A Pro’s Guide to Flawless Threaded Flange Installation
Threaded flanges are essential components for creating strong connections in piping systems without the need for welding, making them the ideal choice for numerous industrial and commercial applications like oil & gas, water supply, fire protection, and chemical plants.
Types of Threaded Flanges
- Standard Threaded Flange: Most common; matches male pipe threads for easy assembly.
- Mild Steel Threaded Flange: Popular for its balance of durability and cost-effectiveness; preferred in low to moderate pressure systems.
- Alloy and Stainless Steel Options: Used when higher corrosion resistance is essential.
Tools and Materials You Need
Before installation, gather:
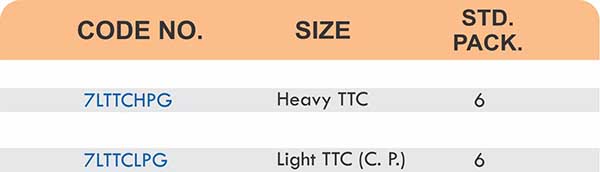
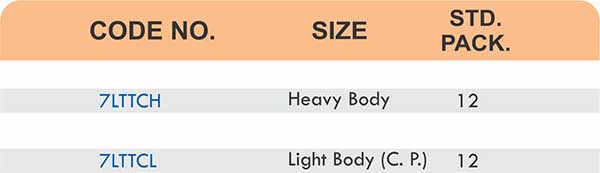
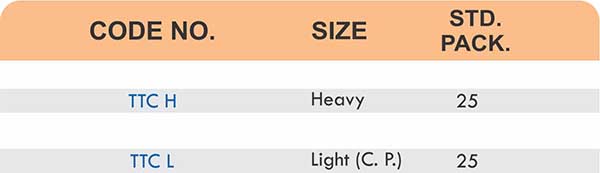
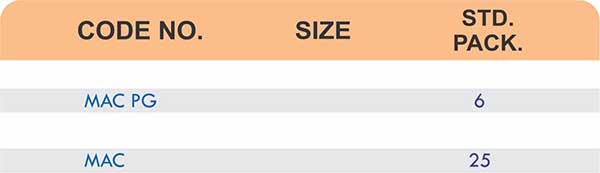
- Threaded flanges (properly rated and sized)
- Matching threaded pipes
- Pipe wrenches & torque wrench
- Teflon tape or pipe thread sealant
- Cleaning cloth / brush
- Gasket (if required)
- Bolts, nuts, and washers
- PPE (gloves, goggles)
Step-by-Step Installation Process
1. Prepare and Inspect Components
Inspect the flanges and pipe ends thoroughly for cracks, rust, misaligned threads, or other damage before assembly. Clean threads using a brush or cloth to remove dirt and leftover sealant.
2. Apply Thread Sealant
Wrap the male pipe threads evenly with Teflon tape or apply pipe thread compound. This step is crucial for preventing leaks and ensuring easy tightening.
3. Thread the Flange
Carefully screw the flange onto the pipe by hand to avoid cross-threading. Use a pipe wrench for final tightening, following the recommended torque values to avoid damaging threads.
4. Align the Flange
Ensure the flange is properly aligned with the mating connection or equipment. Misalignment can cause stress, leaks, and premature failures in the system.
5. Gasket Installation (If Required)
If the flange assembly requires a gasket, select one compatible with your media and pressure. Position the gasket correctly between the mating faces before bolting up for a reliable seal.
6. Bolt Up the Flanges
Align and insert bolts through the flange holes. Tighten the nuts gradually in a crisscross (star) pattern to distribute load evenly and avoid warping. Use a torque wrench to achieve the manufacturer-recommended torque.
7. Leak Testing
Once installation is complete, conduct a leak test with water or air to confirm a leak-free joint. Address any leaks by re-tightening or re-installing as necessary.
8. Final Inspection and Maintenance
Check all connections for alignment, proper bolt torque, and overall stability. Plan regular inspections and maintenance to ensure lasting reliability and safety of the flange connections.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Over-tightening, leading to thread damage
- Misalignment causing mechanical stress
- Skipping the leak test, risking undetected leaks
- Using improper sealant or excessive application
Advantages of Using Threaded Flanges from KK International
- Fast, weld-free installation—no sparks or special equipment needed
- Cost-efficient for retrofitting and repairs
- Durable construction for various pressures and media
- Versatile—available in carbon steel, mild steel, stainless, and alloys
- Full compliance with industry standards
Choosing the Right Threaded Flange
- Match flange material to pipe and fluid type (corrosive/neutral)
- Check pressure class and temperature ratings
- Use gaskets rated for your process media
- Always consult manufacturer data sheets for assembly and torque specs
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can threaded flanges be used in high-temperature, high-pressure systems?
A: Threaded flanges are best for low to moderate pressure and non-critical applications; for high-stress environments, welded or forged flanges are recommended.
Q: How often should flanges be re-checked?
A: Inspect flange connections during routine maintenance cycles—especially after pressure cycling or system vibration.
Q: Are specialized tools needed?
A: A torque wrench and approved sealant are essential for professional, leak-proof installation.
Pro Maintenance Tips
- Periodically re-torque flange bolts in high-vibration environments
- Clean and inspect for corrosion, especially on carbon steel flanges
- Replace worn gaskets during any disassembly.
Conclusion
Mastering threaded flange installation with careful preparation, alignment, and leak testing ensures a reliable, long-lasting connection. By following this professional guide, engineers and maintenance teams can maximize the performance and safety of piping systems, every time.