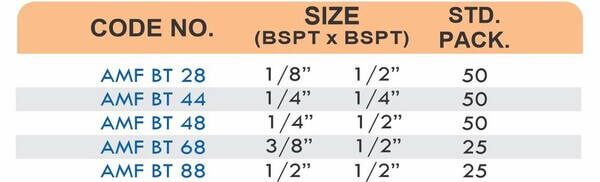
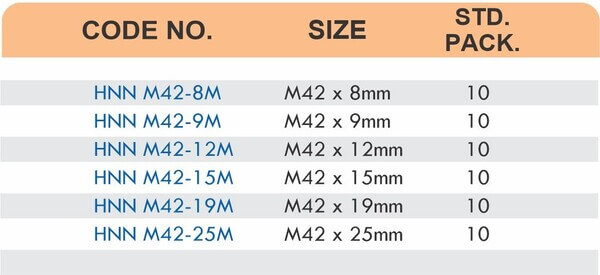
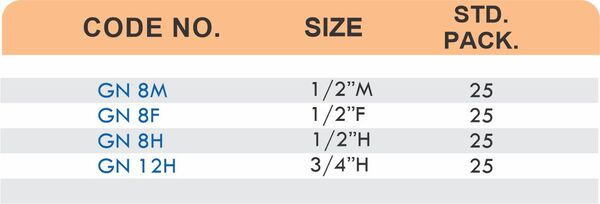
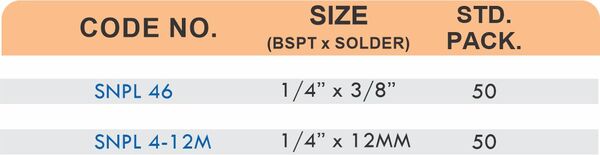
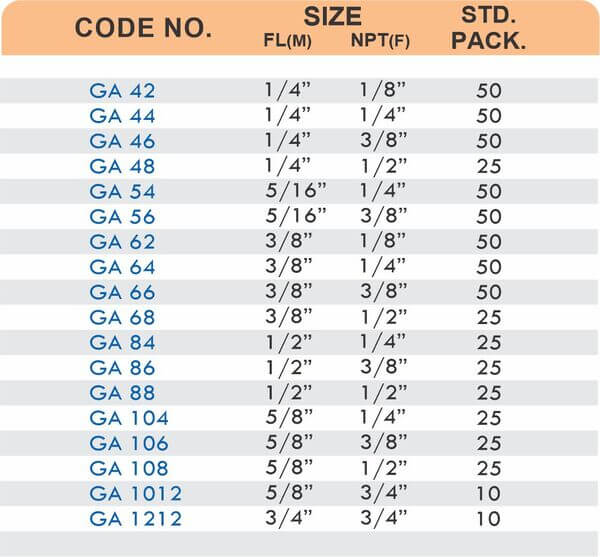
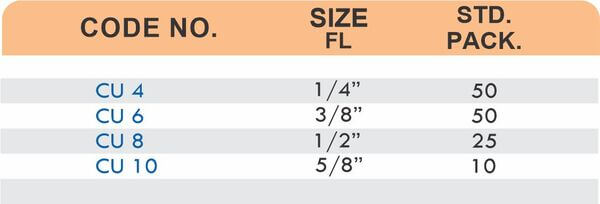
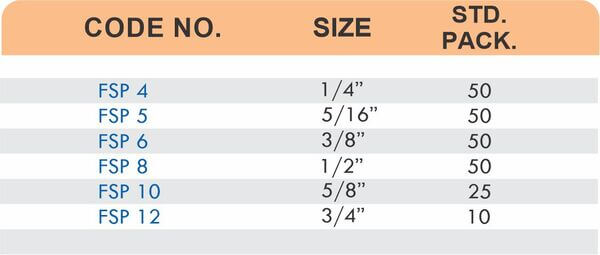
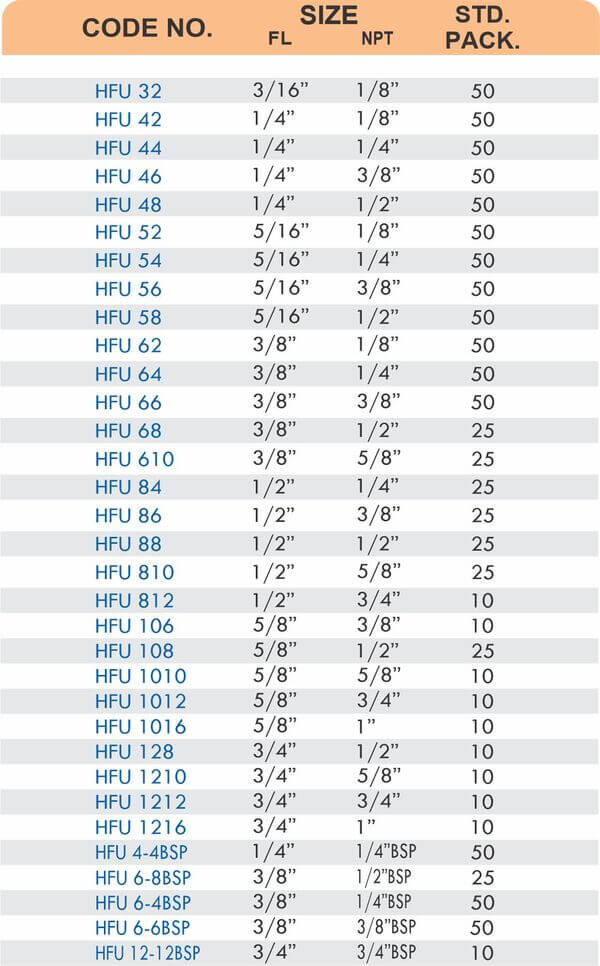
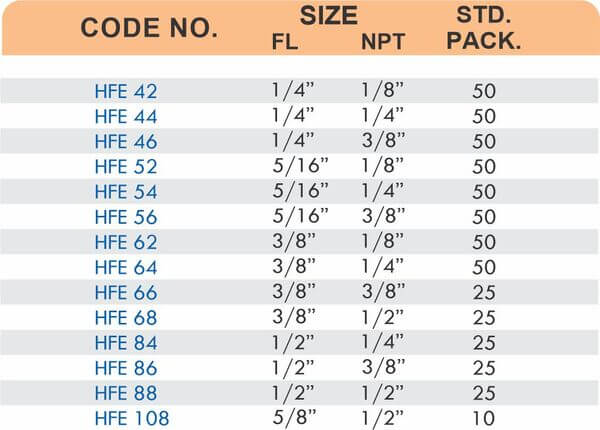
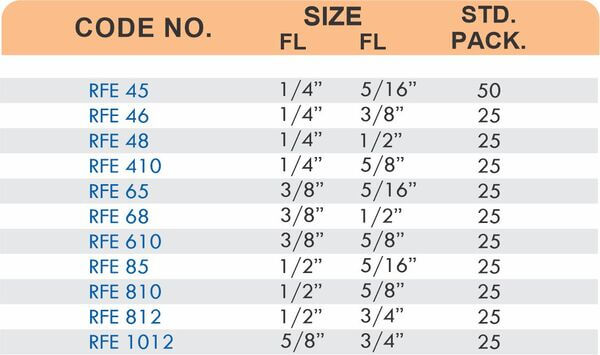
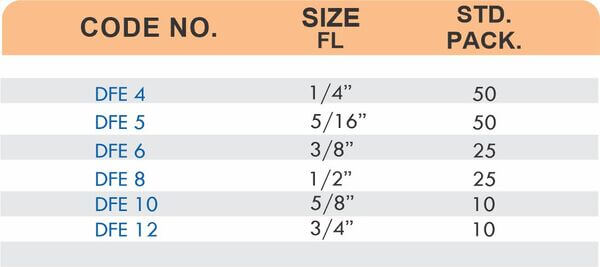
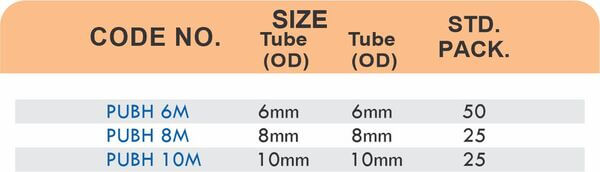
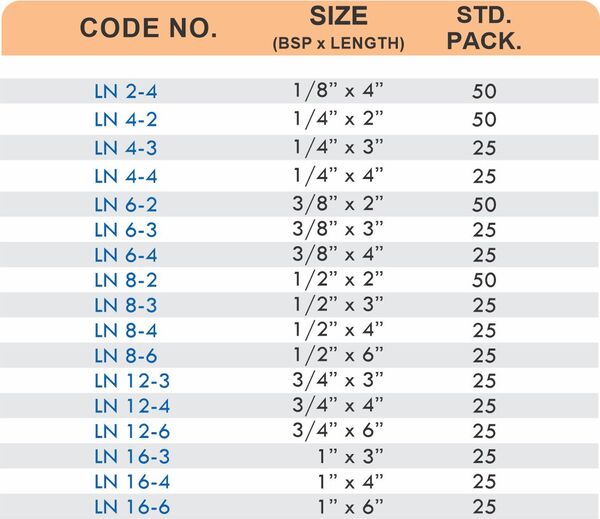
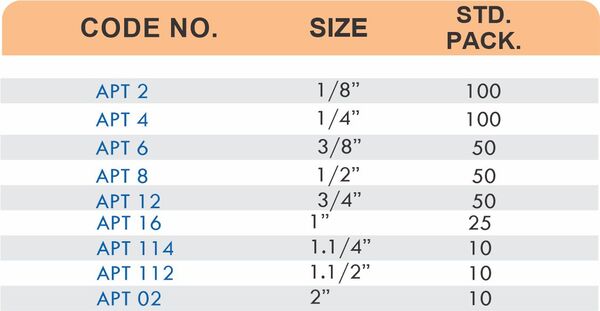
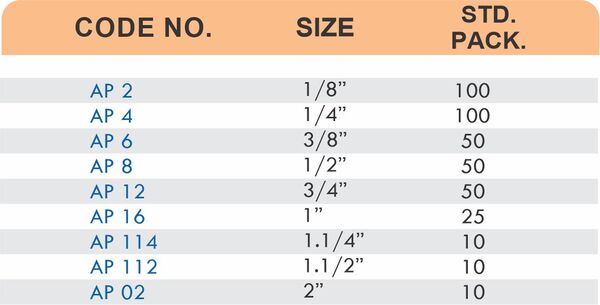
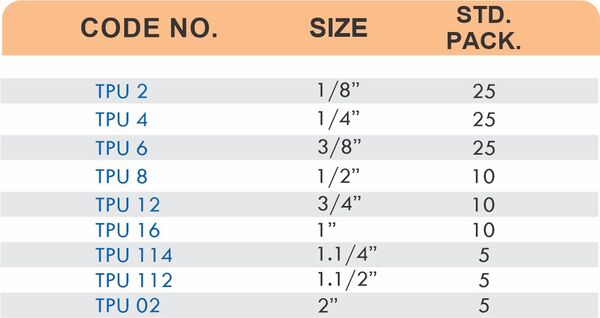
Brass Pipe Fittings: Industrial Strength & Durability
Introduction
Industrial piping failures cost manufacturers an average of $260,000 per incident in downtime, repairs, and lost production. The weak link isn’t usually the pipe itself—it’s the fittings that connect them. Brass pipe fittings eliminate this vulnerability through a combination of corrosion resistance, mechanical strength, and thermal stability that outlasts alternatives by decades.
This guide examines the material properties that make brass fittings industrial-grade, the extreme conditions they withstand, application-specific performance data, and selection criteria that match fittings to system demands without over-specifying.
What Makes Brass Industrially Strong?
Brass combines copper and zinc in ratios that create an alloy harder than copper alone while maintaining superior corrosion resistance compared to steel. The typical 60-40 or 70-30 copper-zinc composition delivers tensile strength between 40,000 and 70,000 PSI depending on the manufacturing process.
Forged brass fittings handle higher pressures than cast versions because the forging process aligns grain structure and eliminates porosity. Small-diameter fittings (under 12mm) withstand pressures up to 3000 PSI, while larger fittings (25mm+) typically rate for 1000-1500 PSI.
The material doesn’t become brittle at low temperatures like some plastics, nor does it crack under thermal shock when hot fluids suddenly cool. This thermal stability keeps joints intact through conditions that fracture alternative materials.
Key Durability Advantages
Corrosion Resistance
Brass naturally resists oxidation in water, oil, and gas environments. The copper content forms a protective patina that prevents deeper corrosion, unlike steel that rusts progressively. In coastal facilities where salt spray corrodes most metals within months, brass fittings operate for years without degradation.
Chemical processing plants use brass for mildly corrosive fluids because the alloy withstands acids and alkalis better than carbon steel. However, ammonia and ammonia compounds cause stress corrosion cracking in standard brass—these applications require ammonia-resistant variants or alternative materials.
Thermal Stability
Brass maintains structural integrity from -65°F to +250°F without softening or becoming brittle. Steam systems operating at 230°F don’t deform brass fittings, while sub-zero refrigeration lines won’t crack during freeze-thaw cycles.
The alloy’s thermal conductivity helps dissipate heat in high-temperature systems, preventing hot spots that weaken joints. This matters in applications where fluid temperatures fluctuate rapidly.
Mechanical Strength
Impact resistance prevents fractures when tools accidentally strike fittings during maintenance. Brass absorbs shock loads that would crack brittle materials like cast iron. The ductility allows slight deformation under extreme stress rather than sudden failure.
Vibration from pumps and motors loosens threaded connections over time, but brass’s anti-galling properties prevent thread seizure. The material doesn’t spark when struck, making it safe for explosive environments where steel fittings pose ignition risks.
Industrial Applications
Chemical Processing
Brass fittings handle corrosive media in pharmaceutical manufacturing, water treatment plants, and chemical distribution systems. The material resists attack from chlorine, bromine, and many organic solvents. Process engineers specify brass where stainless steel exceeds budget constraints but plastic lacks adequate pressure ratings.
Oil and Gas Systems
Hydraulic circuits in heavy equipment use brass compression fittings for their vibration resistance and reusability. Fuel distribution lines benefit from brass’s compatibility with petroleum products and natural gas. The fittings don’t degrade when exposed to diesel, gasoline, or hydraulic oils.
HVAC and Steam Distribution
Commercial HVAC systems rely on brass for refrigerant lines, condensate drains, and hot water distribution. The fittings withstand pressures up to 500 PSI in steam systems while resisting corrosion from condensation. Brass’s thermal conductivity aids heat exchange efficiency in radiator connections.
Automotive and Machinery
Brake line fittings use brass for its vibration resistance and leak-proof performance under repeated pressure cycling. Power steering systems depend on brass fittings that don’t contaminate hydraulic fluids. Engine cooling systems use brass because it tolerates antifreeze and high temperatures without corroding.
Instrumentation and Control
Process measurement systems use small-diameter brass fittings for pressure gauges, flow meters, and pneumatic controls. The material’s stability ensures accurate readings by preventing dimensional changes that affect calibration. Clean assembly leaves no residue that could clog sensitive instruments.
Performance Under Extreme Conditions
Field studies show properly installed brass fittings in industrial water systems last 40+ years without replacement. Marine applications in saltwater environments achieve 15-20 year service lives—triple that of galvanized steel fittings.
Pressure cycling tests demonstrate brass fittings withstand 100,000+ cycles between zero and rated pressure without developing leaks. This fatigue resistance matters in applications with frequent start-stop operations or pulsating flows.
Temperature cycling between -40°F and +200°F for 10,000 cycles causes no measurable dimensional changes in quality brass fittings. Systems subject to daily thermal swings maintain seal integrity for decades.
Maintenance and Longevity Factors
Annual visual inspections catch issues before failures occur. Look for green corrosion (verdigris), which indicates zinc leaching in aggressive water chemistry. White deposits suggest mineral buildup that can restrict flow but doesn’t compromise fitting integrity.
Tighten threaded connections that show moisture or mineral staining before leaks develop. Most brass fitting leaks result from gradual loosening rather than material failure.
Replace fittings showing deep pitting or thread damage immediately. Surface discoloration doesn’t affect performance, but metal loss from corrosion reduces pressure ratings and creates failure risks.
Systems in corrosive environments benefit from dezincification-resistant (DZR) brass that maintains zinc content even when exposed to aggressive water chemistries.
Selection Criteria
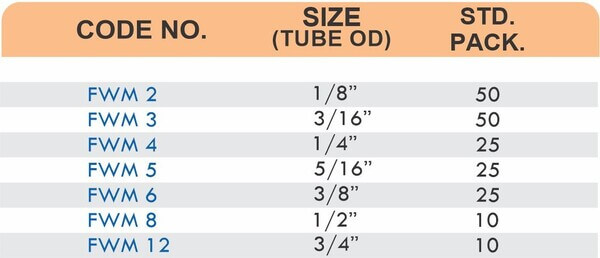
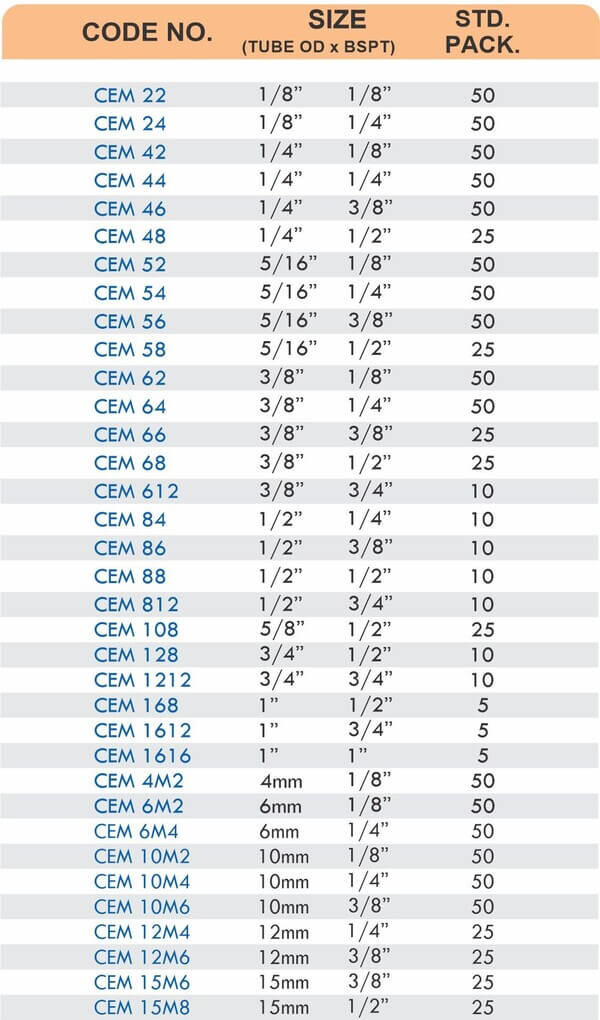
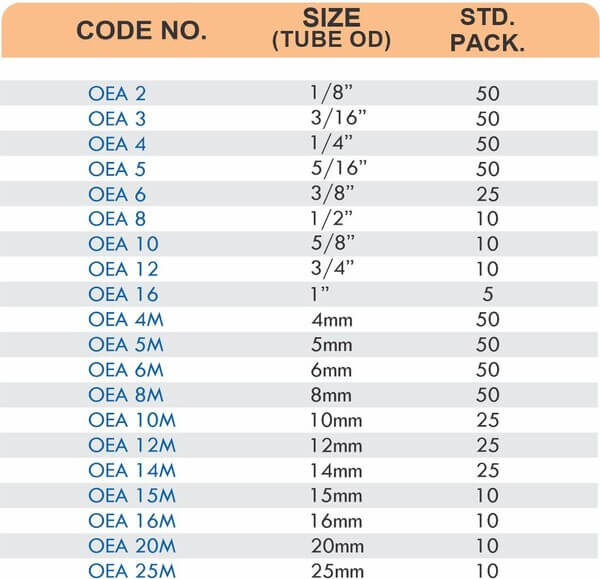
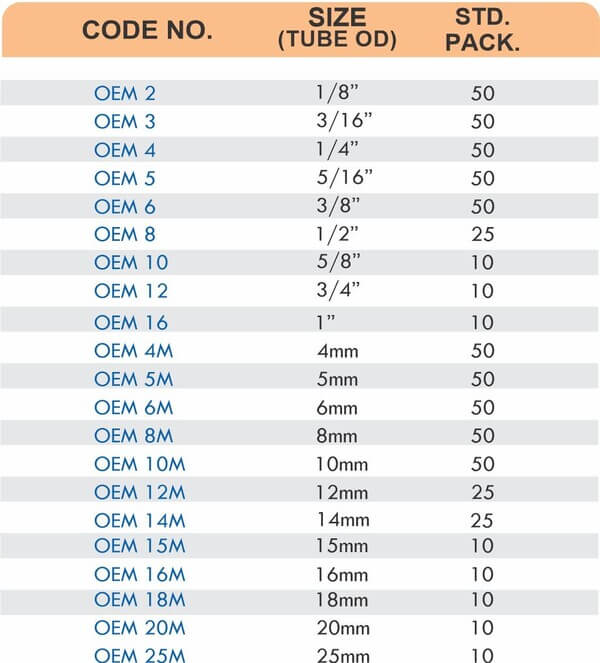
Match fitting pressure ratings to system operating pressures with a minimum 2:1 safety factor. A system operating at 600 PSI needs fittings rated for at least 1200 PSI. Pressure spikes during pump starts or valve closures can briefly exceed normal operating pressures.
Verify temperature compatibility for your specific fluid and operating conditions. Standard brass works for most applications, but high-temperature variants prevent softening above 250°F.
Lead-free brass is mandatory for potable water systems under most building codes. Check NSF/ANSI 61 certification to confirm compliance with drinking water standards.
Material compatibility matters when joining dissimilar metals. Use dielectric unions between brass and steel to prevent galvanic corrosion.
FAQs
How long do brass pipe fittings last in industrial settings?
Properly installed brass fittings in non-aggressive environments last 40+ years without replacement. Harsh chemical or saltwater applications reduce lifespan to 15-20 years, still exceeding steel alternatives. Regular inspection and maintenance extend service life.
Can brass fittings handle steam systems?
Yes, brass withstands steam temperatures up to 250°F and typical steam pressures. Use forged brass rather than cast for higher pressure steam applications. Insulate fittings to prevent heat loss and protect personnel from burns.
Are brass fittings safe for flammable gas systems?
Brass is inherently non-sparking and safe for natural gas, propane, and other flammable gases. Use thread sealant rated for gas service, not standard plumber’s tape. Check local codes for specific certification requirements.
Do brass fittings corrode in coastal environments?
Standard brass resists saltwater corrosion better than steel but will eventually develop patina and surface corrosion. Dezincification-resistant (DZR) brass significantly extends life in marine environments. Annual cleaning and inspection prevent accelerated degradation.
What pressure ratings should I specify for hydraulic systems?
Hydraulic circuits typically operate at 1000-3000 PSI depending on equipment. Specify fittings rated at least 1.5 times your maximum system pressure. Small-diameter brass compression fittings handle up to 3045 PSI; larger sizes have proportionally lower ratings.
Conclusion
Brass pipe fittings deliver industrial-grade performance through corrosion resistance, thermal stability, and mechanical strength that outlasts alternatives in demanding environments. The material withstands extreme temperatures, high pressures, and corrosive media while maintaining dimensional stability for decades. Select based on your specific pressure, temperature, and chemical exposure requirements rather than defaulting to oversized specifications.
Upgrade your industrial piping systems with fittings engineered for long-term reliability and minimal maintenance demands.
K K International manufactures industrial-strength brass pipe fittings that meet international standards for pressure, temperature, and corrosion resistance across chemical processing, oil and gas, HVAC, and manufacturing applications. Our product range includes forged brass fittings for high-pressure systems, DZR variants for corrosive environments, and lead-free certified components for potable water compliance.
Visit kkinternational.co.in to explore our complete industrial catalog, access technical specifications with pressure-temperature curves, and connect with our engineering team for application-specific fitting selection that optimizes performance and longevity in your critical piping systems.