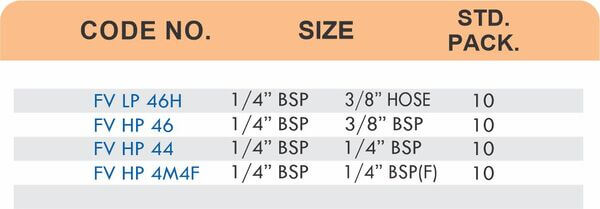
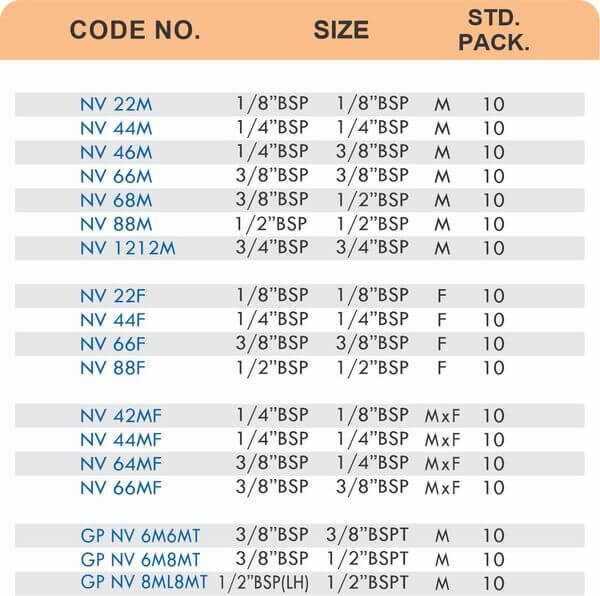
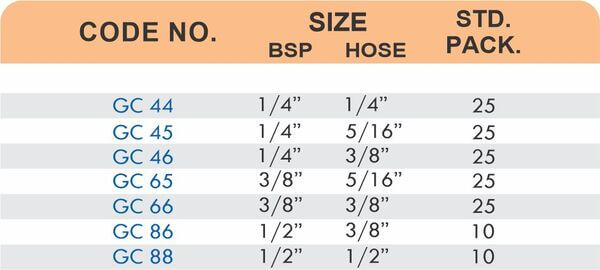
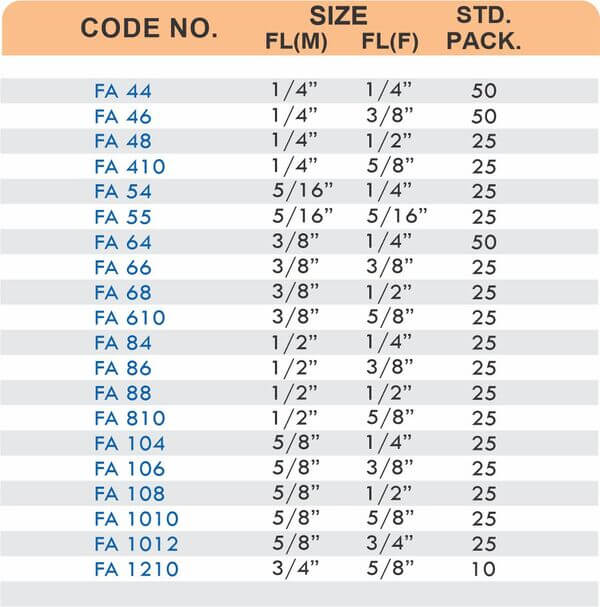
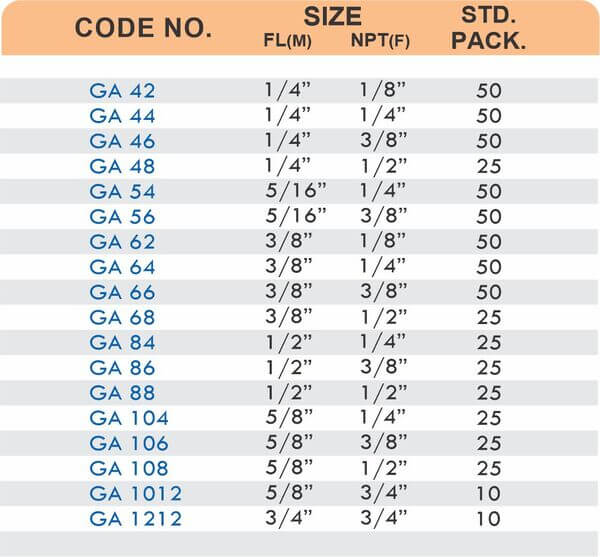
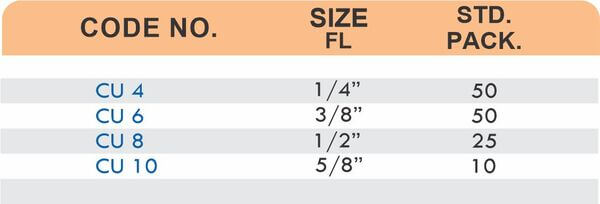
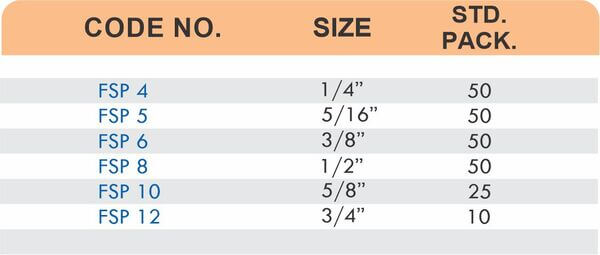
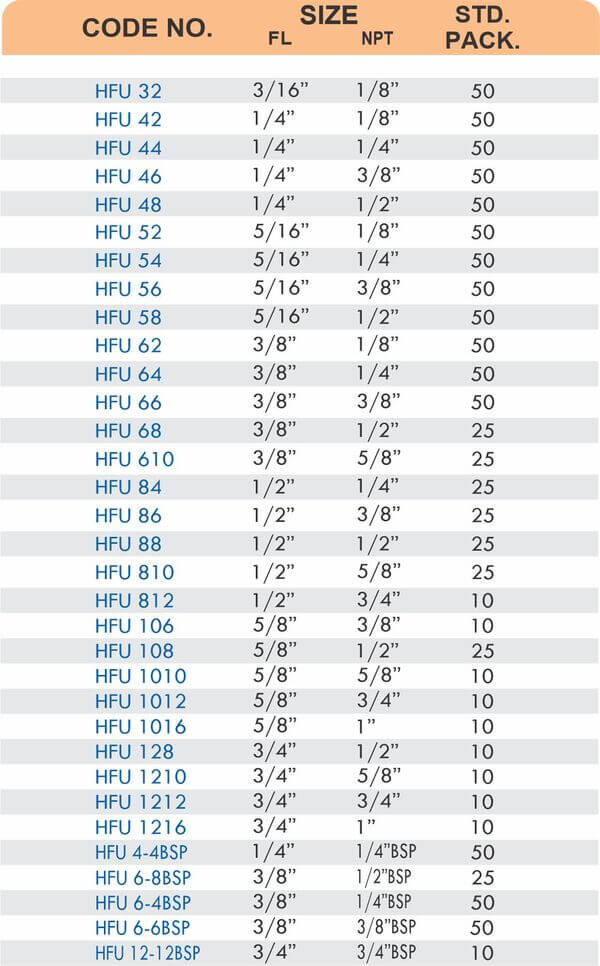
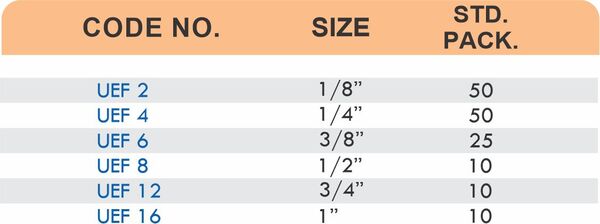
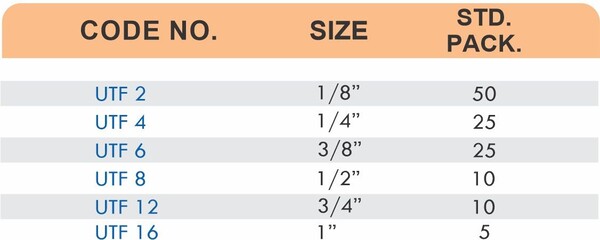
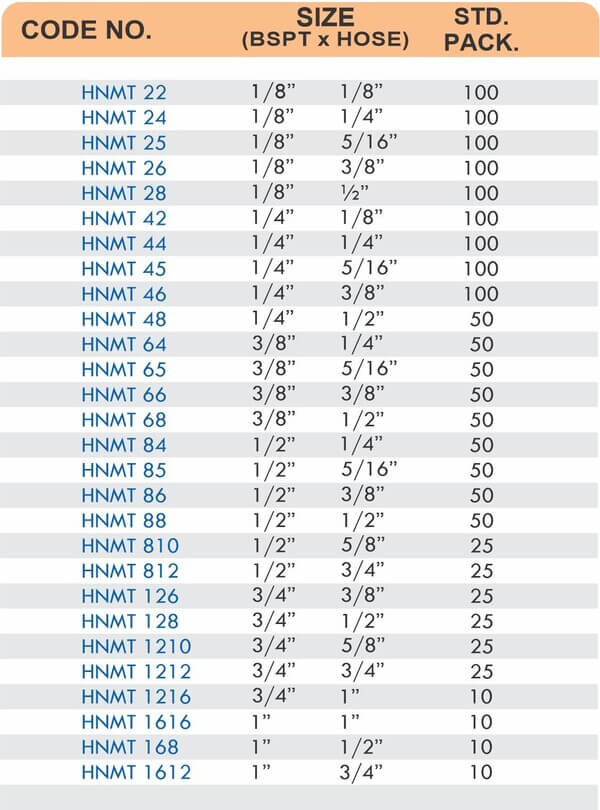
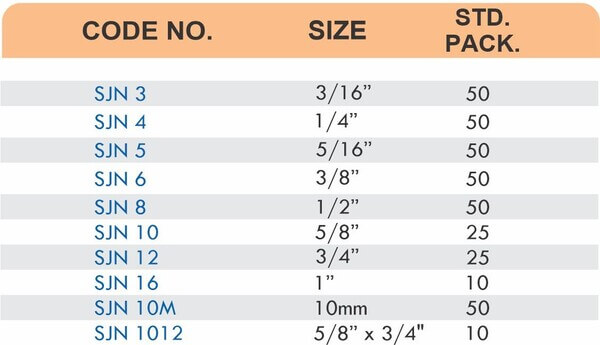
4 Styles and 5 Advantages of Brass Fittings (Compression, Hose, Pipe, Tube)
Selecting fittings based on price alone leaves you with leak-prone connections, frequent replacements, and downtime that costs more than you saved. The wrong fitting style wastes installation time; the wrong material fails under pressure. Brass fittings eliminate both problems when you match the correct style to your application and leverage the material’s inherent advantages.
This guide breaks down the four primary brass fitting styles—compression, hose, pipe, and tube—and explains the five performance advantages that make brass the preferred choice across plumbing, industrial, and instrumentation systems. You’ll learn which style handles your specific connection needs and why brass outperforms alternatives in durability, installation speed, and total cost of ownership.
Four Styles of Brass Fittings
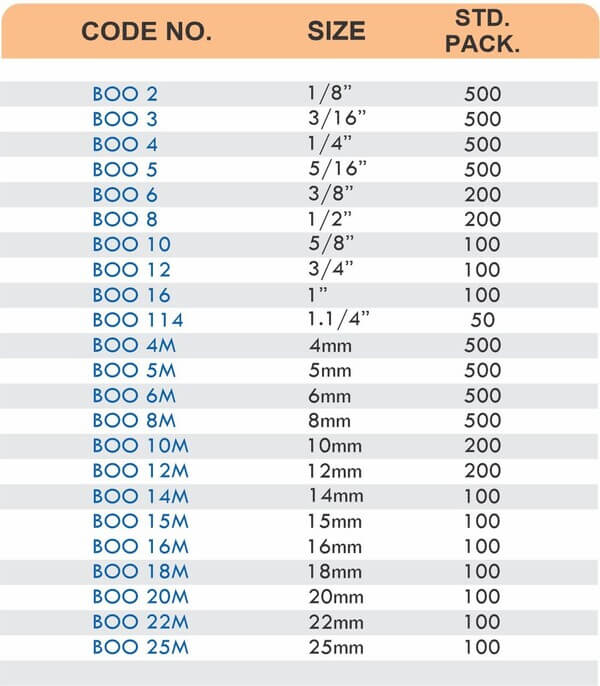
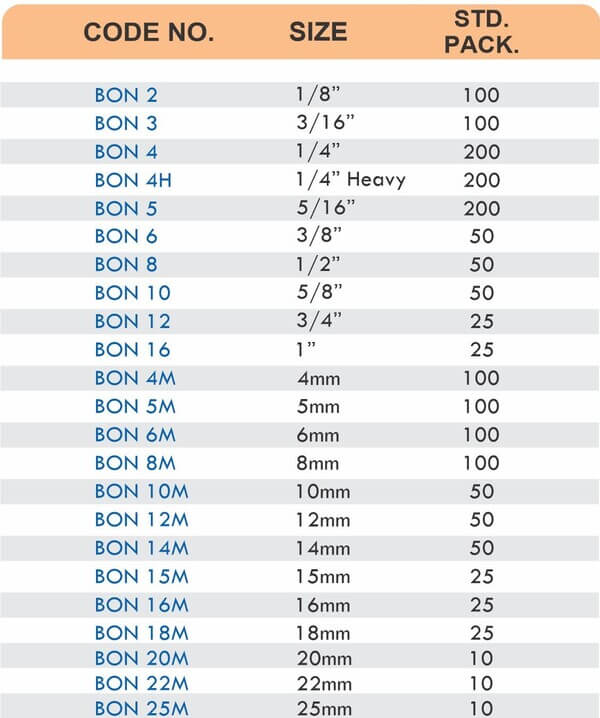
Compression Fittings
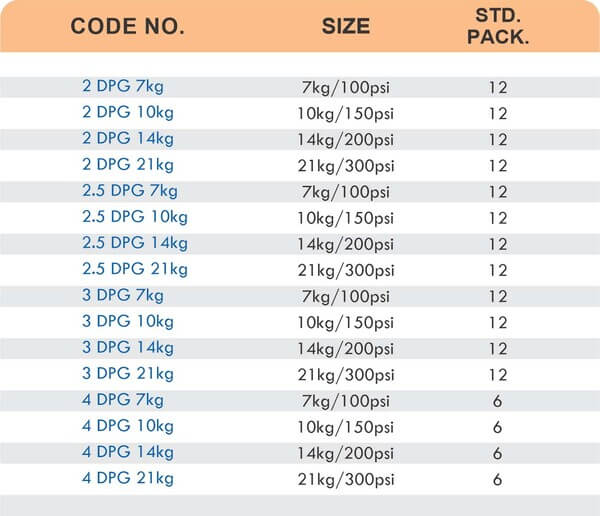
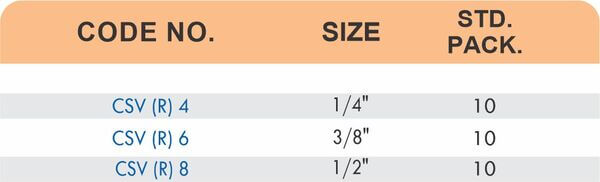
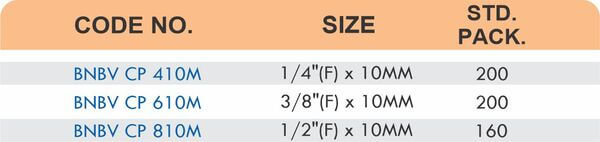
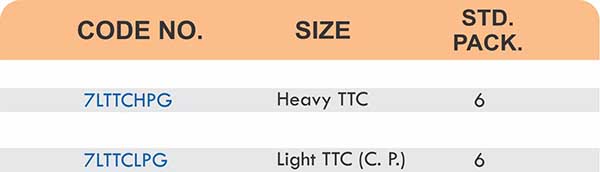
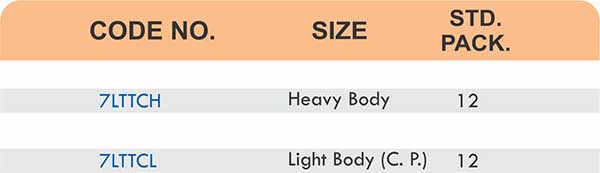
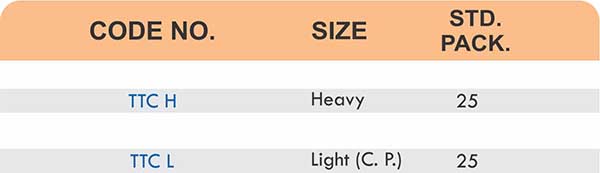
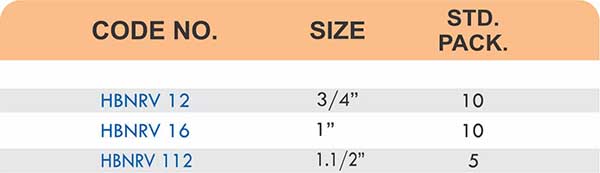
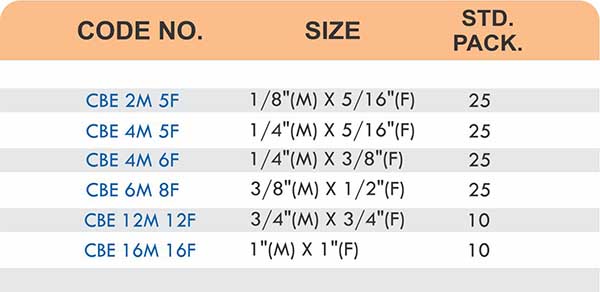
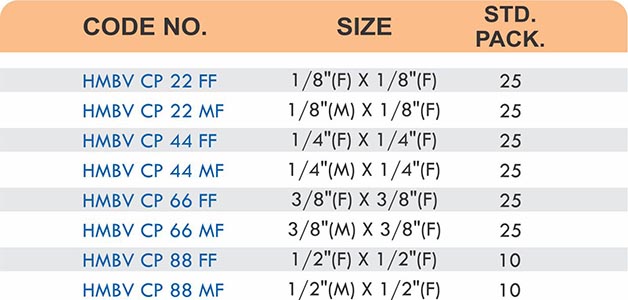
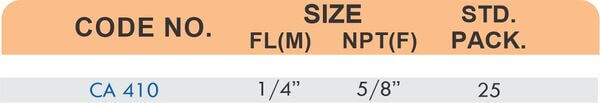
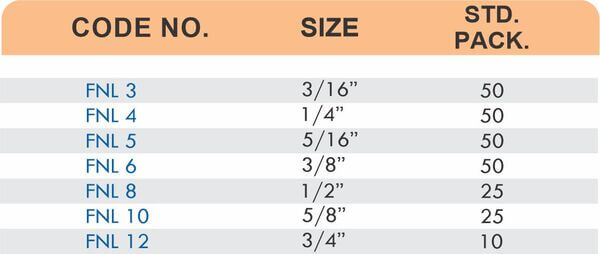
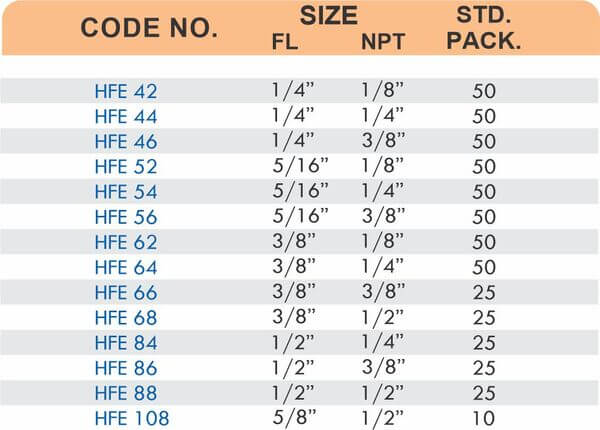
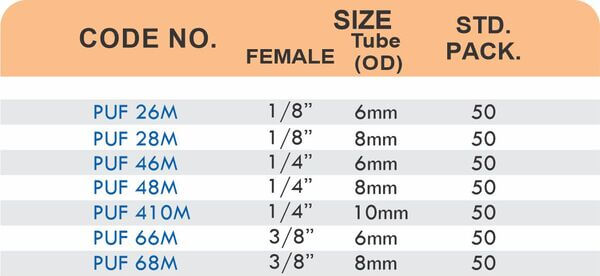
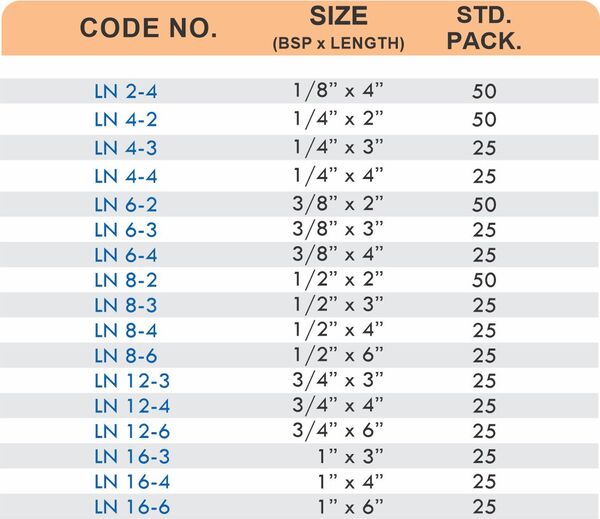
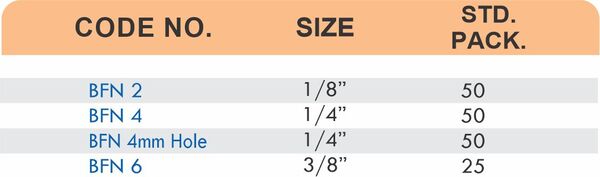
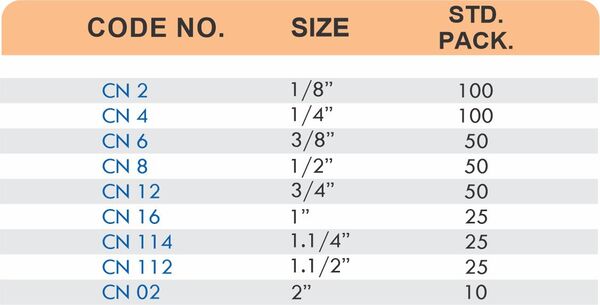
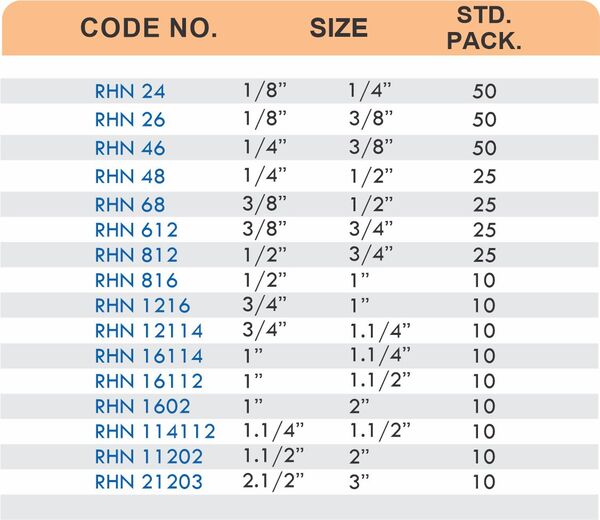
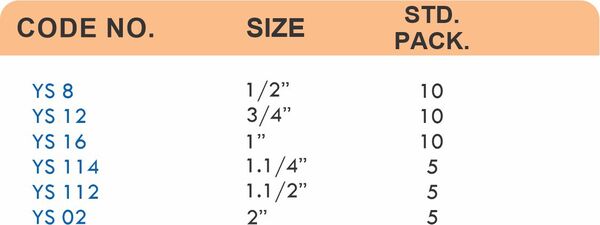
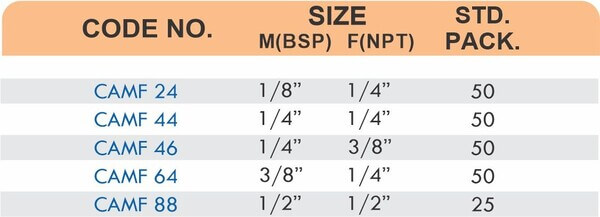
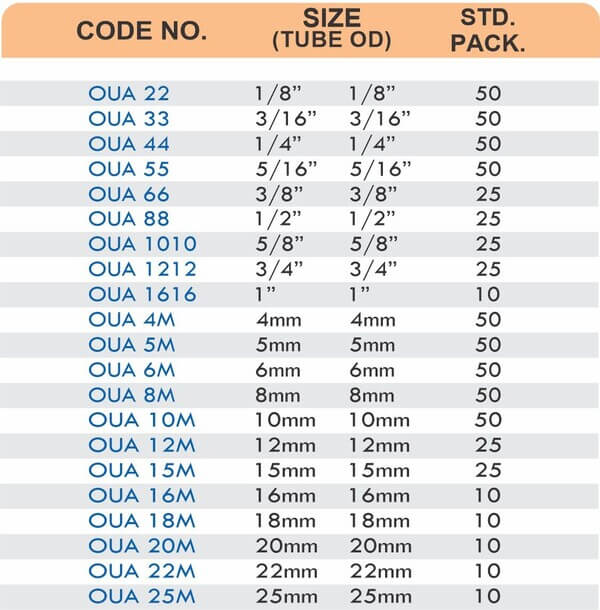
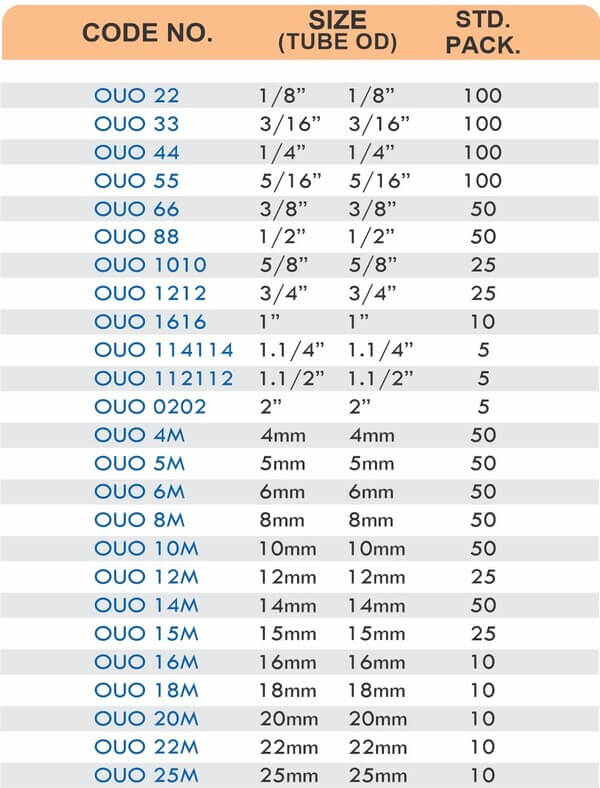
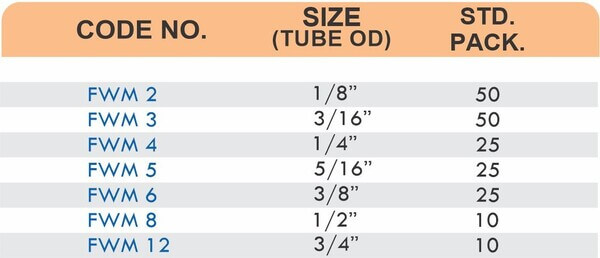
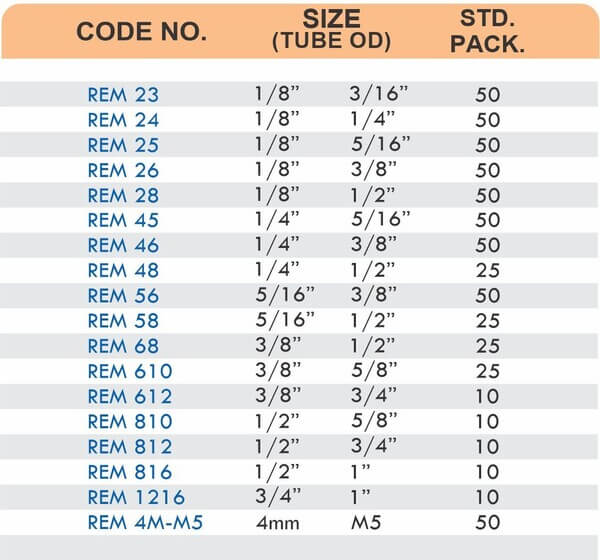
Compression fittings join pipes or tubes through mechanical pressure without heat or adhesive. They consist of three parts: a body, a compression nut, and a ferrule that deforms when tightened to create a watertight seal. These fittings work with copper, PEX, CPVC, and PE-RT tubing across water supply lines, refrigeration systems, and instrumentation circuits.
The no-solder installation makes compression fittings ideal for tight spaces, occupied buildings, and applications where open flames create hazards. You can disassemble and reassemble them multiple times—a capability that soldered or welded joints can’t match. They handle high-pressure applications reliably when sized correctly and installed according to manufacturer torque specifications.
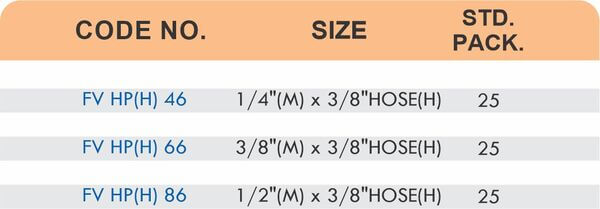
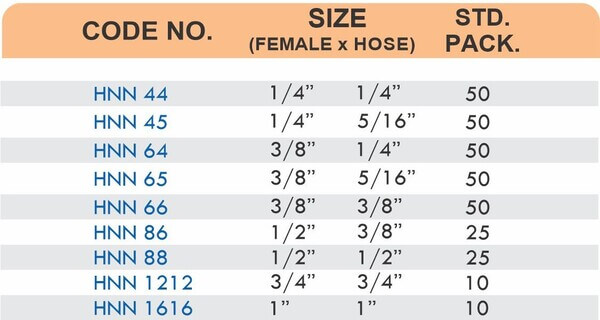
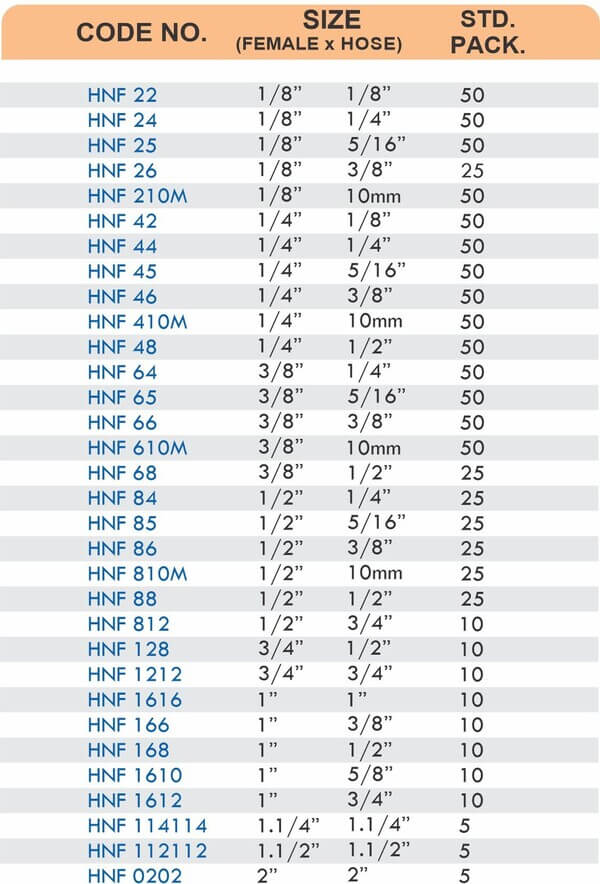
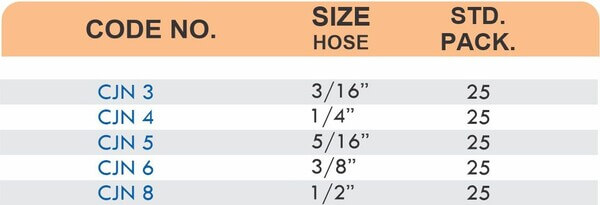
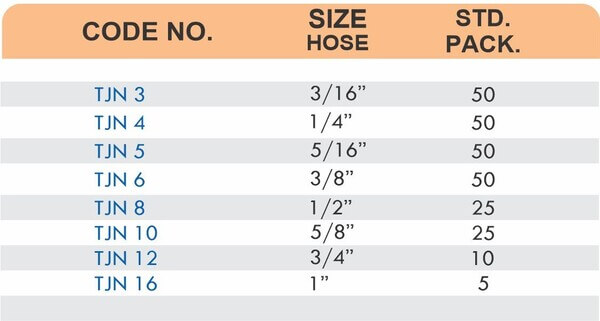
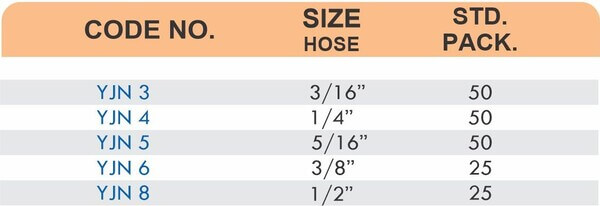
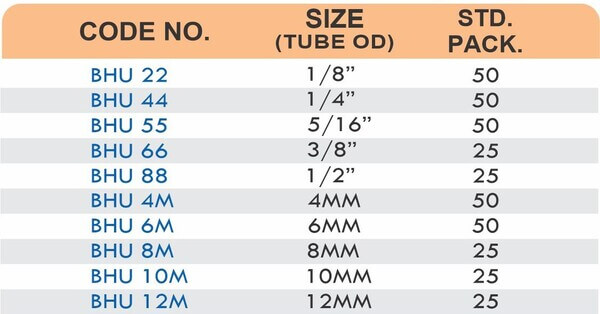
Hose Fittings (Hose Barbs)
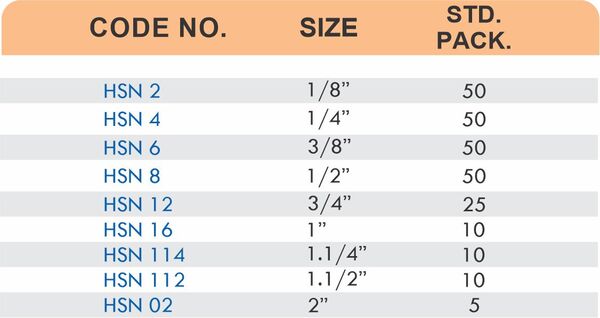
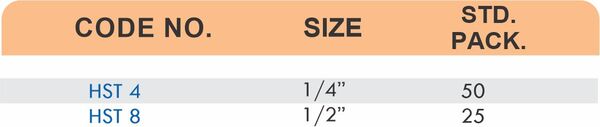
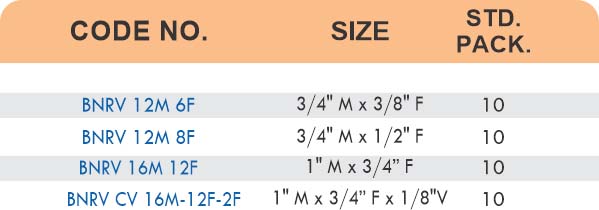
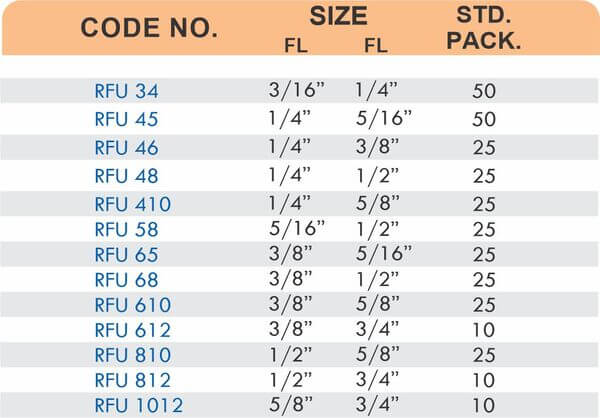
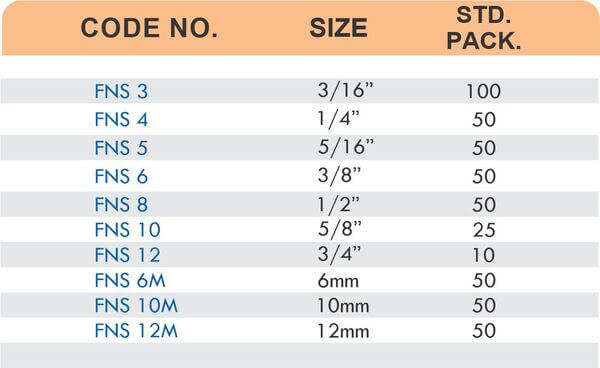
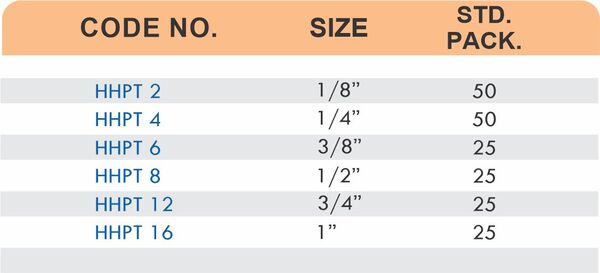
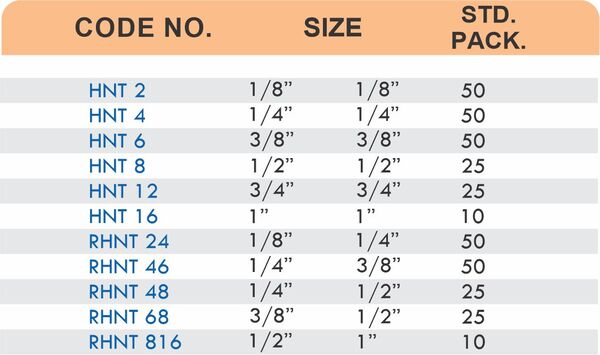
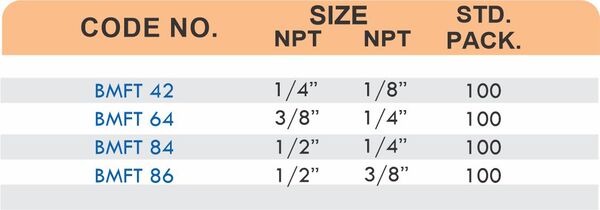
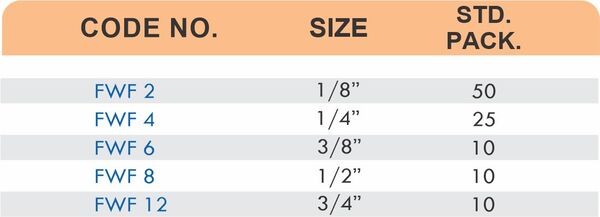
Hose barbs connect flexible hoses to rigid piping or tubing through a tapered or ribbed barb that inserts inside the hose. One end features the barb; the other has threads or a plain surface for pipe connection. The barb design grips the inner hose wall while a clamp secures the outer diameter, creating a double-seal mechanism.
Common applications include irrigation systems, fuel lines, vacuum systems, and pneumatic circuits where flexible connections absorb vibration or allow movement. Brass hose barbs resist corrosion from moisture, fertilizers, and many chemicals that would degrade plastic or aluminum alternatives. The ribbed barb design prevents hose slippage even under pressure cycling.
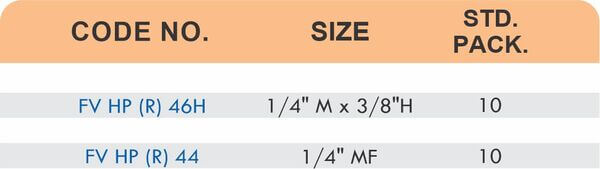
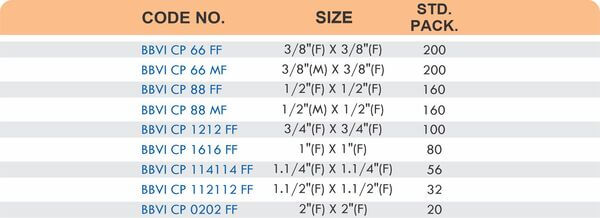
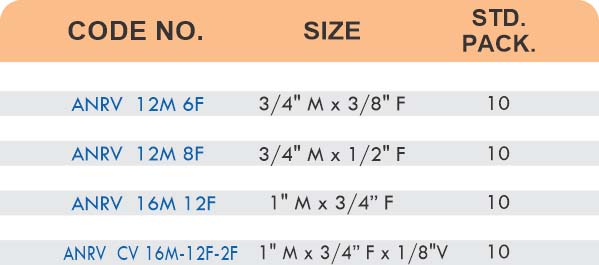
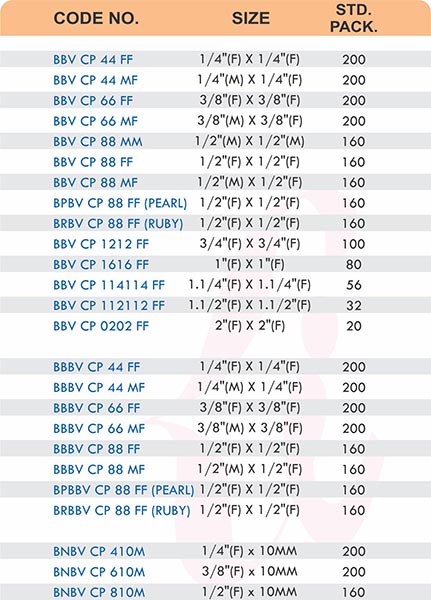
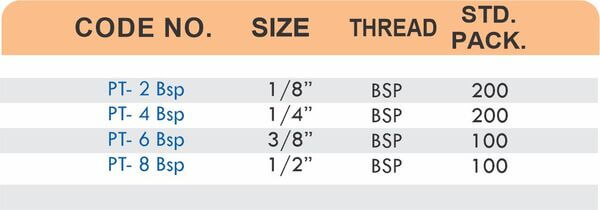
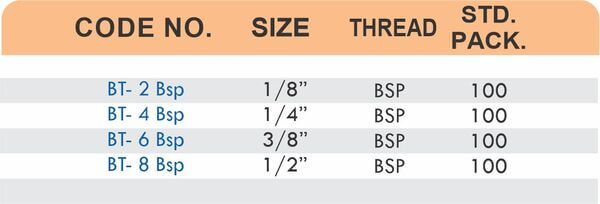
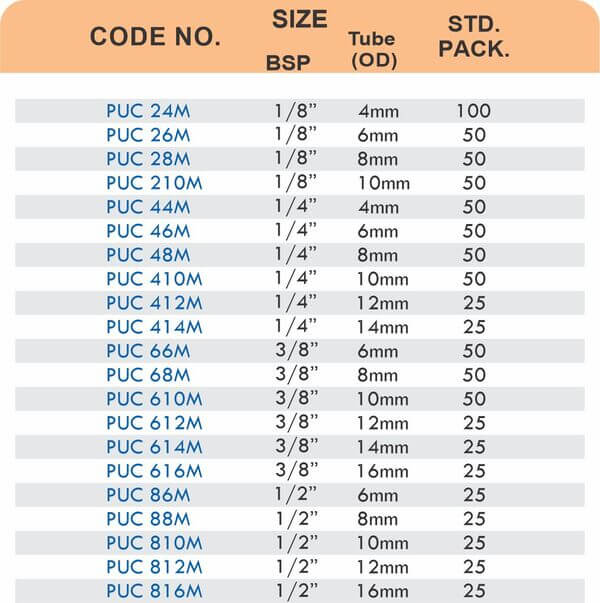
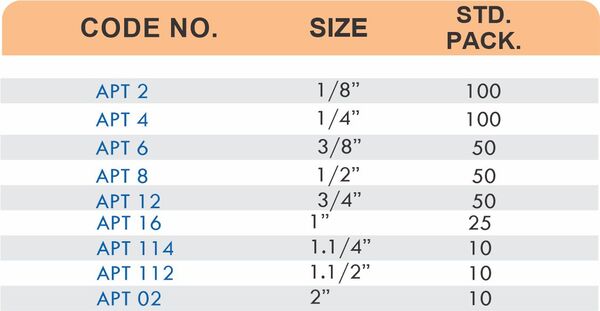
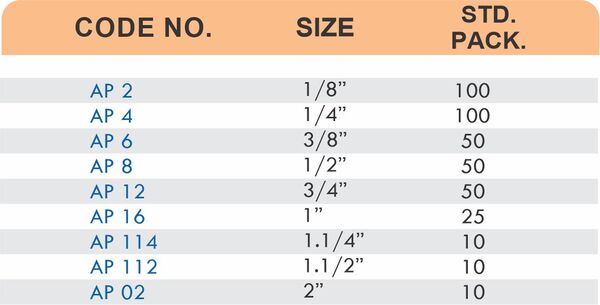
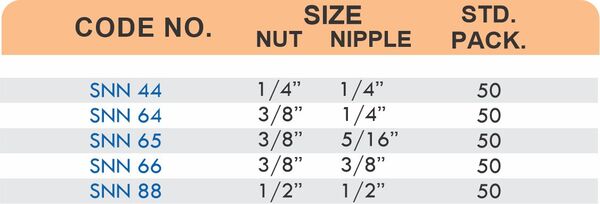
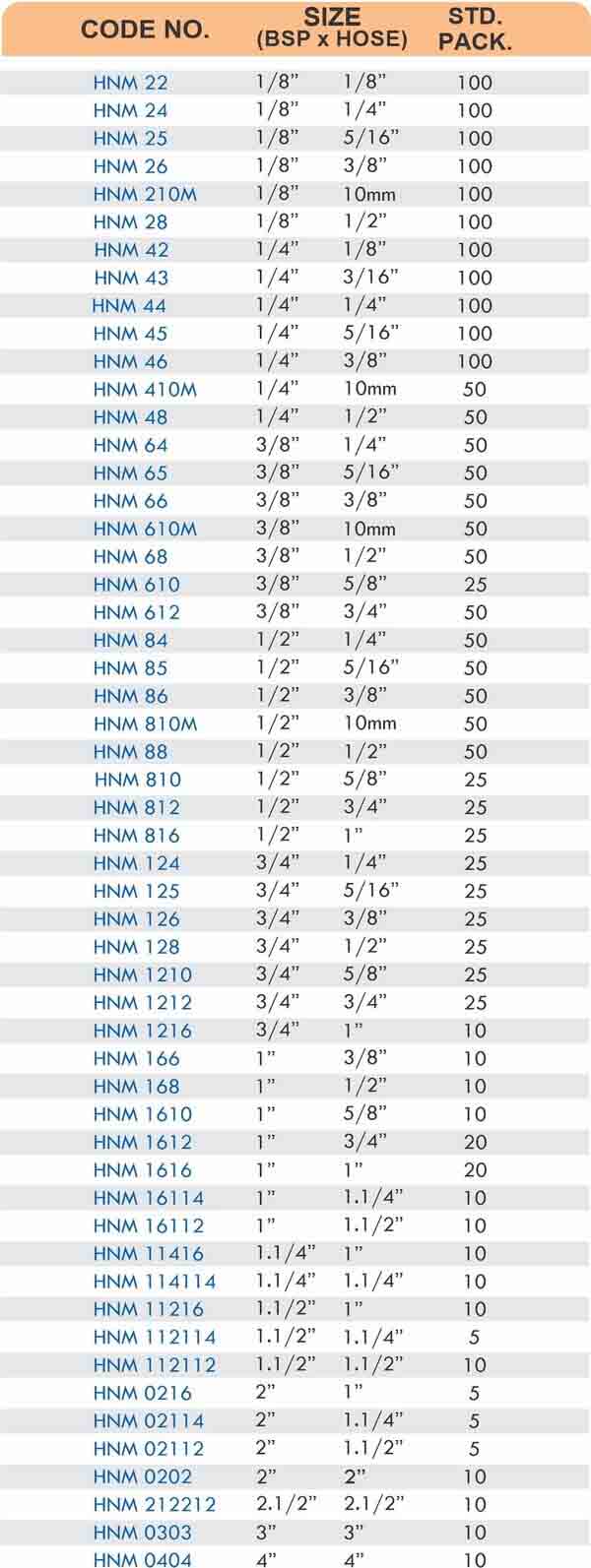
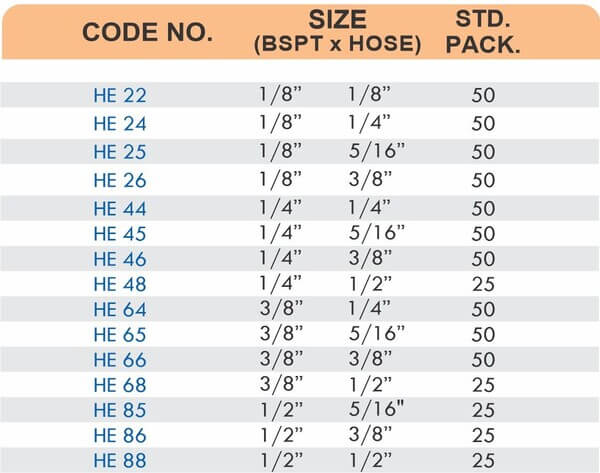
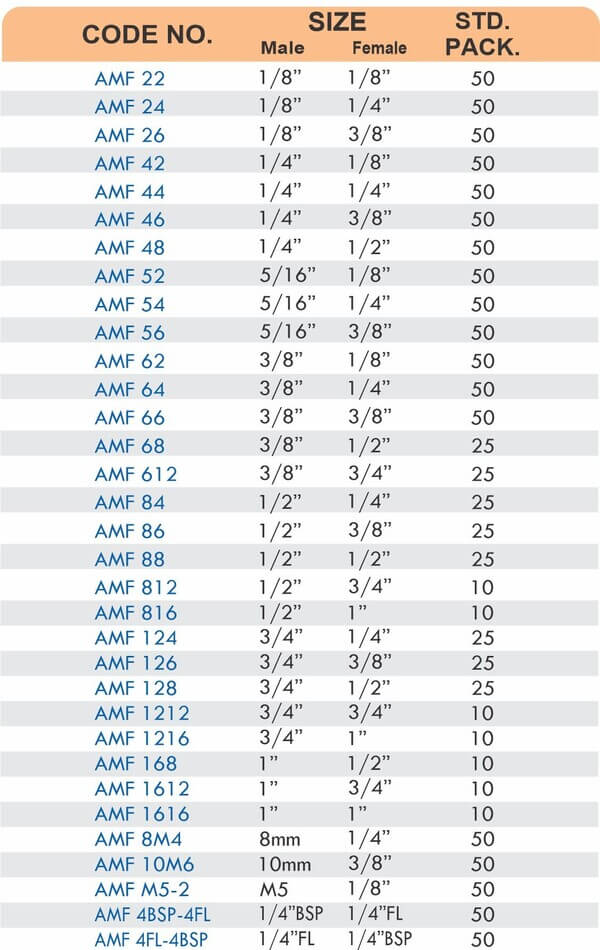
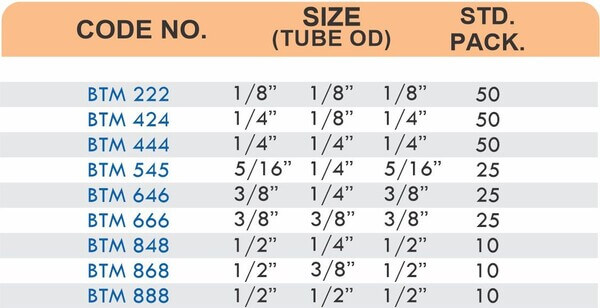
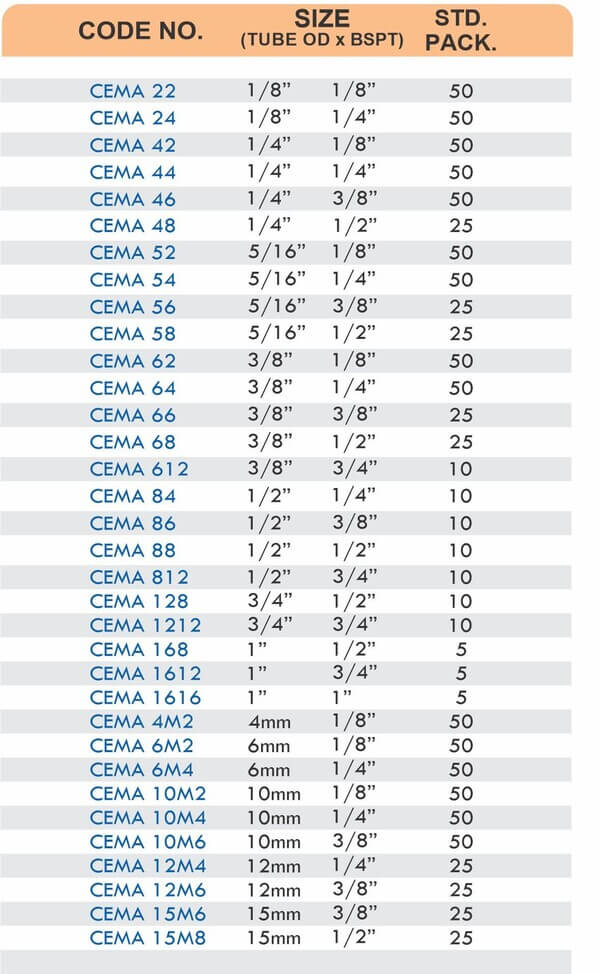
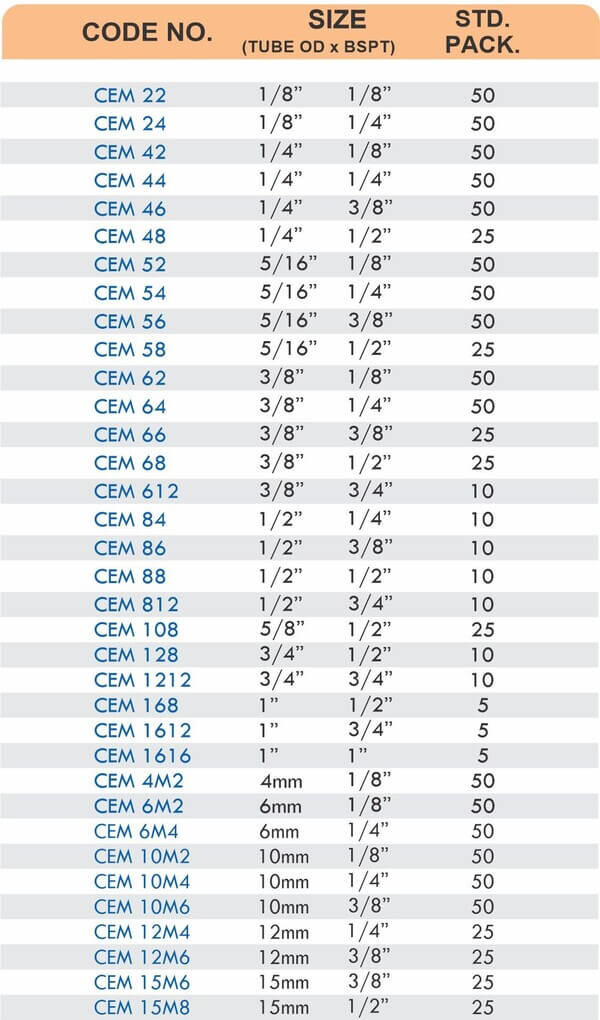
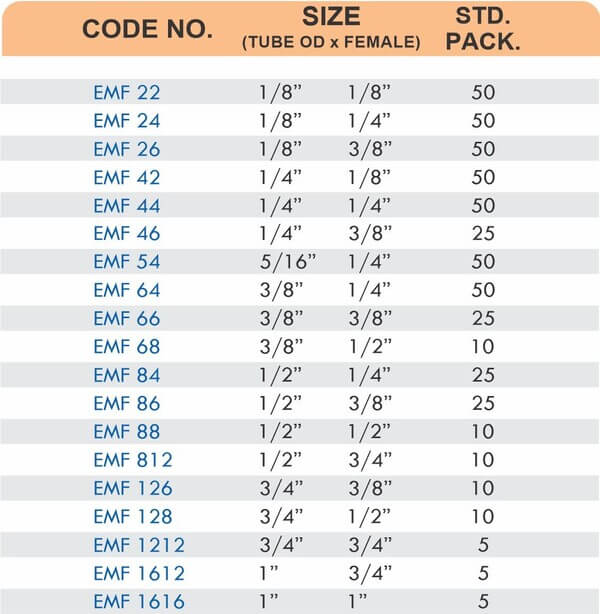
Pipe Fittings
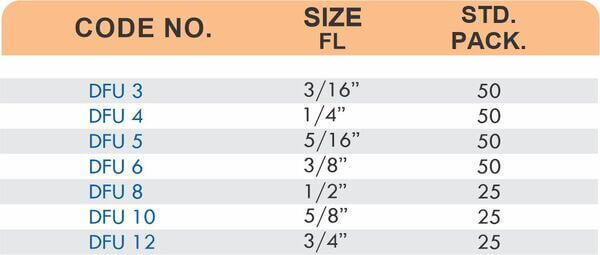
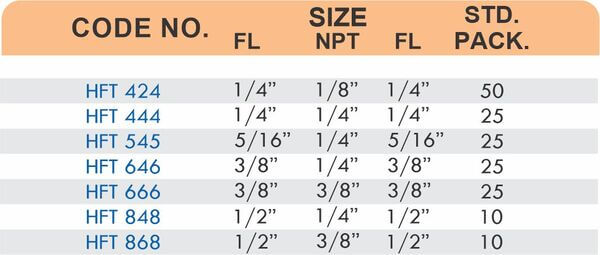
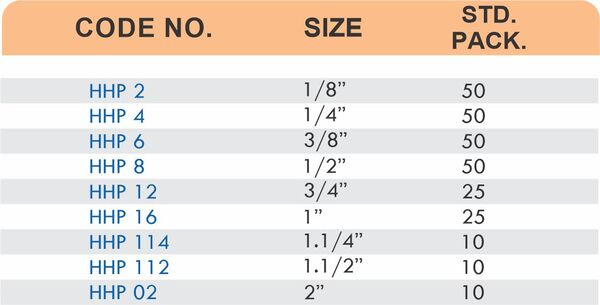
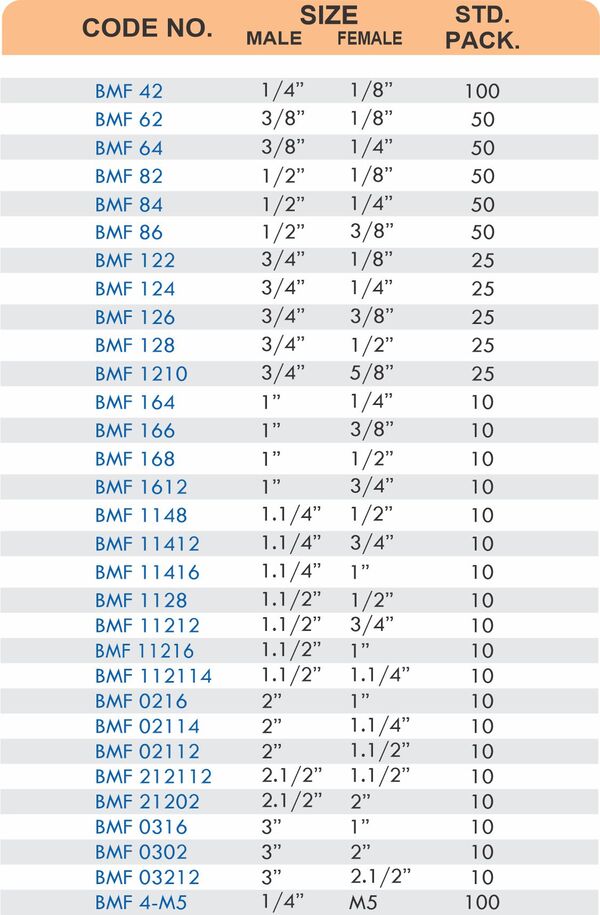
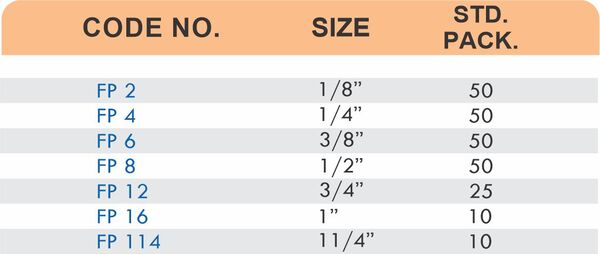
Brass pipe fittings connect threaded pipes and change flow direction or diameter. Standard configurations include elbows (90-degree and 45-degree), tees, couplings, reducers, bushings, and nipples. Each serves a specific layout function—elbows redirect flow, tees create branches, reducers transition between pipe sizes, and bushings adapt thread sizes.
These fittings dominate plumbing and heating systems because they install quickly with basic wrenches and form reliable seals with pipe thread sealant. Brass pipe fittings handle potable water, steam, compressed air, and natural gas depending on pressure ratings and local codes. The threaded design allows field assembly without specialized equipment.
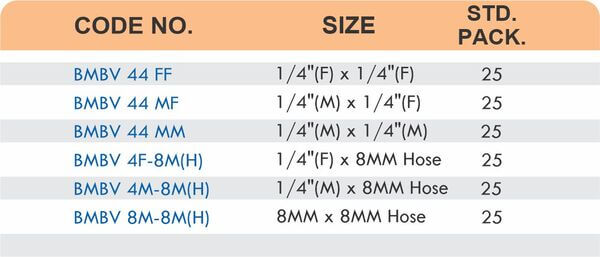
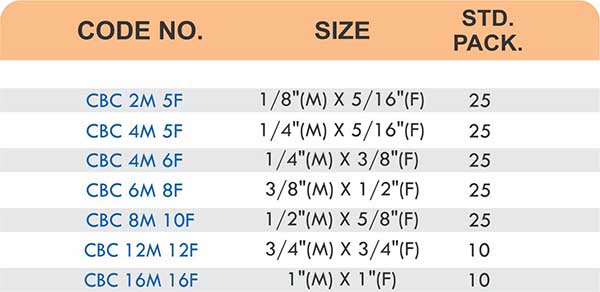
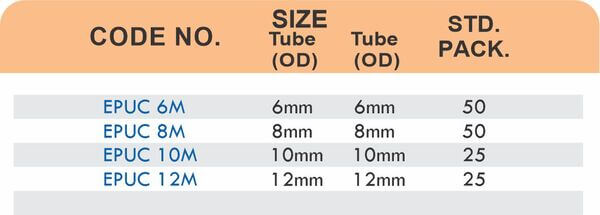
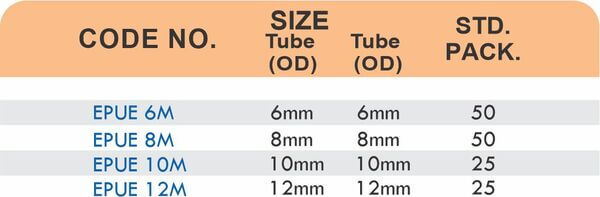
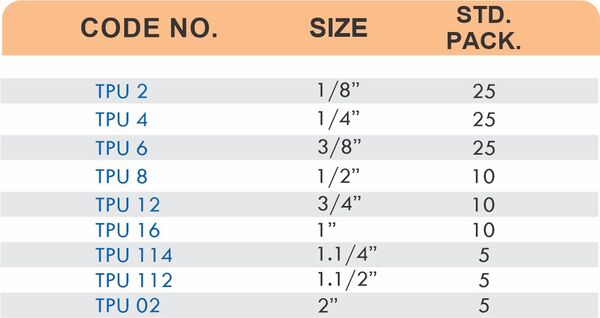
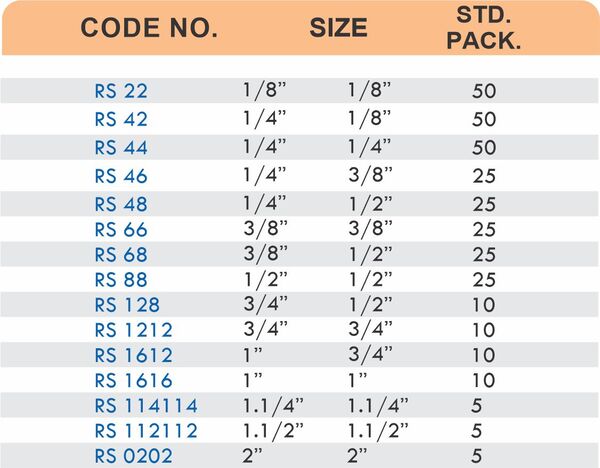
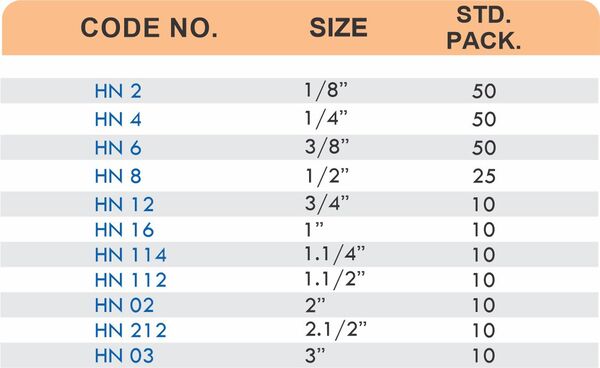
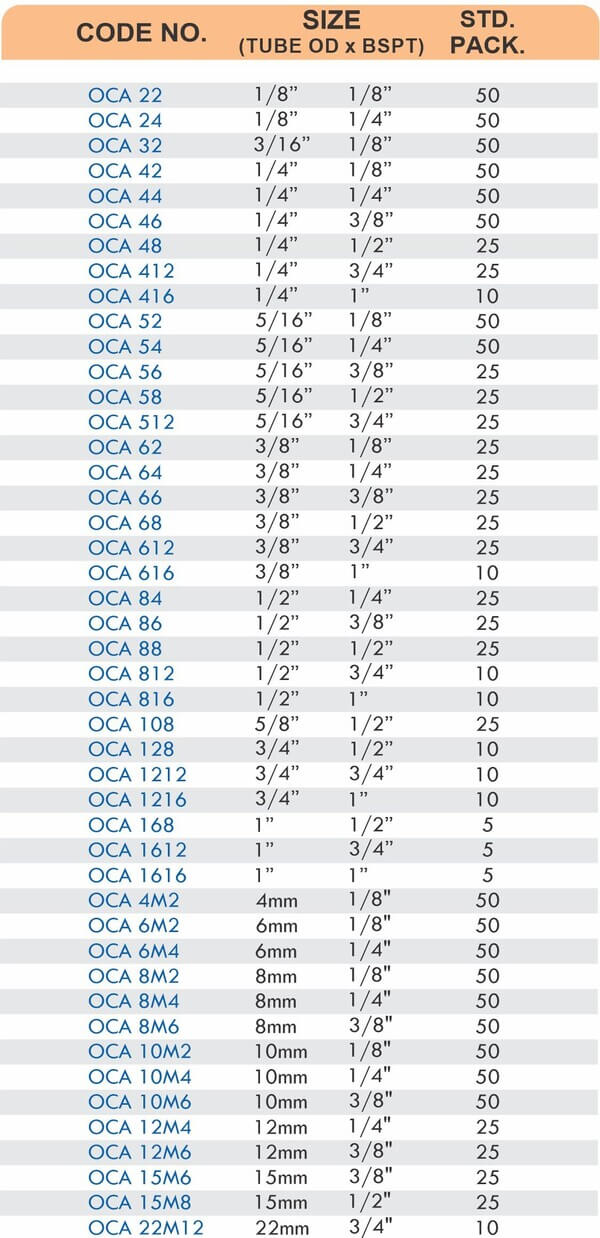
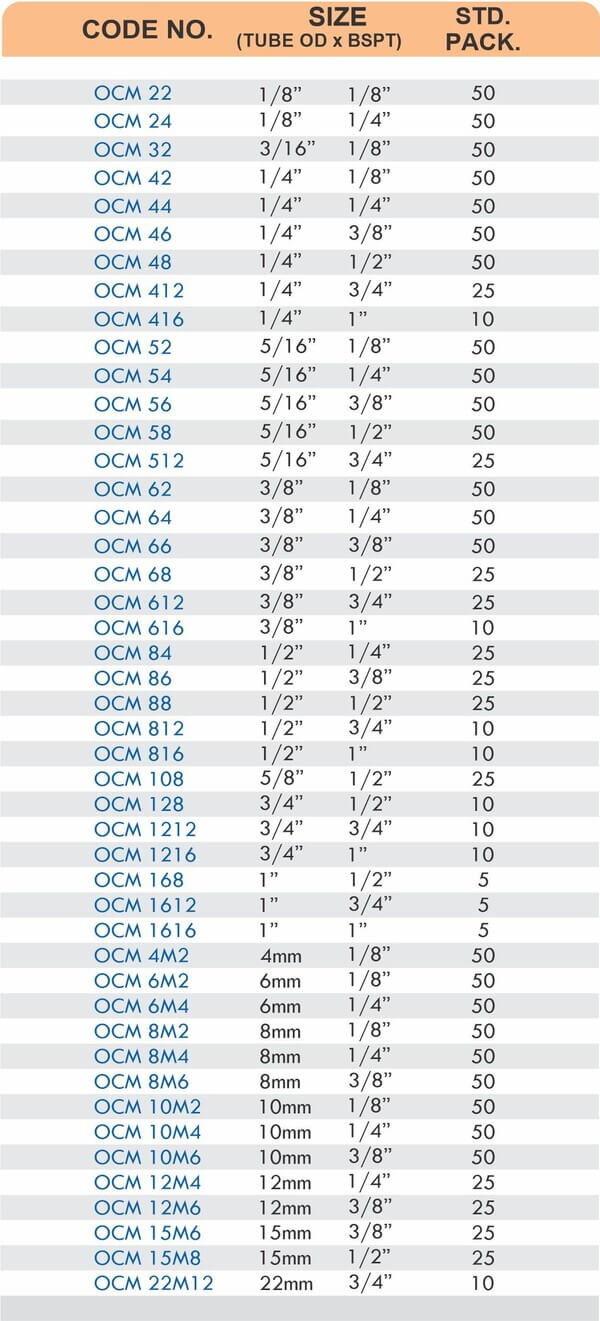
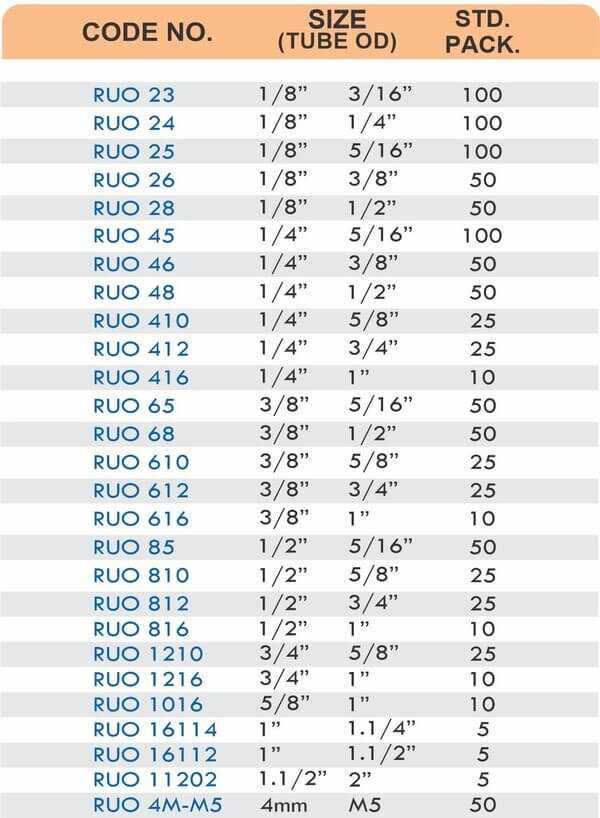
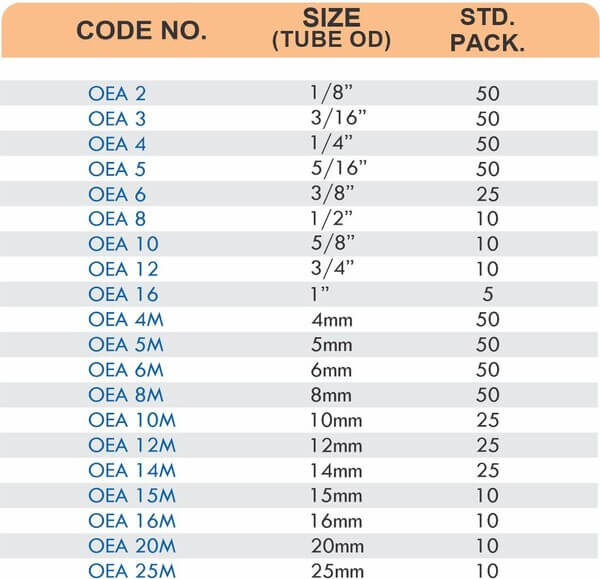
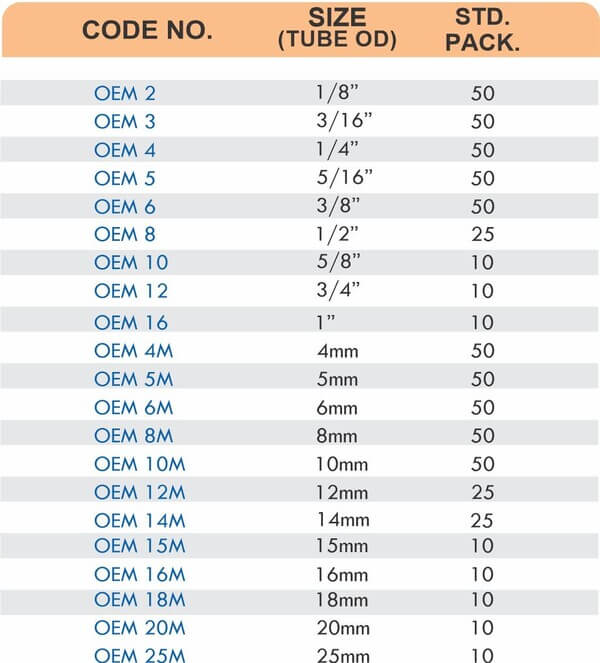
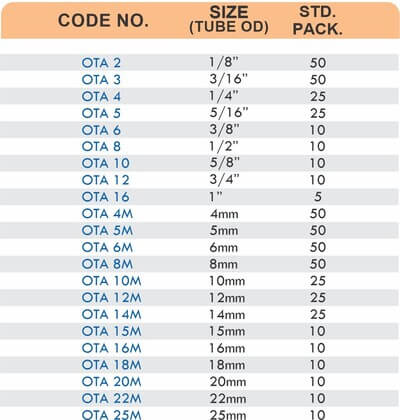
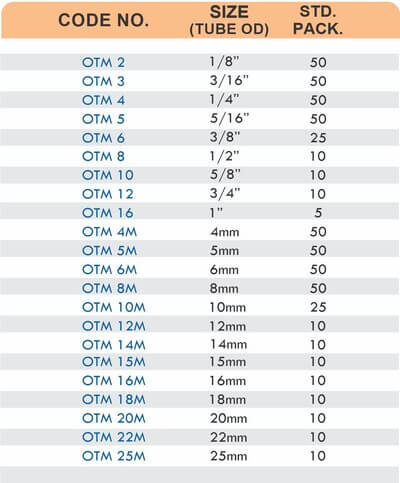
Tube Fittings
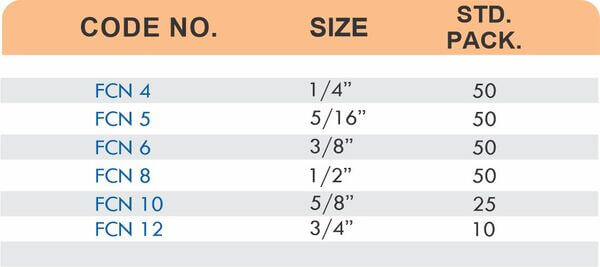
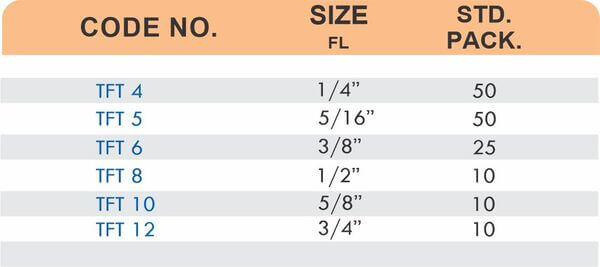
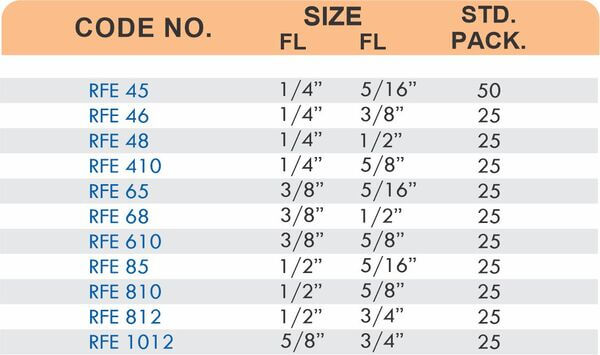
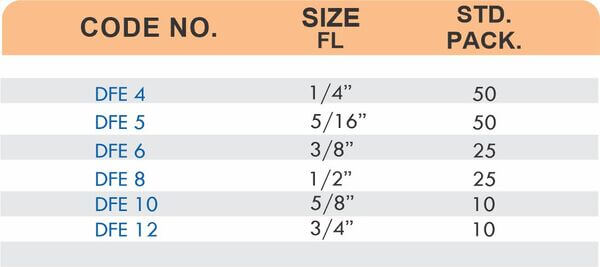
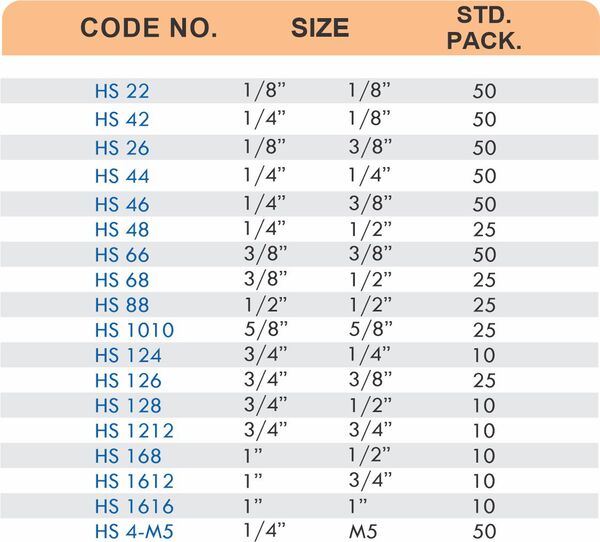
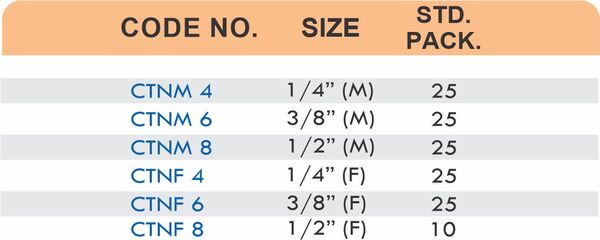
Tube fittings connect thin-wall tubing in instrumentation, hydraulic, and pneumatic systems where precision and compact size matter. Types include compression tube fittings, flare fittings, and push-to-connect varieties. Compression tube fittings use a ferrule system similar to pipe compression fittings but sized for smaller diameter tubing with tighter tolerances.
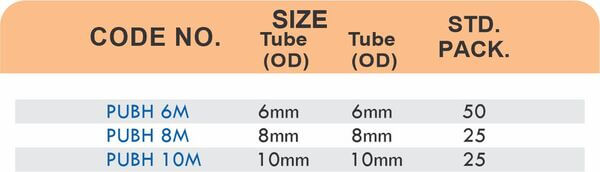
Flare fittings work by expanding the tube end into a cone shape that seats against a matching surface—common in gas applications and automotive systems. Push-to-connect tube fittings use internal collets and O-rings to grip tubing when pushed in, allowing tool-free installation. Brass tube fittings excel in applications requiring frequent disconnection, such as test equipment and modular machinery.
Five Advantages of Brass Fittings
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Brass resists dezincification, pitting, and oxidation in water, air, and many chemical environments. Unlike steel fittings that rust within months in moisture-heavy settings, brass maintains structural integrity for decades. The alloy composition creates a protective patina that prevents progressive corrosion—critical for buried lines, outdoor installations, and marine applications.
Field data shows brass fittings in potable water systems regularly exceed 30-year service lives without replacement. Steel fittings in the same conditions fail within 5-10 years due to rust and scale buildup. This durability gap translates directly to lower lifecycle costs despite higher initial brass pricing.
Wide Material Compatibility
Brass fittings work with copper, aluminum, PEX, CPVC, polyethylene, and other brass components without galvanic corrosion concerns. This compatibility simplifies material selection and allows mixing pipe types within a single system. You can transition from copper supply lines to PEX distribution using brass fittings without introducing corrosion cells.
The antimicrobial properties of brass make it required by code in many potable water applications. Bacteria don’t colonize brass surfaces as readily as plastic, reducing biofilm formation in water lines. This benefit matters for healthcare facilities, food processing plants, and public water systems where contamination control is mandatory.
High Pressure and Temperature Tolerance
Brass fittings handle pressures from 200 PSI in standard plumbing to 3,000 PSI in hydraulic applications depending on style and size. Temperature range spans -65°F to 400°F without material failure or deformation. This performance envelope covers most industrial, commercial, and residential applications without requiring exotic alloys or special configurations.
Plastic fittings fail at temperatures above 180°F and pressures above 150 PSI—conditions brass handles routinely. Steel fittings tolerate similar pressures but corrode rapidly, requiring expensive coatings or stainless grades. Brass delivers the performance of steel with the corrosion resistance of plastic at a middle price point.
Ease of Installation and Maintenance
Brass compression and push-to-connect fittings are installed without specialized tools, training, or hot work permits. Installation time runs 60-70% faster than soldered connections and 40-50% faster than welded joints. The reduced labor cost offsets higher material cost on projects with numerous connections.
Maintenance accessibility separates brass from permanent connection methods. You can disassemble brass compression fittings for inspection, cleaning, or line modification without cutting pipes or destroying fittings. This flexibility cuts downtime during repairs and allows system upgrades without complete line replacement.
Reusability and Long Service Life
Brass fittings disassemble and reassemble 2-4 times before requiring ferrule replacement. Plastic fittings typically fail after one disassembly; soldered joints require complete rework. This reusability matters for systems requiring periodic maintenance, seasonal shutdowns, or phased installations where temporary connections later become permanent.
The material itself doesn’t fatigue under pressure cycling or thermal expansion like plastics do. Brass maintains mechanical properties through thousands of pressure and temperature cycles. Combined with corrosion resistance, this stability delivers service lives measured in decades rather than years.
Applications Across Industries
Brass fittings serve residential plumbing for water supply, waste lines, and gas distribution. Commercial buildings use them in HVAC systems, fire suppression lines, and process piping. Industrial applications include hydraulic power units, pneumatic controls, instrumentation circuits, and chemical transfer systems.
Automotive and marine sectors depend on brass for fuel lines, coolant systems, and hydraulic steering. The vibration resistance and corrosion tolerance prove essential in mobile equipment. Agricultural irrigation systems use brass hose barbs and pipe fittings for durability in outdoor, seasonal service with fertilizer-laden water.
FAQs
Can I mix brass fittings with different pipe materials?
Yes, brass works with copper, PEX, CPVC, aluminum, and galvanized steel without galvanic corrosion issues in most applications. Use dielectric unions when connecting brass to dissimilar metals in high-conductivity environments like saltwater systems. Always check local codes for specific material combinations in potable water and gas systems.
Do brass compression fittings need sealant or tape?
No. Compression fittings seal through ferrule deformation, not thread sealing. Adding sealant or tape interferes with proper ferrule contact and can cause leaks. Threaded brass pipe fittings do require pipe thread sealant or tape on the male threads for a watertight seal.
How do I know which brass fitting style to choose?
Match the style to your connection type: compression for rigid tubing that might need future disassembly, hose barbs for flexible hose connections, pipe fittings for threaded pipe systems, and tube fittings for precision instrumentation. Consider whether you need directional changes, size transitions, or branch connections when selecting the specific fitting configuration.
Are brass fittings safe for drinking water?
Yes, brass fittings meeting NSF/ANSI Standard 61 are approved for potable water systems. Look for lead-free brass designations for drinking water applications—these contain less than 0.25% lead per federal Safe Drinking Water Act requirements. Standard brass works for non-potable applications without restrictions.
What causes brass fittings to leak?
Over-tightening compression fittings deforms the ferrule excessively and creates leaks rather than preventing them. Under-tightening leaves insufficient compression for a seal. Mixing components from different manufacturers causes dimensional mismatches. Using damaged, scratched, or corroded fittings prevents proper sealing surface contact.
Choose the Right Style
Brass fittings deliver reliable connections when you match the style to your application requirements and leverage the material’s inherent advantages. Compression fittings for disassembly needs, hose barbs for flexible connections, pipe fittings for threaded systems, and tube fittings for precision work. The corrosion resistance, pressure tolerance, installation speed, and reusability make brass the practical choice across most fluid and gas handling applications.
KK International supplies precision-manufactured brass fittings in all four styles—compression, hose, pipe, and tube configurations—engineered to international quality standards. Our product range covers residential, commercial, and industrial applications with consistent performance and reliable delivery across India. Browse our complete brass fitting catalog at kkinternational.co.in or contact our technical team for application-specific recommendations and bulk pricing. Get fittings that connect right, seal tight, and last.