-proof performance under constant pressure. Refrigerant hoses connect to condensers and evaporators using brass adapters compatible with modern refrigerants. The material doesn’t contaminate air streams or introduce particles into clean systems.
Chemical Transfer
Mild acids, solvents, and industrial cleaners move through hoses connected with brass fittings rated for chemical service. The material resists attack from many organic compounds while maintaining pressure integrity. Check compatibility charts for aggressive chemicals like ammonia that corrode standard brass.
Installation Best Practices
Cut hoses with sharp blades perpendicular to the axis—uneven cuts prevent full insertion onto barbs. Remove loose material from hose ends that could enter the fluid system. Measure insertion depth and mark hoses to verify full seating.
For barbed fittings, lubricate hose interiors with compatible fluid before pushing onto barbs. This reduces installation force and prevents hose tearing. Position clamps 3-6mm from the hose end, covering all barbs.
Tighten clamps until the hose compresses visibly but doesn’t bulge excessively. Over-tightening cuts through hose walls; under-tightening allows blow-off under pressure. Use calibrated clamp drivers for critical applications.
Thread brass adapters by hand first to prevent cross-threading. Apply thread sealant or tape to male threads only. Tighten with wrenches to manufacturer’s torque specifications—typically 1 to 1.5 turns past hand-tight for small fittings.
Maintenance and Longevity
Inspect visible fittings quarterly for green corrosion, hose deterioration near clamps, and fluid seepage. Tighten clamps showing moisture before leaks develop. Replace hoses that harden or crack near fittings—the fitting itself often remains serviceable.
Brass fittings in properly maintained systems function for 20+ years without replacement. Outdoor installations need more frequent inspection due to temperature cycling and UV exposure affecting hoses more than fittings.
Disassemble compression and threaded fittings annually in critical systems to inspect seal surfaces. Replace worn O-rings or ferrules while reusing brass bodies and nuts that show no thread damage.
Selection Criteria
Match fitting pressure ratings to maximum system pressure with 1.5x safety margin. A 200 PSI irrigation system needs fittings rated for at least 300 PSI. Verify temperature compatibility for your specific fluid and operating conditions.
Choose barb diameter matching hose inner diameter—tight fit prevents blow-off while loose fit leaks immediately. Multi-barb designs provide better grip for high-pressure or vibration-prone applications.
Thread types must match equipment ports, NPT fittings won’t seal properly in BSP threads. Verify thread pitch and diameter before ordering adapters for international equipment.
FAQs
Q: Can brass hose fittings be used with gasoline and diesel fuel?
A: Yes, brass resists degradation from petroleum products and is commonly used in fuel systems. Use fuel-rated hoses and clamps designed for hydrocarbon service. Check local codes for specific certification requirements in automotive applications.
Q: How do I prevent hose blow-off from barbed fittings?
A: Use multi-barb fittings with at least three ridges for pressures above 100 PSI. Install two clamps per connection in critical systems. Verify hose inner diameter matches barb specifications—oversized hoses won’t grip adequately.
Q: Are brass fittings compatible with all chemicals?
A: No, ammonia and ammonium compounds cause stress corrosion cracking in standard brass. Strong oxidizing acids attack the copper content. Consult chemical compatibility charts before specifying brass for corrosive fluids. Alternative materials may be required for aggressive chemicals.
Q: Can I reuse brass hose fittings after removing hoses?
A: Barbed fittings reuse successfully if barbs show no damage or deformation. Threaded adapters reuse indefinitely when threads remain intact. Replace compression ferrules and seals after disassembly. Clean all components before reassembly.
Q: What causes brass fittings to leak after installation?
A: Inadequate hose insertion onto barbs creates leak paths around the first barb. Loose clamps allow hose expansion under pressure. Cross-threaded adapters don’t seal properly. Verify full barb insertion and proper clamp positioning before pressurizing systems.
Conclusion
Brass hose fittings deliver leak-free fluid handling through corrosion resistance, pressure capability, and mechanical durability that outlasts plastic and resists the corrosion that destroys steel. The variety of barbed, threaded, and compression designs covers applications from low-pressure irrigation to high-pressure hydraulics. Select based on your fluid type, pressure demands, and connection method rather than price alone.
Upgrade your fluid handling systems with fittings engineered for decades of reliable service and minimal maintenance requirements.
K K International manufactures precision brass hose fittings across all major types including barb, threaded, compression, and quick-connect designs for industrial, automotive, agricultural, and HVAC fluid systems. Our product range meets international standards for pressure ratings, chemical compatibility, and temperature performance with custom configurations available for specialized applications. Visit kkinternational.co.in to explore our complete catalog of brass hose fittings, access technical specifications including pressure-temperature curves and chemical compatibility charts, and connect with our engineering team for application-specific recommendations that ensure leak-free performance in your critical fluid handling systems.