Are Brass Compression Fittings Right? Pros & Cons Explained
Introduction
Most pipe connection failures happen within the first year of installation. The culprit? Wrong fitting choice. Brass compression fittings solve a core problem in plumbing and industrial systems—they create leak-proof connections without specialized tools or open flames. Yet many buyers overlook critical factors that determine whether these fittings suit their specific needs. This guide breaks down the real advantages, hidden drawbacks, and practical considerations you need before investing. You’ll learn what brass compression fittings are, when they outperform alternatives, where they fall short, and how to choose the right type for your application.
What Are Brass Compression Fittings?
Brass compression fittings connect pipes through mechanical pressure rather than soldering or welding. The system uses three core components: a fitting body, a compression ring (ferrule), and a cap nut. When you tighten the nut, the ferrule compresses between two tapers, creating a metal-to-metal seal that indents the tube at two contact points.
This design delivers a joint capable of withstanding pressures far beyond normal usage—up to 3045 PSI for smaller diameter tubes in hydraulic applications. The symmetrical compression ring provides dual sealing action, minimizing any tendency for the tube to rotate during installation.
Advantages of Brass Compression Fittings
No Heat Required
Unlike soldered joints, brass compression fittings eliminate fire hazards during installation. You don’t need a torch, flux, or specialized training. This matters in occupied buildings, near flammable materials, or when working in tight spaces where open flames pose risks.
Reusable and Adjustable
These fittings can be disassembled and reconnected multiple times without losing integrity. If you need to modify a system, add equipment, or perform maintenance, you simply loosen the nut. Traditional soldered joints require cutting and re-soldering, wasting time and materials.
Immediate Pressure Testing
Compression fittings allow instant pressurization after assembly. No waiting for solder to cool or cure times for adhesives. This speeds up installation schedules and reduces downtime in industrial settings.
Corrosion Resistance
Brass naturally resists corrosion in water systems. The alloy combines copper and zinc, creating a material that withstands continuous moisture exposure better than steel fittings. This extends system lifespan and reduces maintenance frequency.
Connects Dissimilar Materials
You can join copper, brass, aluminum, and certain plastic tubes with the same fitting type. This versatility simplifies inventory management and allows system upgrades without complete overhauls.
Disadvantages of Brass Compression Fittings
Vulnerability to Vibration
Compression fittings loosen under constant vibration or mechanical stress. Applications with pumps, motors, or mobile equipment require additional securing methods or alternative connection types. A study of industrial failures shows vibration accounts for 34% of compression fitting leaks.
Bulkier Profile
These fittings extend farther from the pipe than soldered joints. In confined spaces like wall cavities or under cabinets, the extra bulk complicates installation. The protruding nuts also snag on tools and materials during maintenance work.
Higher Weight
Brass compression fittings weigh more than plastic alternatives. For high-rise buildings or ceiling-mounted systems, the cumulative weight impacts structural calculations and support requirements. This adds cost to framing and hangers.
Potential for Overtightening
Excessive torque cracks the ferrule or deforms the tube. Yet insufficient tightening causes leaks. The narrow acceptable range demands attention during installation—typically 1 to 1.5 turns past hand-tight for most sizes.youtube
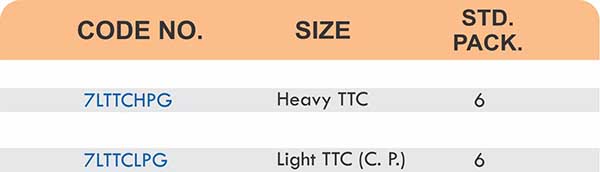
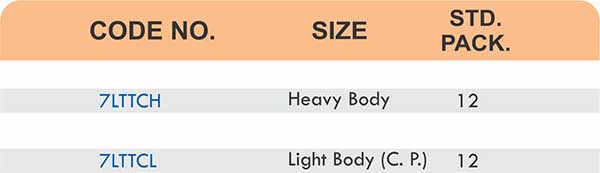
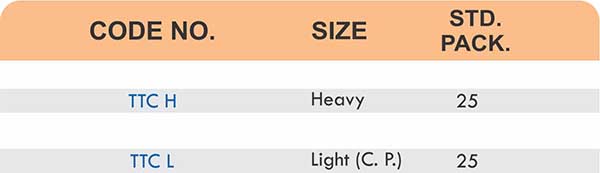
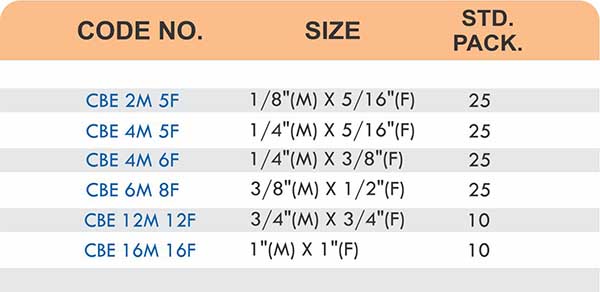
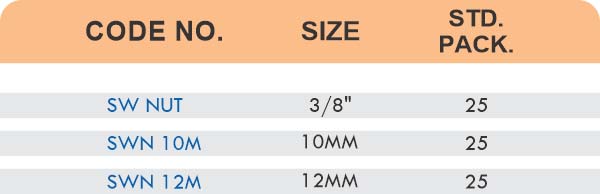
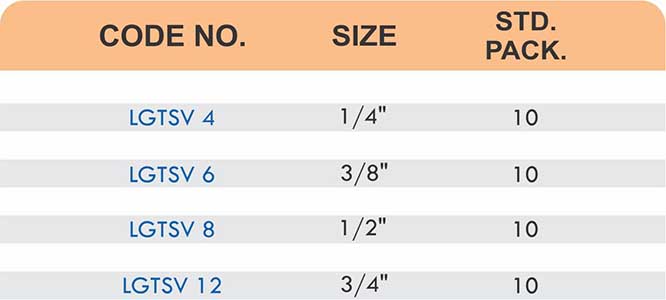
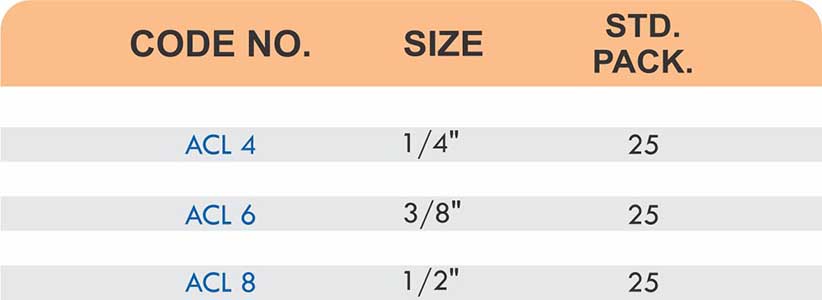
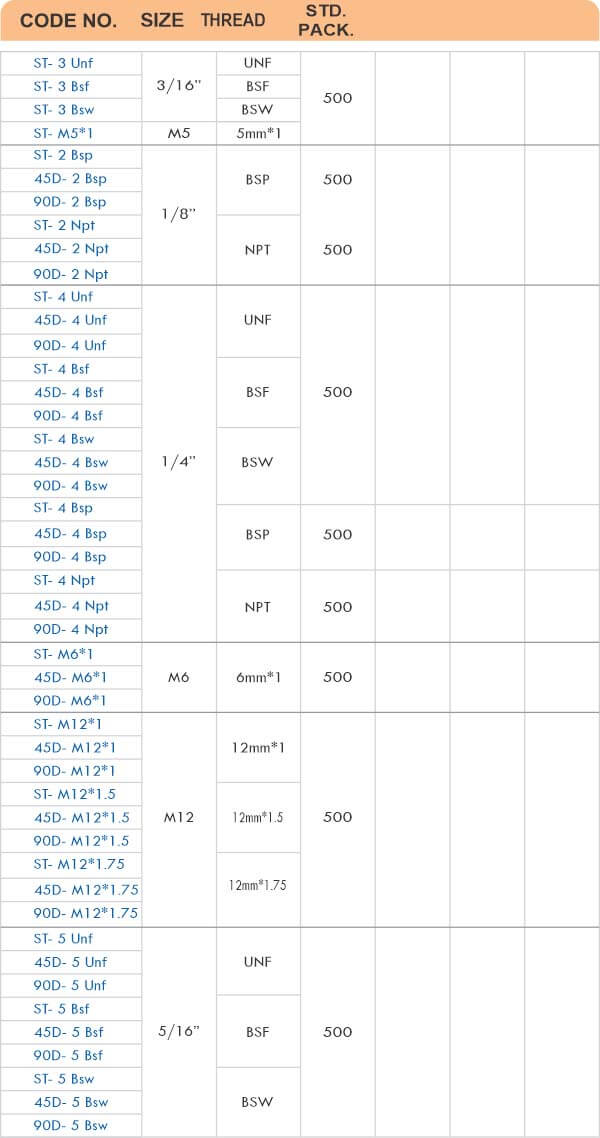
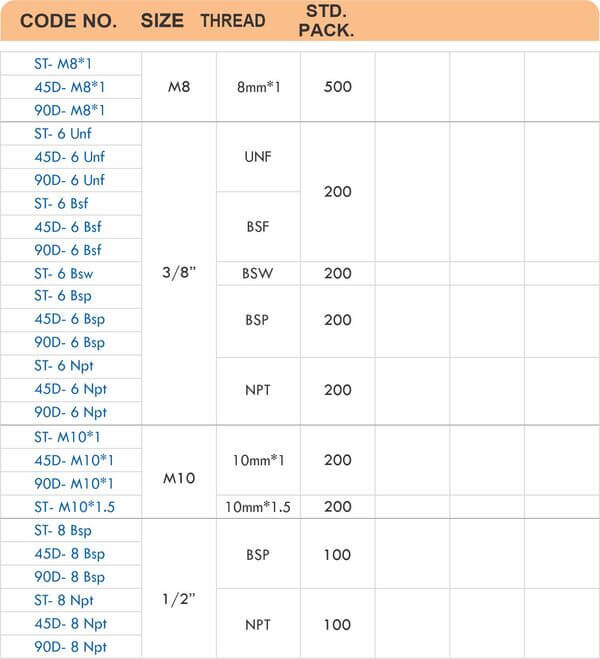
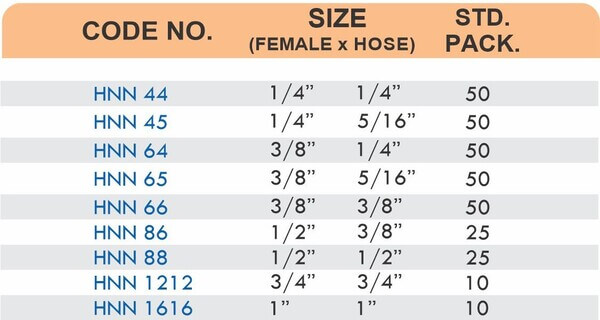
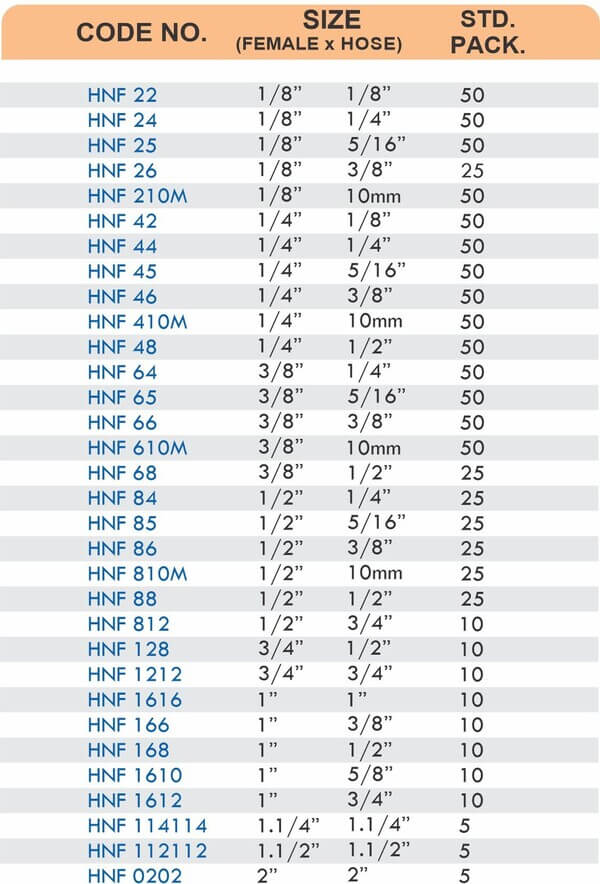
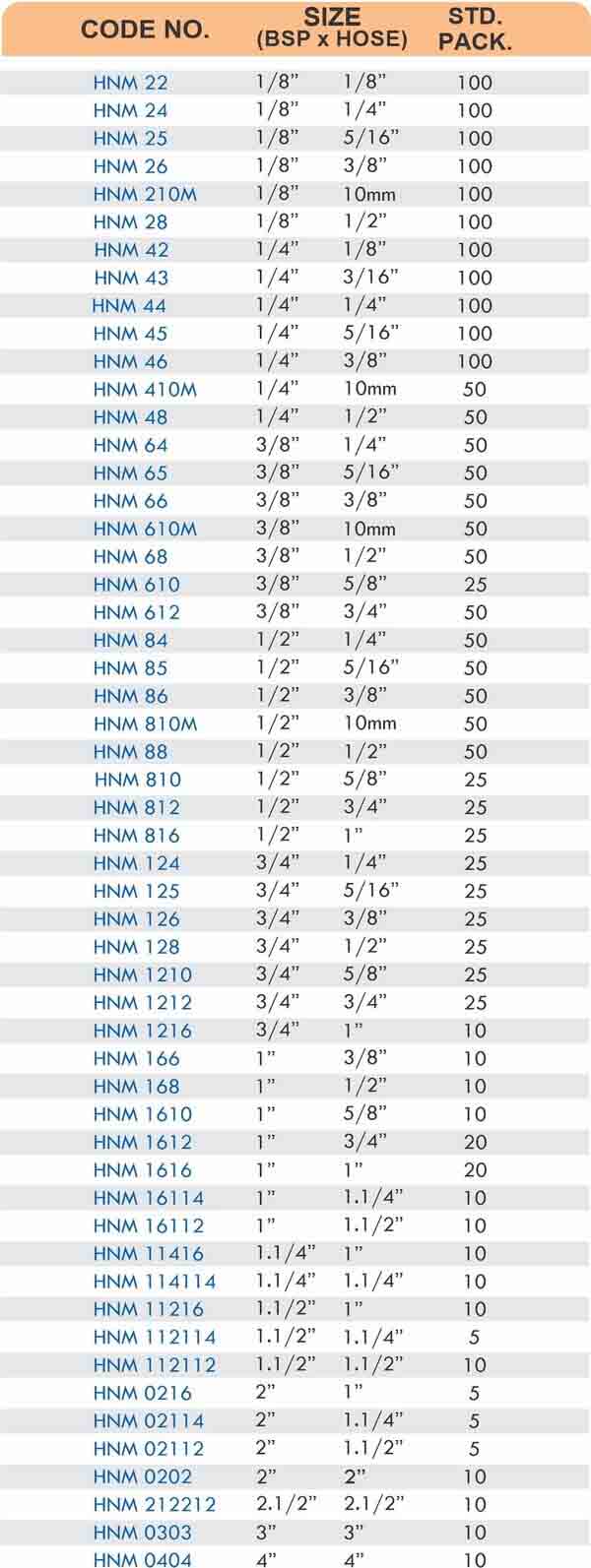
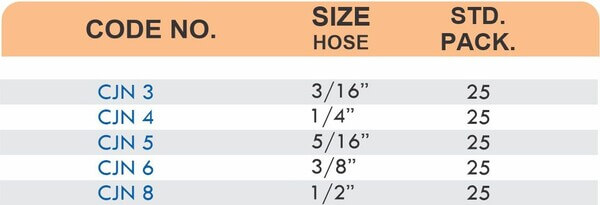
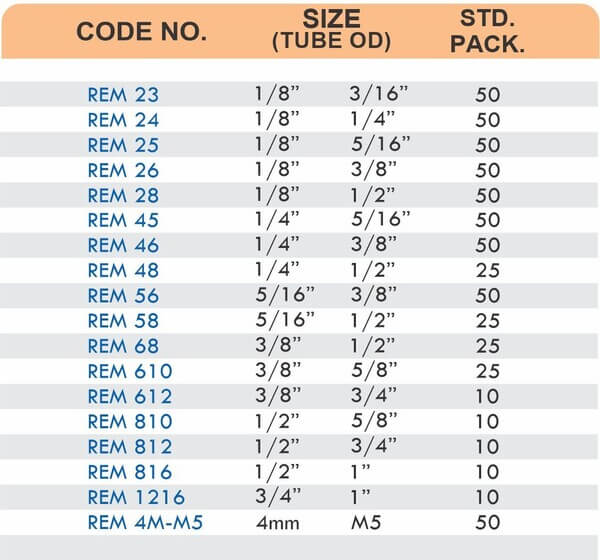
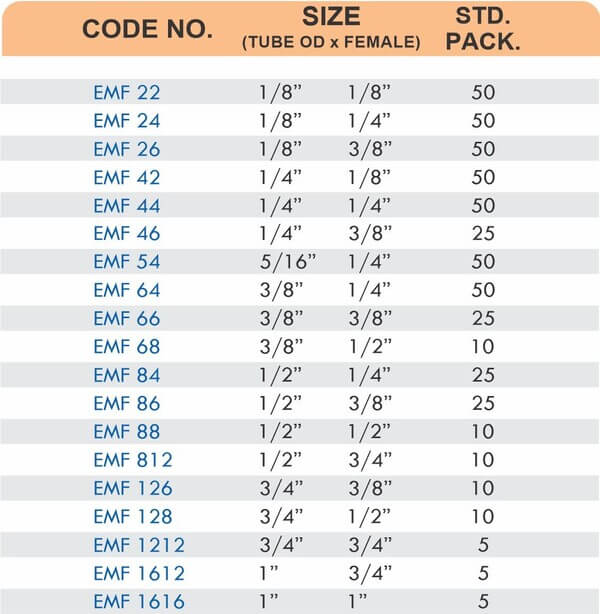
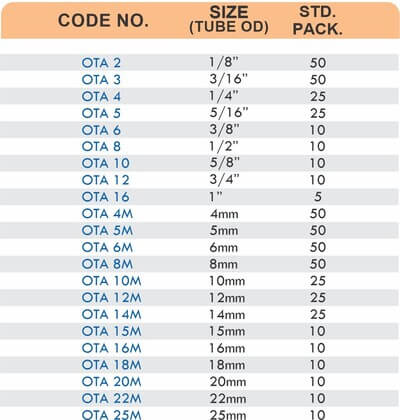
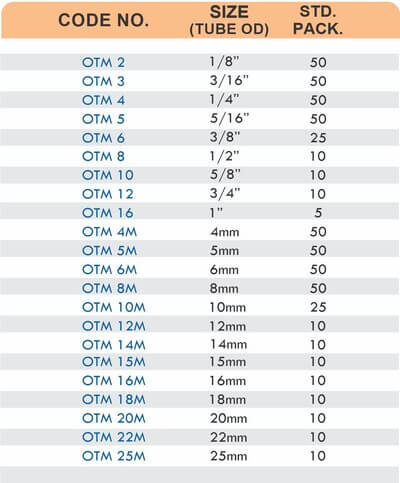
Types of Brass Compression Fittings
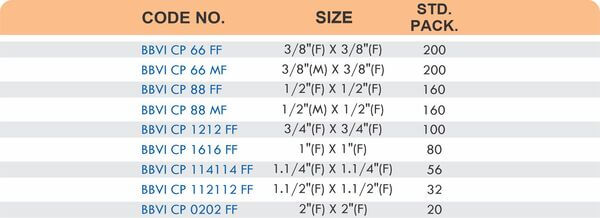
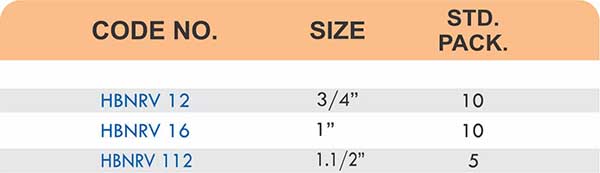
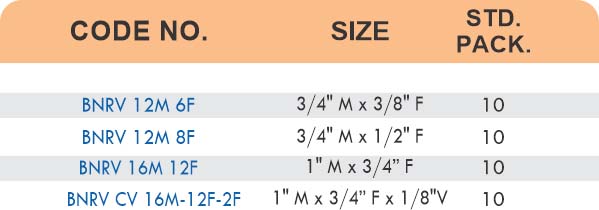
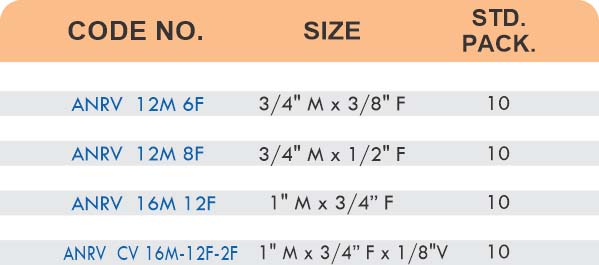
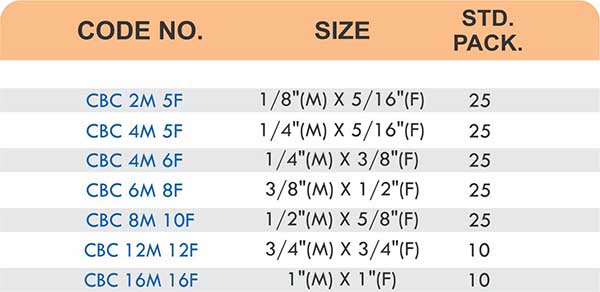
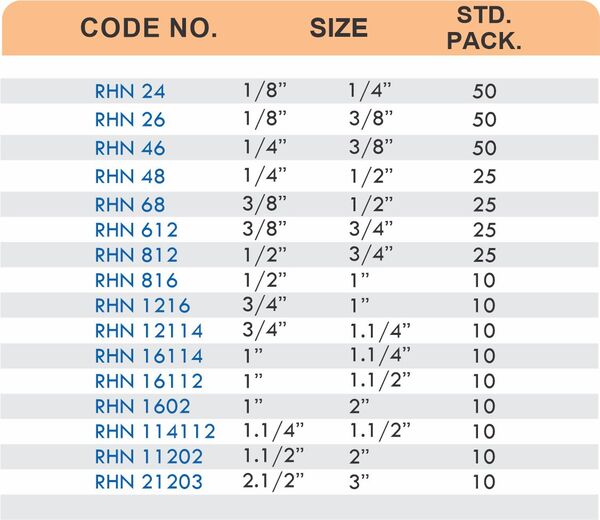
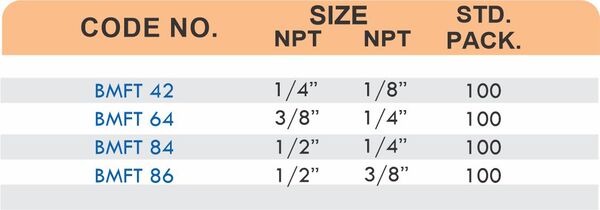
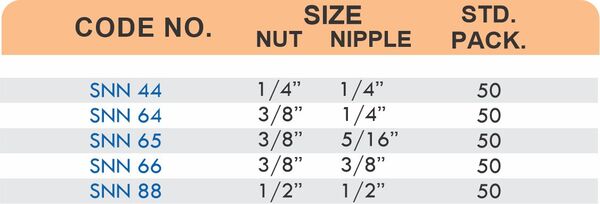
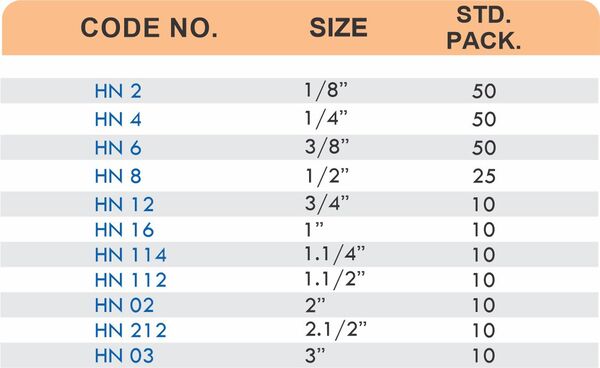
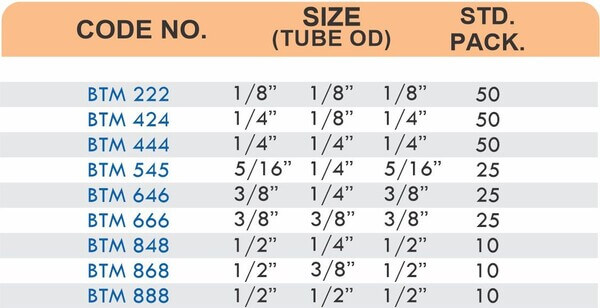
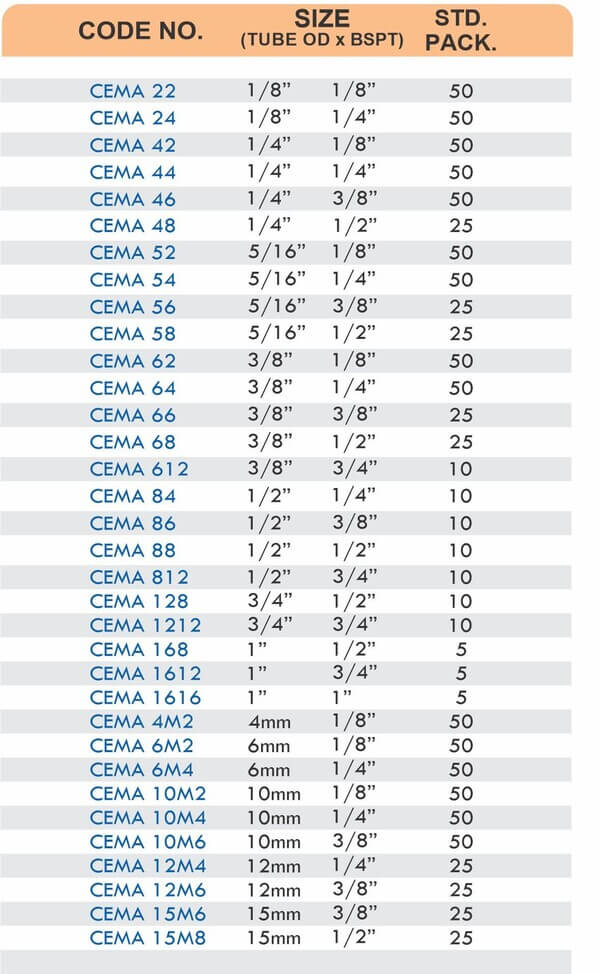
Straight couplings join tubes of equal diameter in a direct line. Elbow fittings create 90-degree or 45-degree turns without bending the tube itself. Tee fittings branch one line into two directions, supporting complex distribution networks.
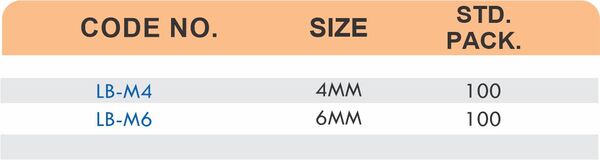
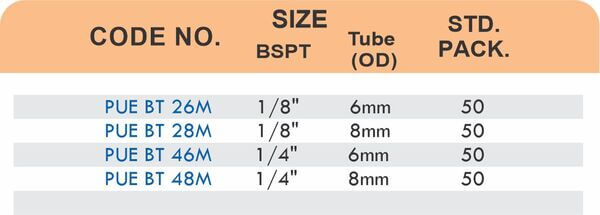
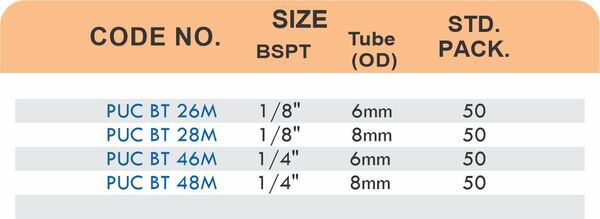
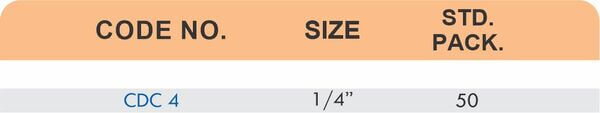
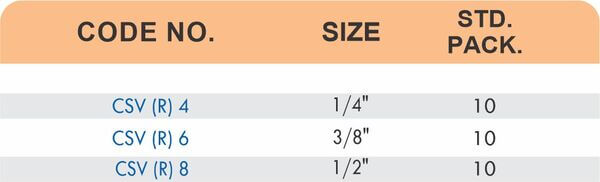
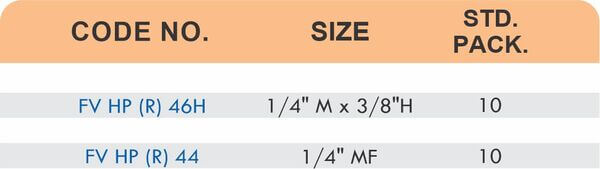
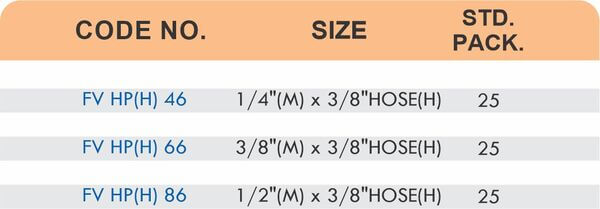
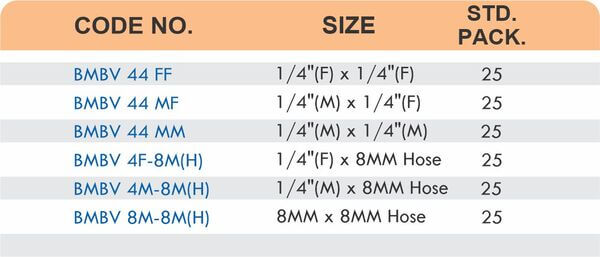
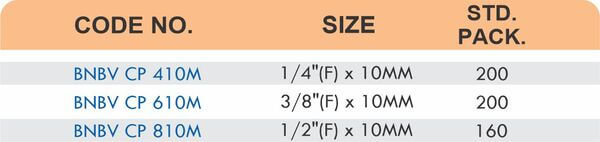
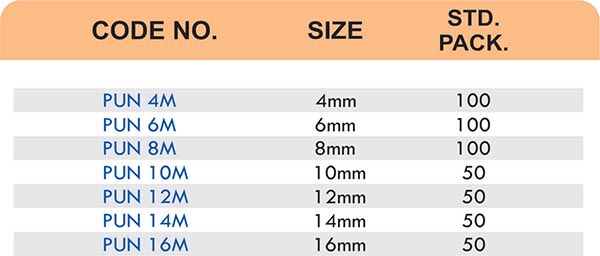
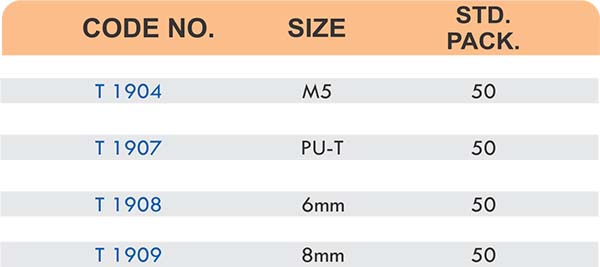
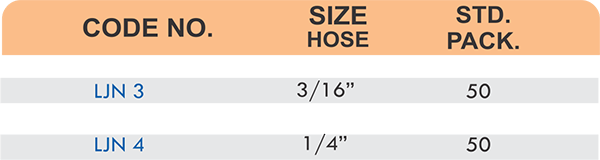
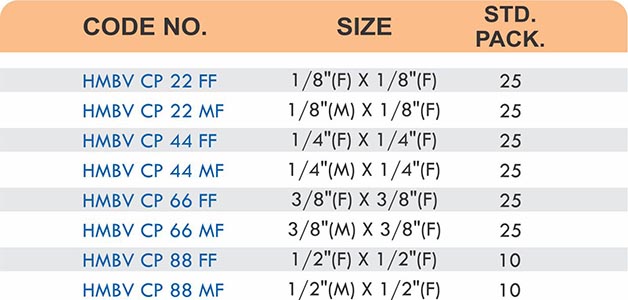
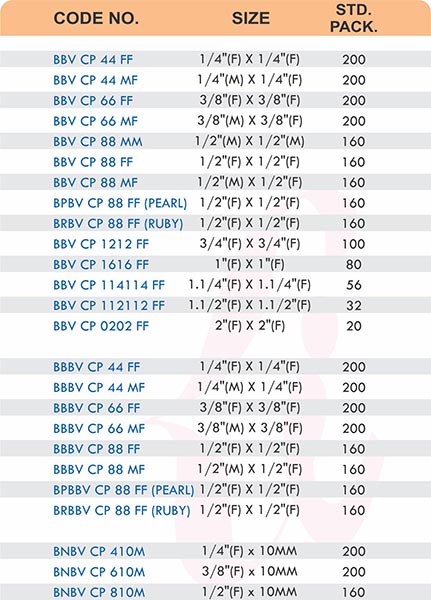
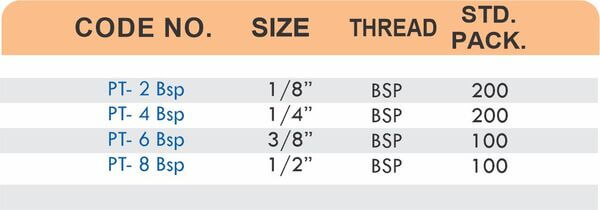
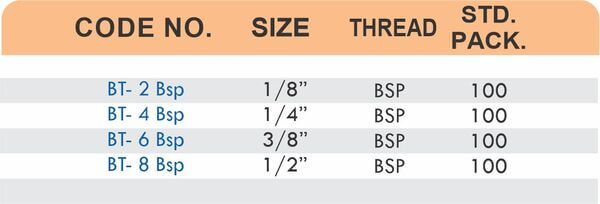
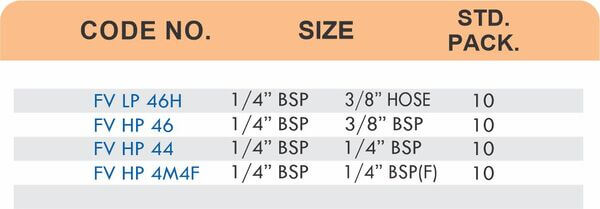
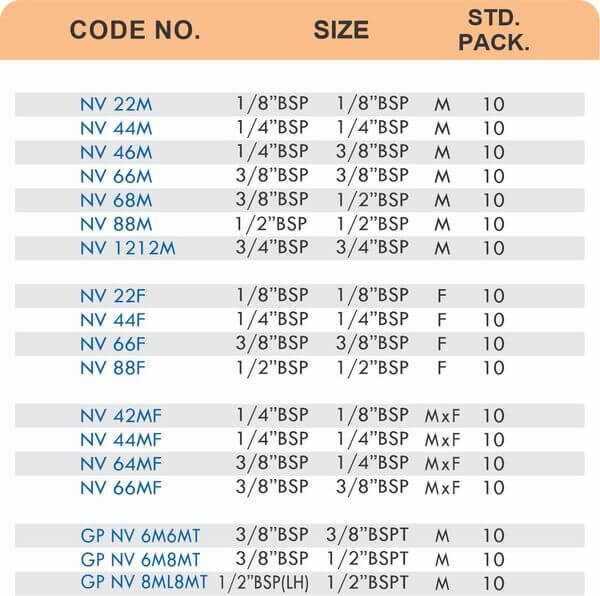
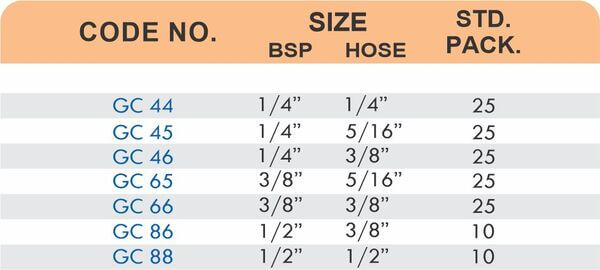
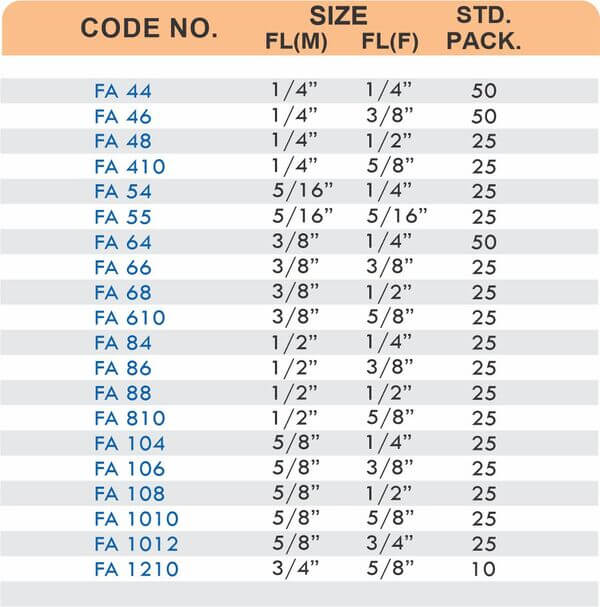
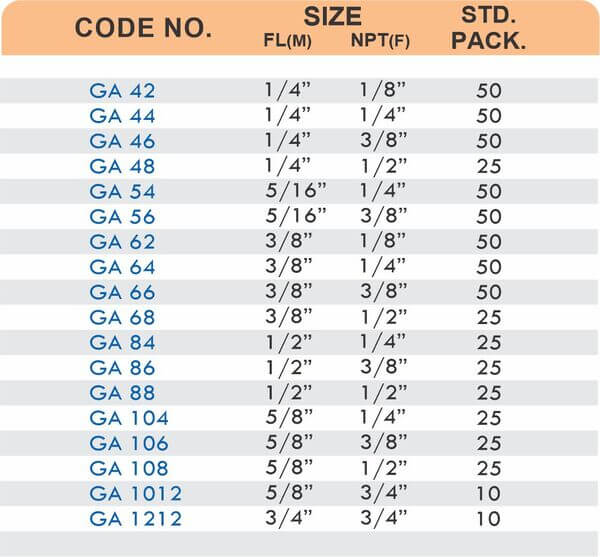
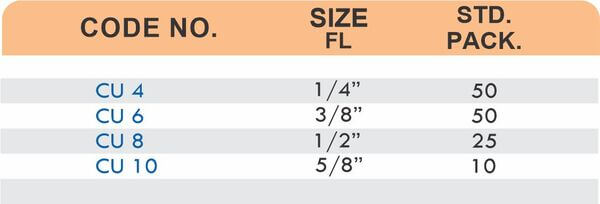
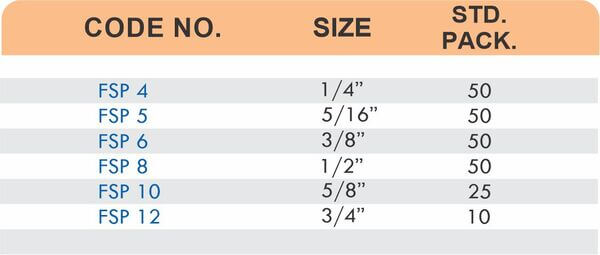
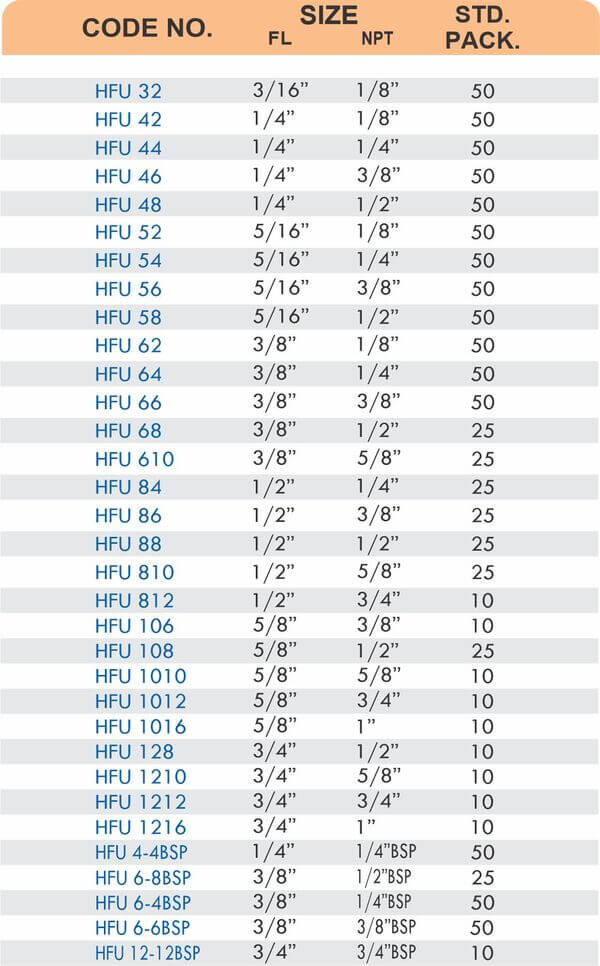
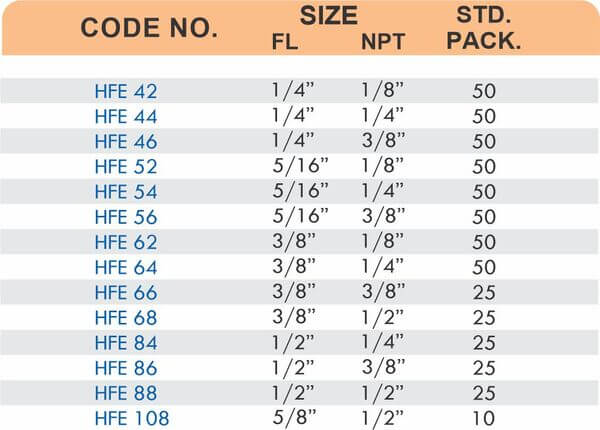
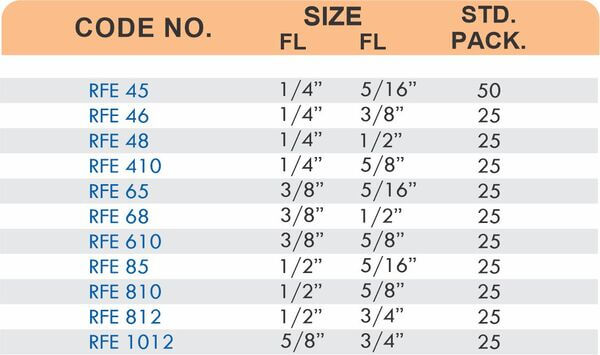
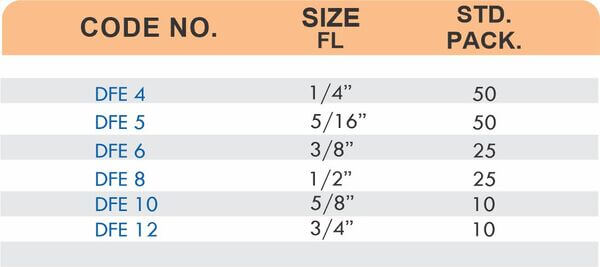
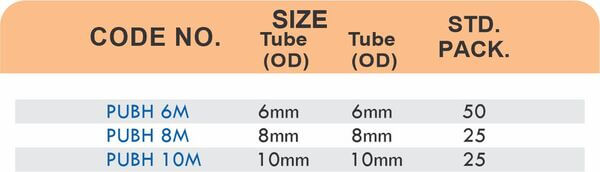
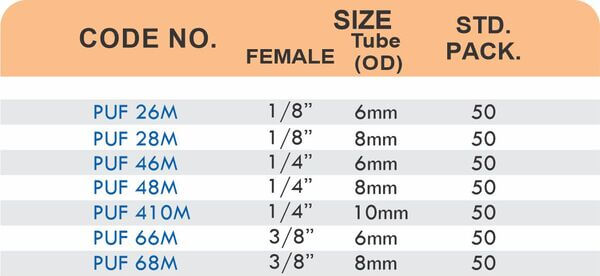
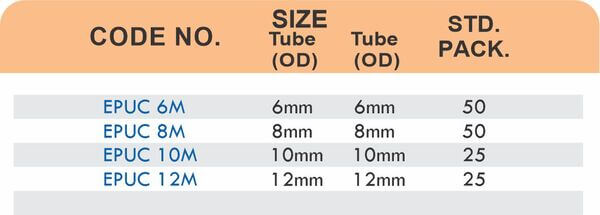
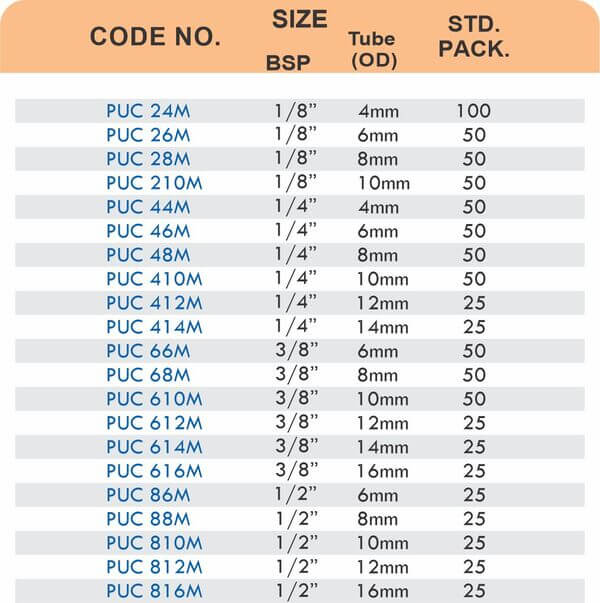
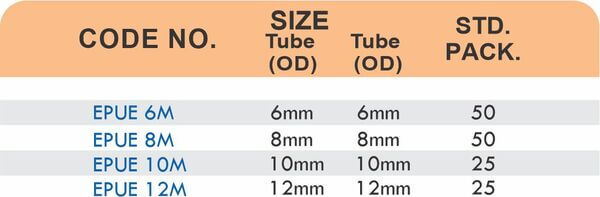
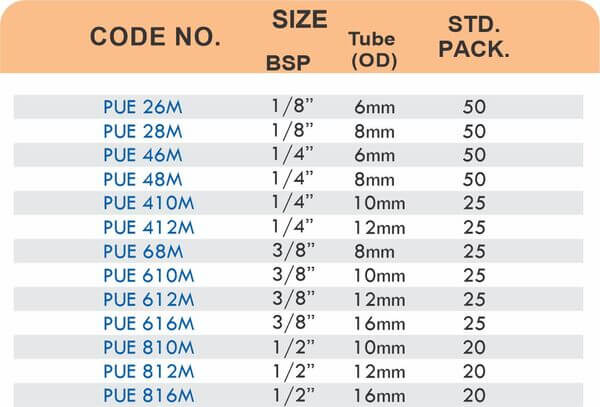
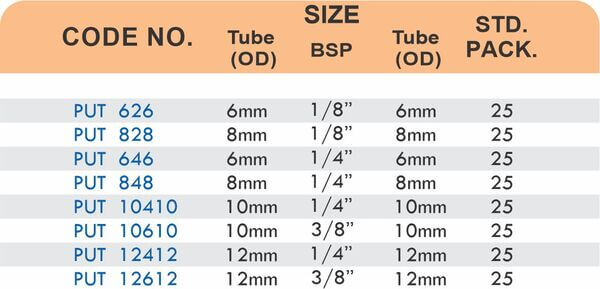
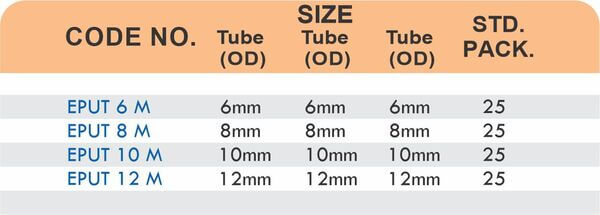
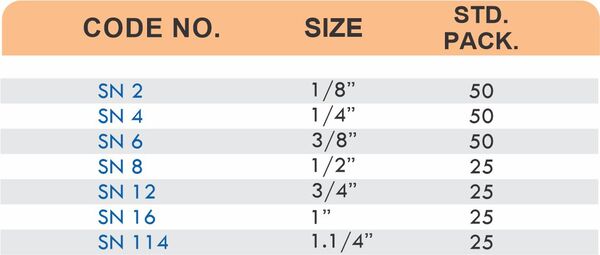
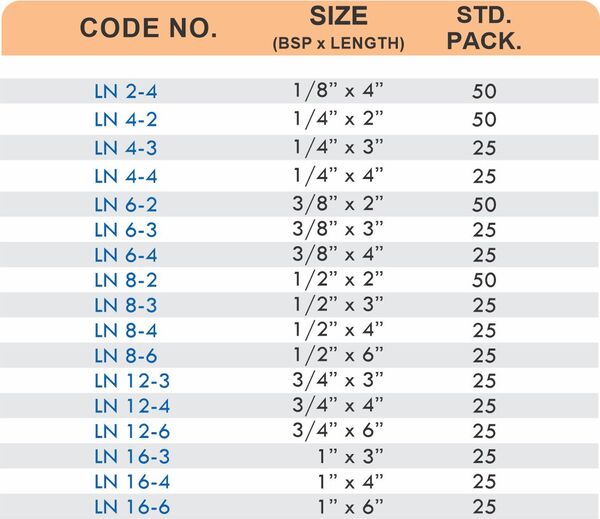
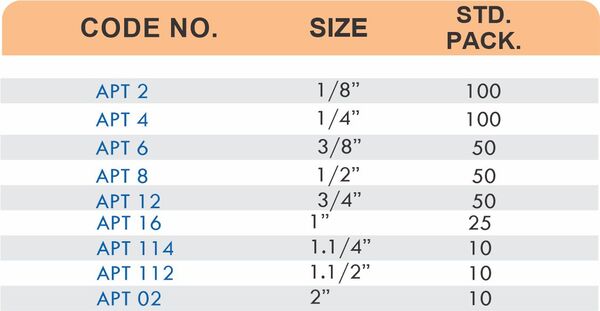
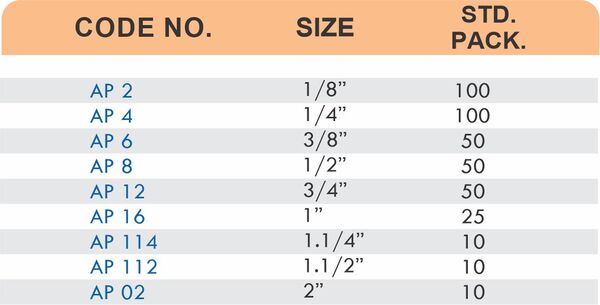
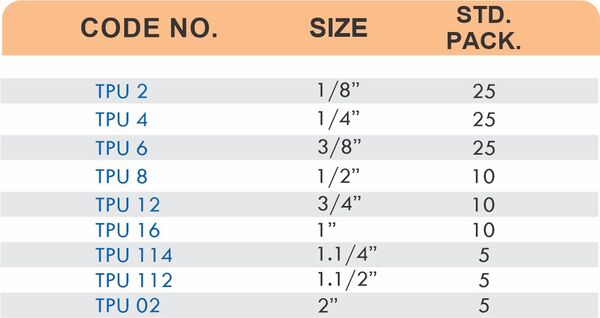
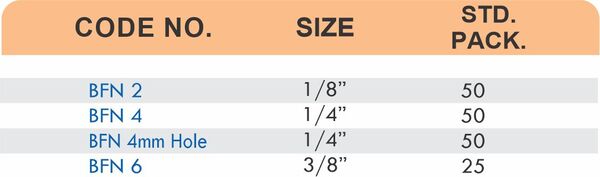
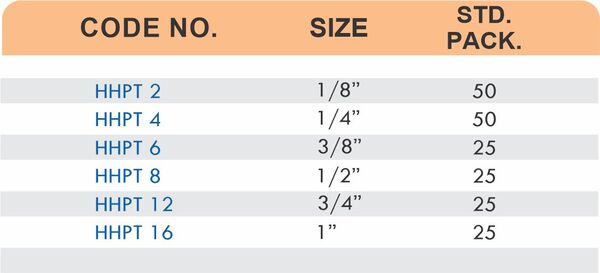
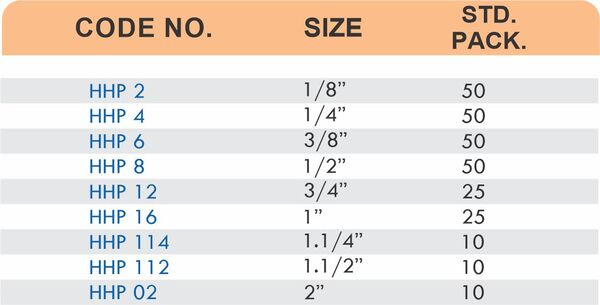
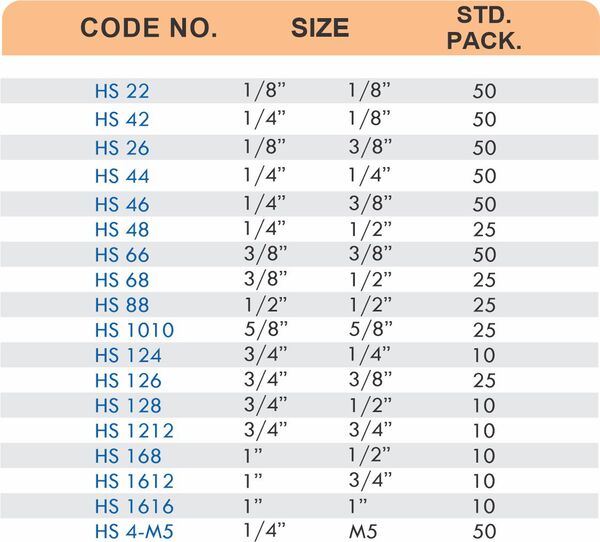
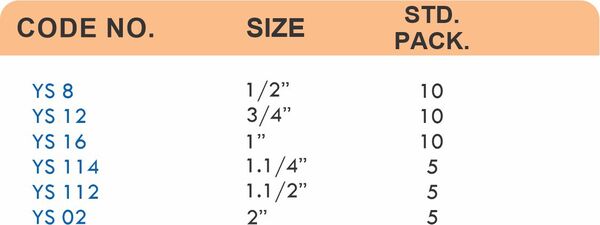
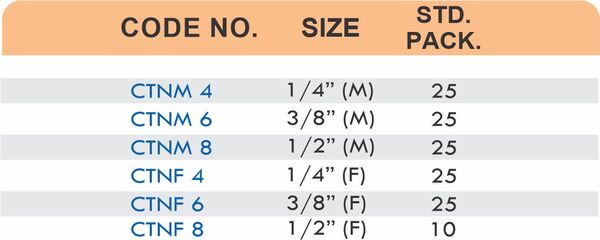
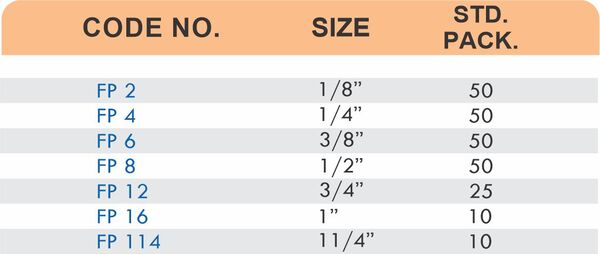
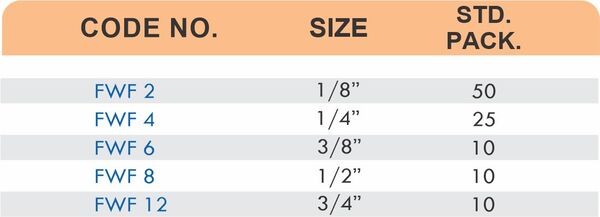
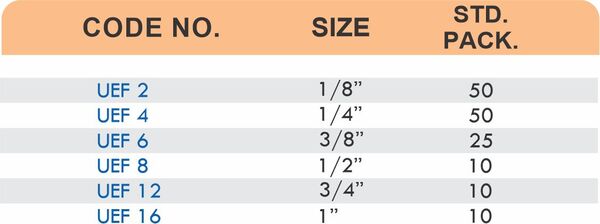
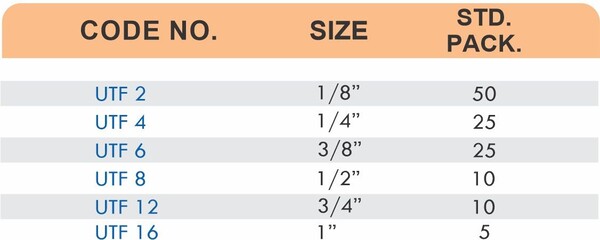
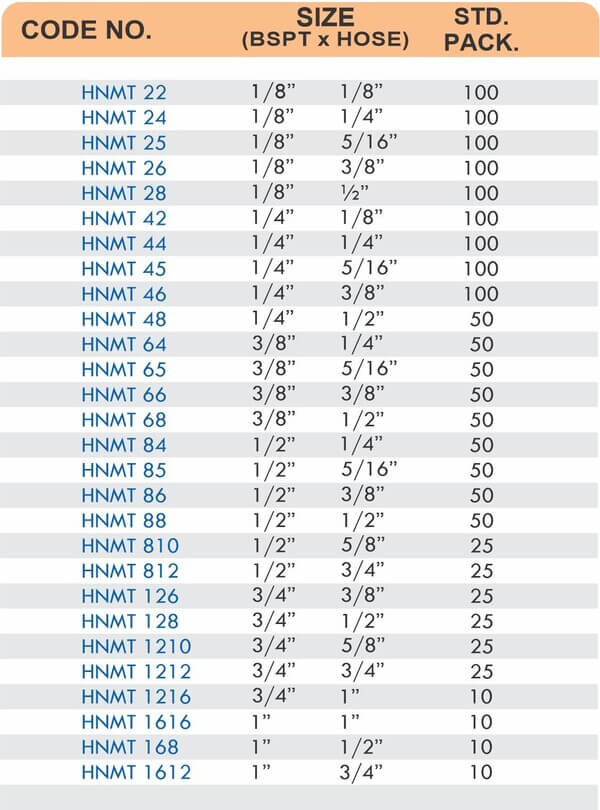
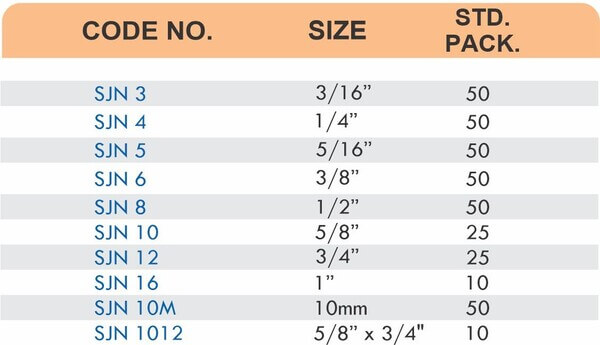
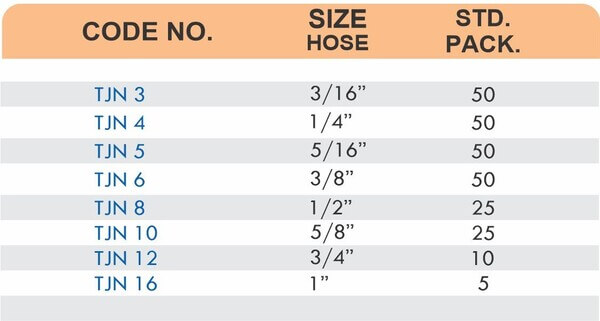
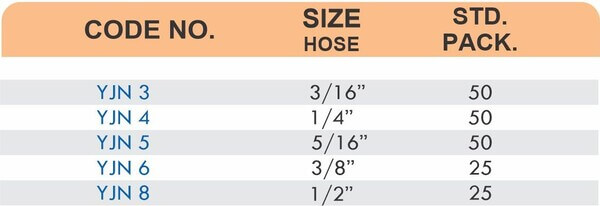
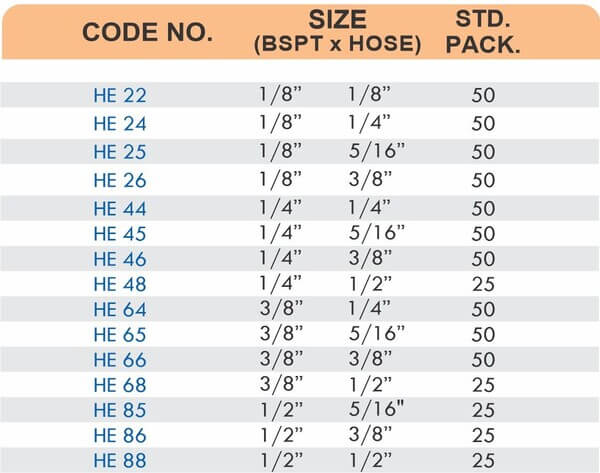
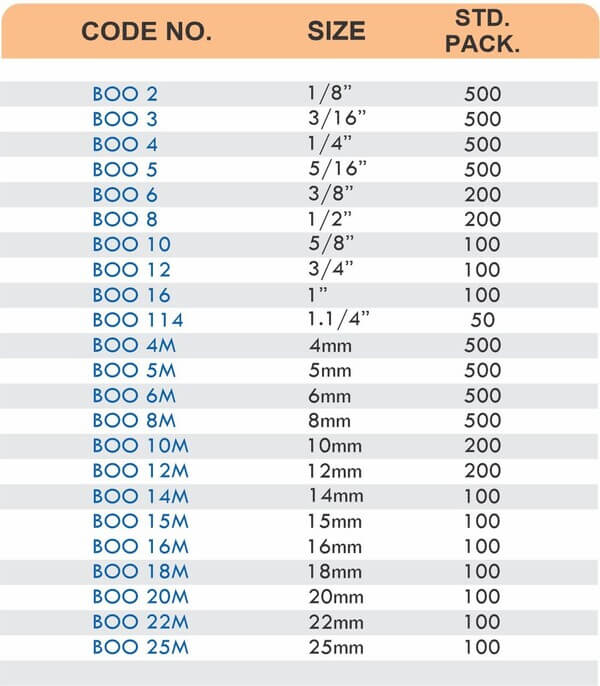
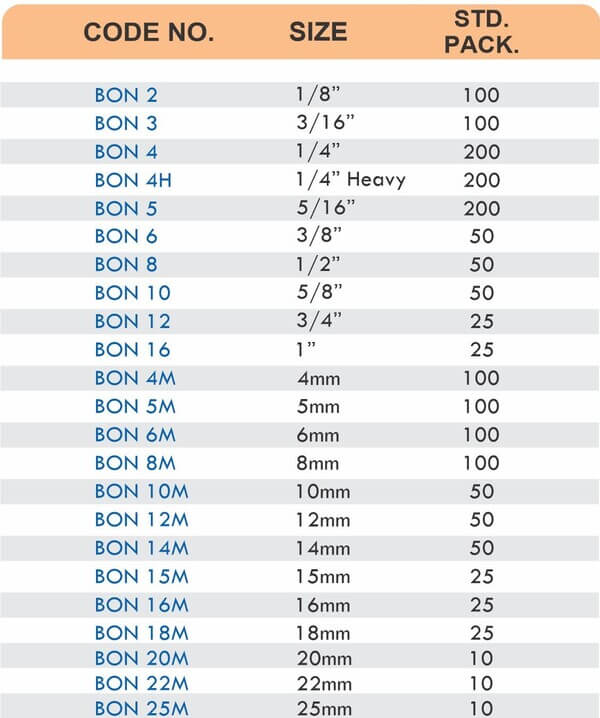
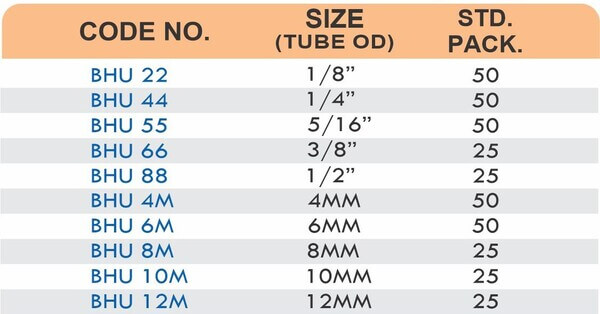
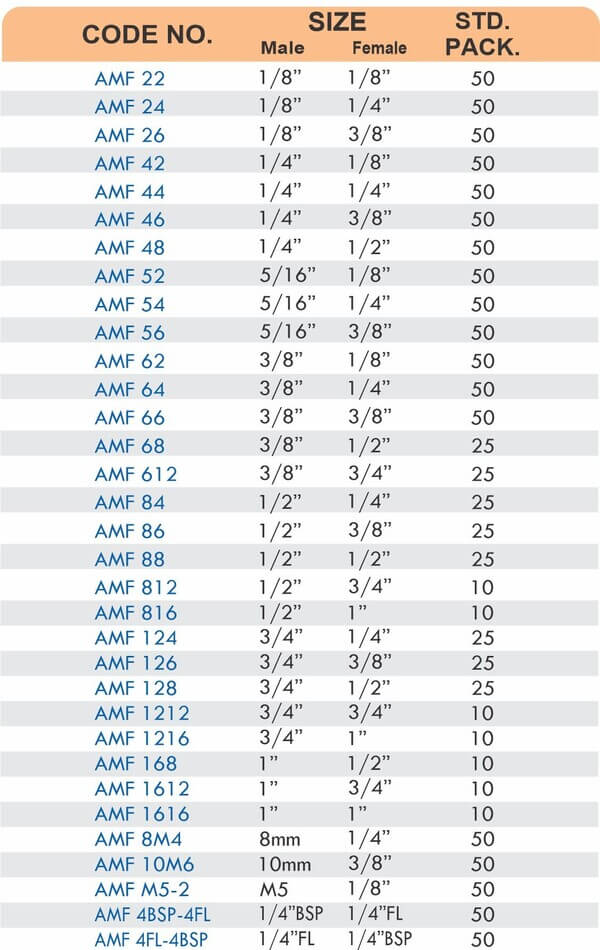
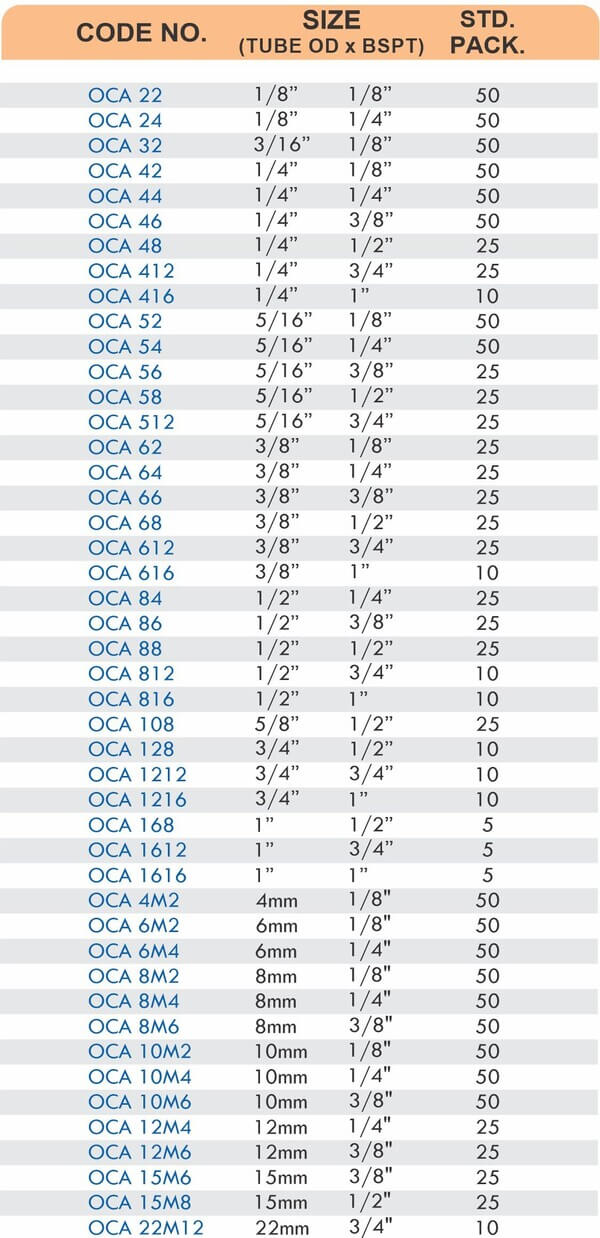
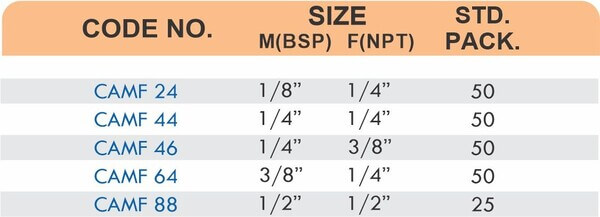
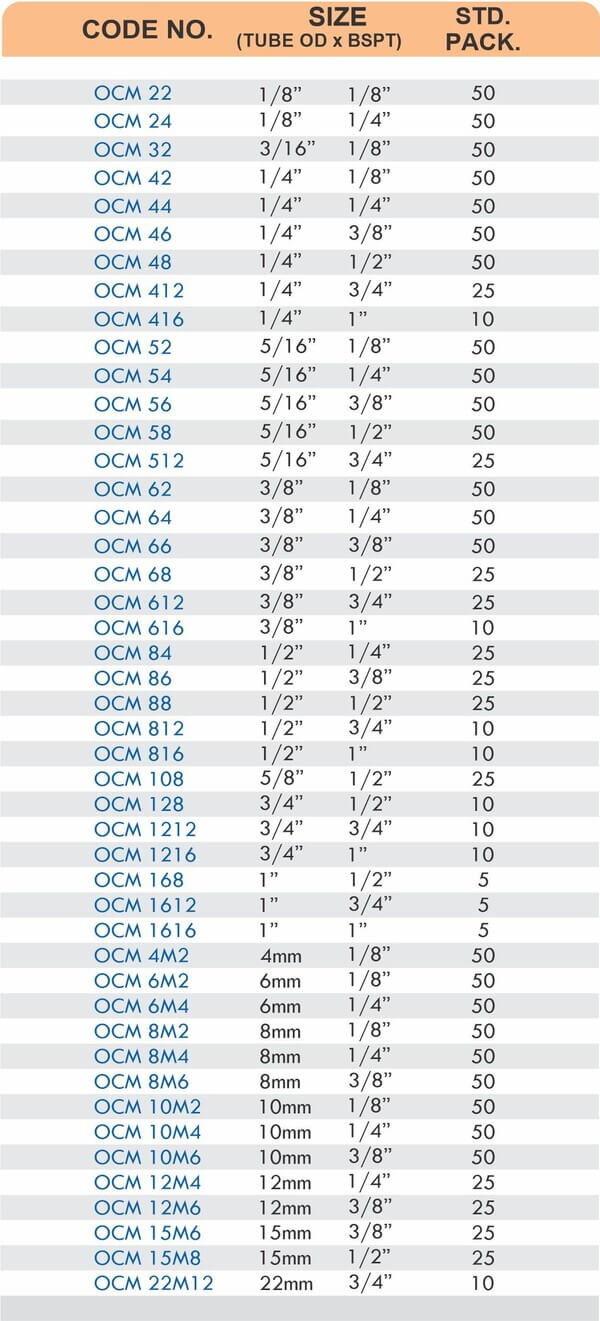
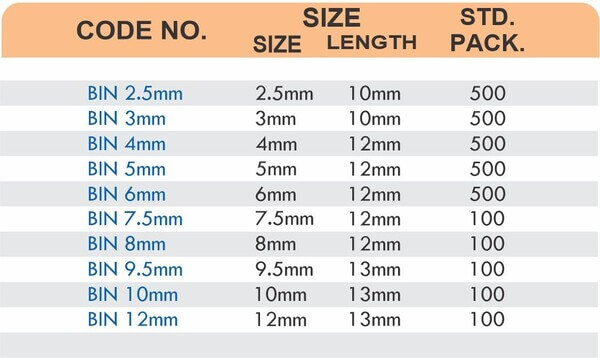
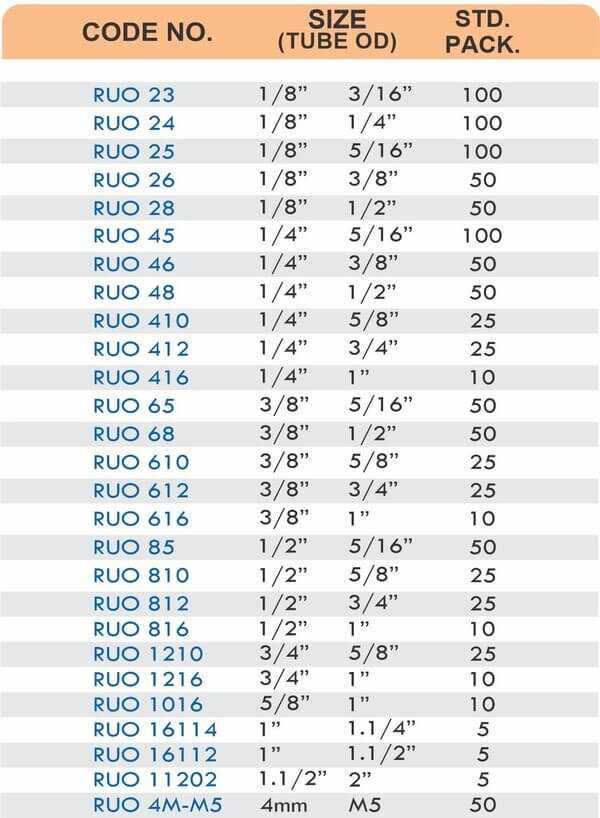
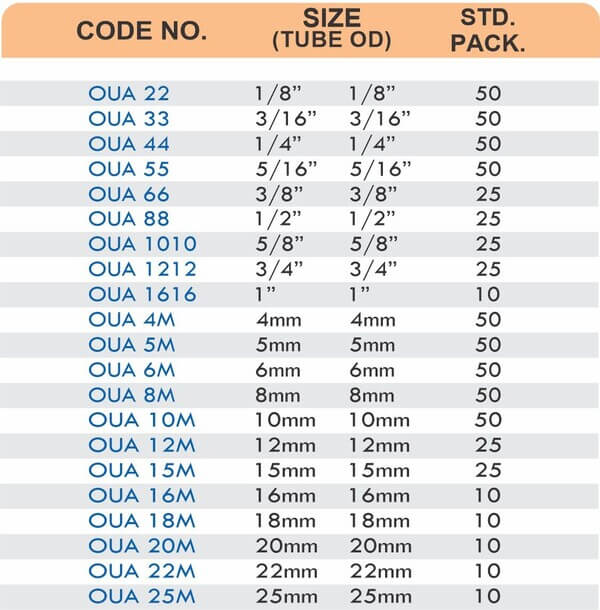
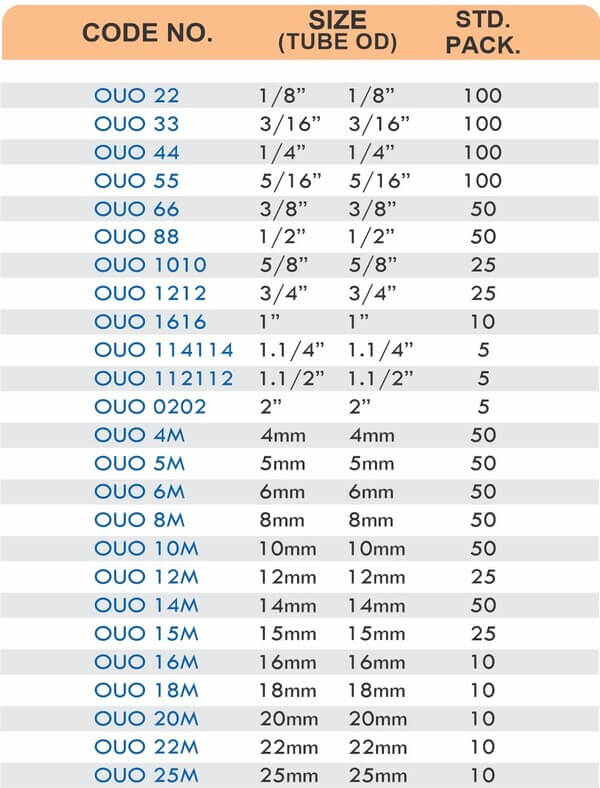
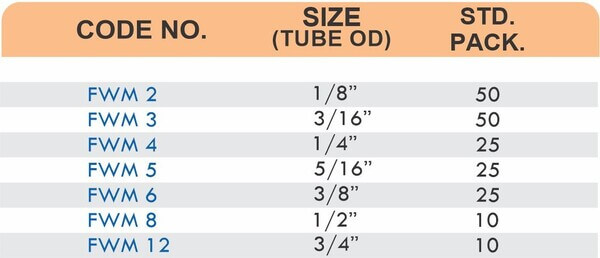
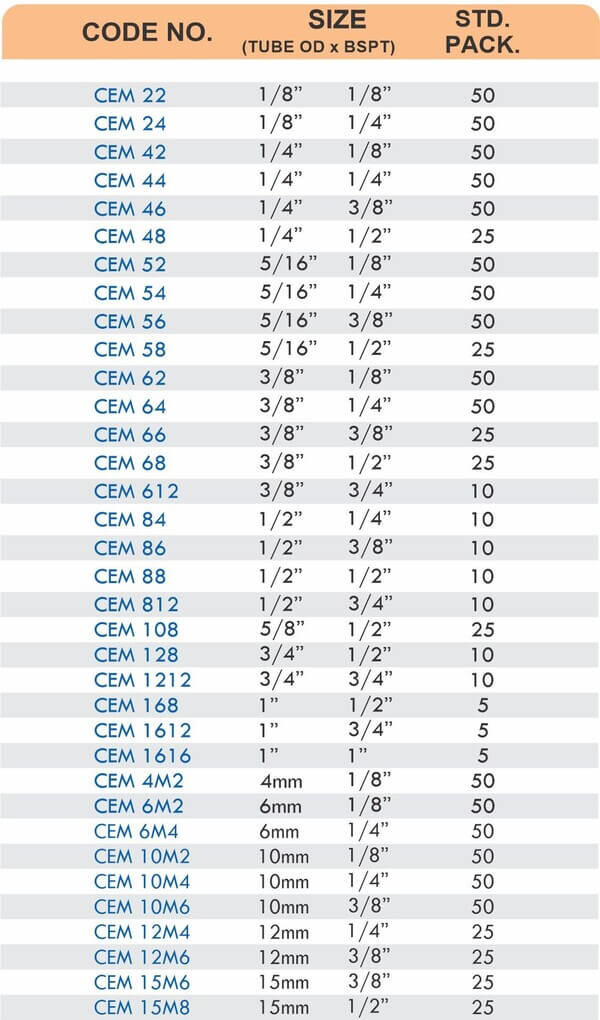
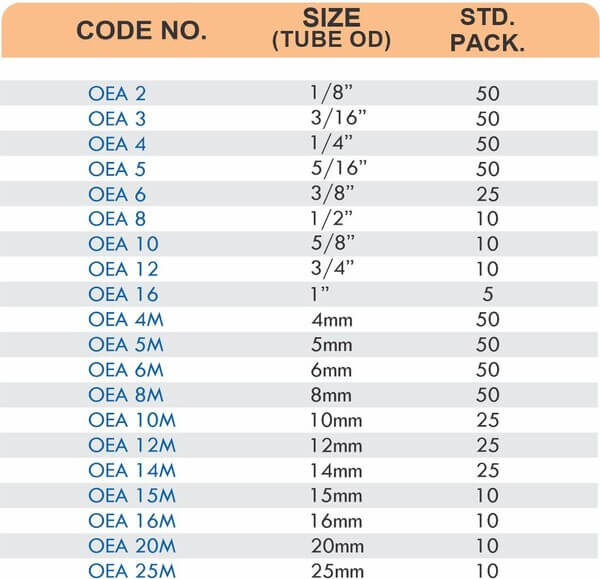
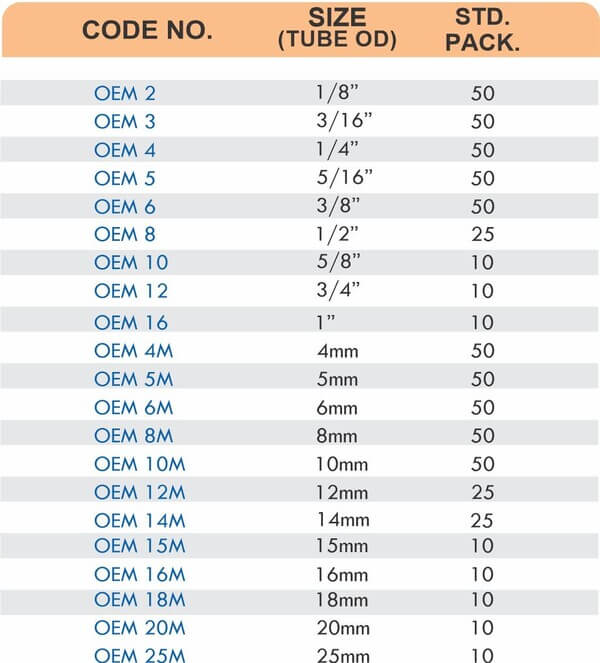
Reducers connect tubes of different diameters. Bulkhead fittings pass through walls or panels while maintaining seal integrity. Each type comes in sizes ranging from 4mm to 108mm for specialized industrial applications.
Common Applications
Plumbing Systems
Residential and commercial water lines use brass compression fittings for shut-off valves, fixture connections, and manifold assemblies. The no-flame installation protects surrounding materials during construction.
Gas and Oil Lines
Industrial facilities rely on these fittings for fuel distribution where pressure ratings reach 210 bar. The leak-proof seal prevents hazardous material release while allowing system modifications.
HVAC Equipment
Refrigerant lines and condensate drains use compression fittings for field serviceability. Technicians can disconnect and reconnect lines during equipment replacement without specialized tools.
Instrumentation and Control
Process industries use brass compression fittings for gauge connections and sample ports. The vibration resistance matters less in stationary applications, while the reusability supports calibration and testing cycles.
Installation Best Practices
Cut tubes square using a proper tube cutter, not a hacksaw. Uneven cuts prevent full insertion and compromise the seal. Remove all burrs from inside and outside edges with a deburring tool.
Slide the nut onto the tube first, followed by the ferrule with the tapered end facing the fitting body. Insert the tube until it contacts the internal stop. Tighten by hand as far as possible, then add the recommended number of turns with a wrench.
For 6mm to 15mm fittings, add 1 to 1.5 turns past hand-tight. Larger sizes require fewer turns. Never use serrated-jaw tools that damage the soft brass surface. A drop of thread sealant on the threads (not the ferrule) helps achieve proper torque.
Performance in Different Environments
Brass compression fittings handle temperatures from -65°F to +250°F without degradation. This range covers most industrial and commercial applications. However, extreme temperature cycling can loosen connections over time.
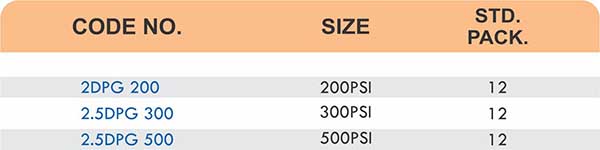
Pressure ratings vary by size. Smaller 4mm to 6mm fittings support up to 3045 PSI in hydraulic systems, while 25mm fittings drop to 1015 PSI. Always verify the fitting specifications match your system requirements before selection.
Coastal or chemical environments require dezincification-resistant (DZR) brass variants. Standard brass can corrode when exposed to specific water chemistries or industrial fluids. DZR brass maintains integrity in these harsh conditions.
FAQs
Can brass compression fittings be reused after disassembly?
Yes, but inspect the ferrule for cracks or deformation. If the compression ring shows damage, replace it before reassembly. The fitting body and nut typically withstand multiple uses without issue.
Do these fittings work with plastic tubing?
Some compression fittings accept plastic tubes with acetal sleeves that prevent crushing. However, pressure ratings drop significantly compared to metal tubing. Verify compatibility before mixing materials.
How do I know if I’ve tightened enough?
After the recommended wrench turns, pressurize the system and check for leaks. If weeping occurs, add a quarter-turn at a time until it stops. Never exceed 2.5 total turns past hand-tight.
Should compression fittings be used underground?
No. Brass compression fittings are not recommended for below-ground applications where inspection and maintenance access is limited. Use soldered or welded joints in buried installations.
Conclusion
Brass compression fittings offer a practical middle ground between permanent soldered joints and quick-connect systems. They excel in accessible locations where reusability matters and vibration stays minimal. The no-flame installation, immediate pressure capability, and corrosion resistance make them a solid choice for most commercial and industrial piping needs. Yet the bulkier profile, vibration sensitivity, and precise tightening requirements mean they’re not universal solutions.
Choose based on your specific environment, pressure demands, and maintenance access. When the conditions align, brass compression fittings deliver decades of leak-free performance.
K K International supplies precision-engineered brass compression fittings that meet international standards for plumbing, HVAC, and industrial applications. Our product range covers all major sizes and configurations with guaranteed pressure ratings and corrosion resistance. Visit kkinternational.co.in to explore our complete catalog and request technical specifications for your next project.